Yirui Liu
KV-CoRE: Benchmarking Data-Dependent Low-Rank Compressibility of KV-Caches in LLMs
Feb 05, 2026Abstract:Large language models rely on kv-caches to avoid redundant computation during autoregressive decoding, but as context length grows, reading and writing the cache can quickly saturate GPU memory bandwidth. Recent work has explored KV-cache compression, yet most approaches neglect the data-dependent nature of kv-caches and their variation across layers. We introduce KV-CoRE KV-cache Compressibility by Rank Evaluation), an SVD-based method for quantifying the data-dependent low-rank compressibility of kv-caches. KV-CoRE computes the optimal low-rank approximation under the Frobenius norm and, being gradient-free and incremental, enables efficient dataset-level, layer-wise evaluation. Using this method, we analyze multiple models and datasets spanning five English domains and sixteen languages, uncovering systematic patterns that link compressibility to model architecture, training data, and language coverage. As part of this analysis, we employ the Normalized Effective Rank as a metric of compressibility and show that it correlates strongly with performance degradation under compression. Our study establishes a principled evaluation framework and the first large-scale benchmark of kv-cache compressibility in LLMs, offering insights for dynamic, data-aware compression and data-centric model development.
VeRPO: Verifiable Dense Reward Policy Optimization for Code Generation
Jan 07, 2026Abstract:Effective reward design is a central challenge in Reinforcement Learning (RL) for code generation. Mainstream pass/fail outcome rewards enforce functional correctness via executing unit tests, but the resulting sparsity limits potential performance gains. While recent work has explored external Reward Models (RM) to generate richer, continuous rewards, the learned RMs suffer from reward misalignment and prohibitive computational cost. In this paper, we introduce \textbf{VeRPO} (\textbf{V}erifiable D\textbf{e}nse \textbf{R}eward \textbf{P}olicy \textbf{O}ptimization), a novel RL framework for code generation that synthesizes \textit{robust and dense rewards fully grounded in verifiable execution feedback}. The core idea of VeRPO is constructing dense rewards from weighted partial success: by dynamically estimating the difficulty weight of each unit test based on the execution statistics during training, a dense reward is derived from the sum of weights of the passed unit tests. To solidify the consistency between partial success and end-to-end functional correctness, VeRPO further integrates the dense signal with global execution outcomes, establishing a robust and dense reward paradigm relying solely on verifiable execution feedback. Extensive experiments across diverse benchmarks and settings demonstrate that VeRPO consistently outperforms outcome-driven and RM-based baselines, achieving up to +8.83\% gain in pass@1 with negligible time cost (< 0.02\%) and zero GPU memory overhead.
DF2M: An Explainable Deep Bayesian Nonparametric Model for High-Dimensional Functional Time Series
May 23, 2023



Abstract:In this paper, we present Deep Functional Factor Model (DF2M), a Bayesian nonparametric model for analyzing high-dimensional functional time series. The DF2M makes use of the Indian Buffet Process and the multi-task Gaussian Process with a deep kernel function to capture non-Markovian and nonlinear temporal dynamics. Unlike many black-box deep learning models, the DF2M provides an explainable way to use neural networks by constructing a factor model and incorporating deep neural networks within the kernel function. Additionally, we develop a computationally efficient variational inference algorithm for inferring the DF2M. Empirical results from four real-world datasets demonstrate that the DF2M offers better explainability and superior predictive accuracy compared to conventional deep learning models for high-dimensional functional time series.
EEGNN: Edge Enhanced Graph Neural Networks
Aug 12, 2022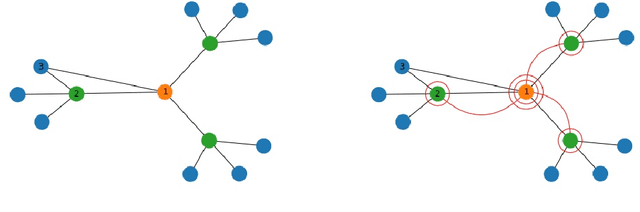
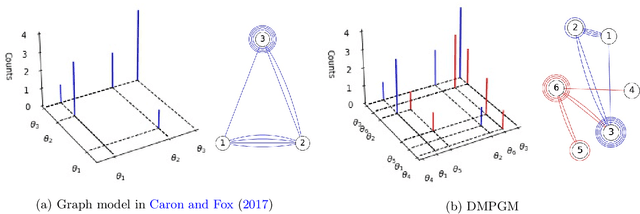
Abstract:Training deep graph neural networks (GNNs) poses a challenging task, as the performance of GNNs may suffer from the number of hidden message-passing layers. The literature has focused on the proposals of over-smoothing and under-reaching to explain the performance deterioration of deep GNNs. In this paper, we propose a new explanation for such deteriorated performance phenomenon, mis-simplification, that is, mistakenly simplifying graphs by preventing self-loops and forcing edges to be unweighted. We show that such simplifying can reduce the potential of message-passing layers to capture the structural information of graphs. In view of this, we propose a new framework, edge enhanced graph neural network(EEGNN). EEGNN uses the structural information extracted from the proposed Dirichlet mixture Poisson graph model, a Bayesian nonparametric model for graphs, to improve the performance of various deep message-passing GNNs. Experiments over different datasets show that our method achieves considerable performance increase compared to baselines.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge