Yizhak Vaisman
Detecting Anomalous Network Communication Patterns Using Graph Convolutional Networks
Nov 30, 2023


Abstract:To protect an organizations' endpoints from sophisticated cyberattacks, advanced detection methods are required. In this research, we present GCNetOmaly: a graph convolutional network (GCN)-based variational autoencoder (VAE) anomaly detector trained on data that include connection events among internal and external machines. As input, the proposed GCN-based VAE model receives two matrices: (i) the normalized adjacency matrix, which represents the connections among the machines, and (ii) the feature matrix, which includes various features (demographic, statistical, process-related, and Node2vec structural features) that are used to profile the individual nodes/machines. After training the model on data collected for a predefined time window, the model is applied on the same data; the reconstruction score obtained by the model for a given machine then serves as the machine's anomaly score. GCNetOmaly was evaluated on real, large-scale data logged by Carbon Black EDR from a large financial organization's automated teller machines (ATMs) as well as communication with Active Directory (AD) servers in two setups: unsupervised and supervised. The results of our evaluation demonstrate GCNetOmaly's effectiveness in detecting anomalous behavior of machines on unsupervised data.
Exploiting Meta-Cognitive Features for a Machine-Learning-Based One-Shot Group-Decision Aggregation
Jan 20, 2022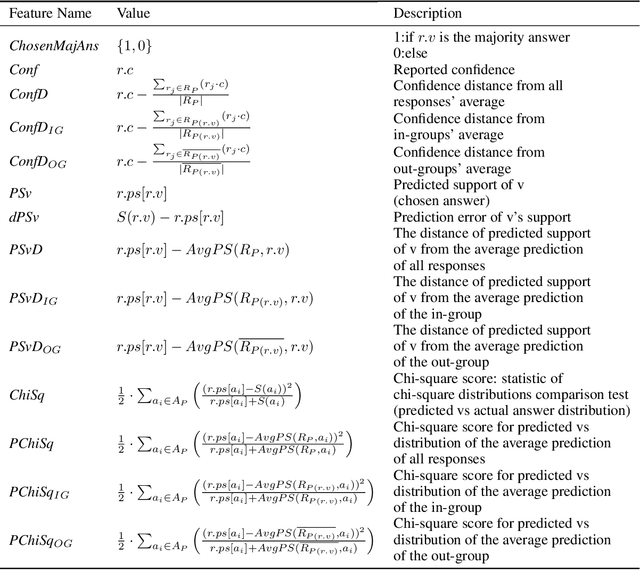
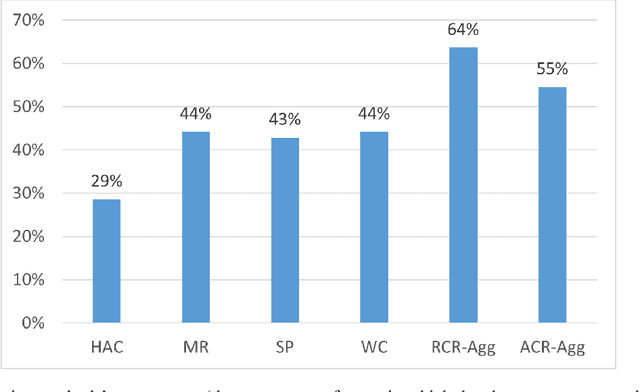
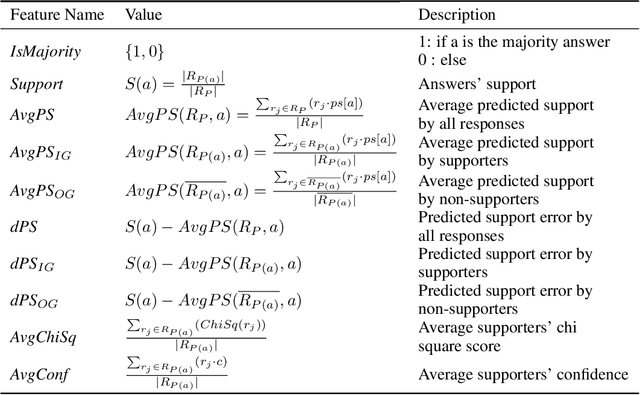
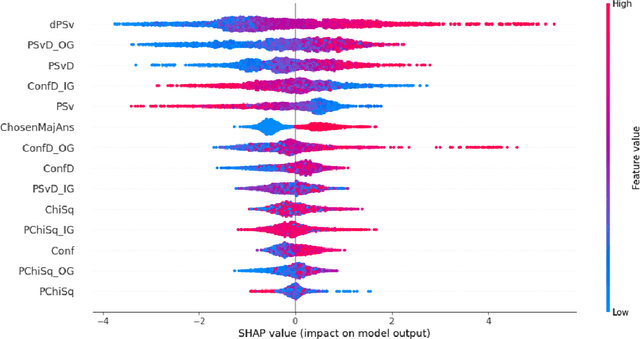
Abstract:The outcome of a collective decision-making process, such as crowdsourcing, often relies on the procedure through which the perspectives of its individual members are aggregated. Popular aggregation methods, such as the majority rule, often fail to produce the optimal result, especially in high-complexity tasks. Methods that rely on meta-cognitive information, such as confidence-based methods and the Surprisingly Popular Option, had shown an improvement in various tasks. However, there is still a significant number of cases with no optimal solution. Our aim is to exploit meta-cognitive information and to learn from it, for the purpose of enhancing the ability of the group to produce a correct answer. Specifically, we propose two different feature-representation approaches: (1) Response-Centered feature Representation (RCR), which focuses on the characteristics of the individual response instances, and (2) Answer-Centered feature Representation (ACR), which focuses on the characteristics of each of the potential answers. Using these two feature-representation approaches, we train Machine-Learning (ML) models, for the purpose of predicting the correctness of a response and of an answer. The trained models are used as the basis of an ML-based aggregation methodology that, contrary to other ML-based techniques, has the advantage of being a "one-shot" technique, independent from the crowd-specific composition and personal record, and adaptive to various types of situations. To evaluate our methodology, we collected 2490 responses for different tasks, which we used for feature engineering and for the training of ML models. We tested our feature-representation approaches through the performance of our proposed ML-based aggregation methods. The results show an increase of 20% to 35% in the success rate, compared to the use of standard rule-based aggregation methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge