Yinzhu Quan
Temporal Tokenization Strategies for Event Sequence Modeling with Large Language Models
Dec 16, 2025Abstract:Representing continuous time is a critical and under-explored challenge in modeling temporal event sequences with large language models (LLMs). Various strategies like byte-level representations or calendar tokens have been proposed. However, the optimal approach remains unclear, especially given the diverse statistical distributions of real-world event data, which range from smooth log-normal to discrete, spiky patterns. This paper presents the first empirical study of temporal tokenization for event sequences, comparing distinct encoding strategies: naive numeric strings, high-precision byte-level representations, human-semantic calendar tokens, classic uniform binning, and adaptive residual scalar quantization. We evaluate these strategies by fine-tuning LLMs on real-world datasets that exemplify these diverse distributions. Our analysis reveals that no single strategy is universally superior; instead, prediction performance depends heavily on aligning the tokenizer with the data's statistical properties, with log-based strategies excelling on skewed distributions and human-centric formats proving robust for mixed modalities.
EconWebArena: Benchmarking Autonomous Agents on Economic Tasks in Realistic Web Environments
Jun 09, 2025Abstract:We introduce EconWebArena, a benchmark for evaluating autonomous agents on complex, multimodal economic tasks in realistic web environments. The benchmark comprises 360 curated tasks from 82 authoritative websites spanning domains such as macroeconomics, labor, finance, trade, and public policy. Each task challenges agents to navigate live websites, interpret structured and visual content, interact with real interfaces, and extract precise, time-sensitive data through multi-step workflows. We construct the benchmark by prompting multiple large language models (LLMs) to generate candidate tasks, followed by rigorous human curation to ensure clarity, feasibility, and source reliability. Unlike prior work, EconWebArena emphasizes fidelity to authoritative data sources and the need for grounded web-based economic reasoning. We evaluate a diverse set of state-of-the-art multimodal LLMs as web agents, analyze failure cases, and conduct ablation studies to assess the impact of visual grounding, plan-based reasoning, and interaction design. Our results reveal substantial performance gaps and highlight persistent challenges in grounding, navigation, and multimodal understanding, positioning EconWebArena as a rigorous testbed for economic web intelligence.
Leveraging Large Language Models for Risk Assessment in Hyperconnected Logistic Hub Network Deployment
Mar 27, 2025Abstract:The growing emphasis on energy efficiency and environmental sustainability in global supply chains introduces new challenges in the deployment of hyperconnected logistic hub networks. In current volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) environments, dynamic risk assessment becomes essential to ensure successful hub deployment. However, traditional methods often struggle to effectively capture and analyze unstructured information. In this paper, we design an Large Language Model (LLM)-driven risk assessment pipeline integrated with multiple analytical tools to evaluate logistic hub deployment. This framework enables LLMs to systematically identify potential risks by analyzing unstructured data, such as geopolitical instability, financial trends, historical storm events, traffic conditions, and emerging risks from news sources. These data are processed through a suite of analytical tools, which are automatically called by LLMs to support a structured and data-driven decision-making process for logistic hub selection. In addition, we design prompts that instruct LLMs to leverage these tools for assessing the feasibility of hub selection by evaluating various risk types and levels. Through risk-based similarity analysis, LLMs cluster logistic hubs with comparable risk profiles, enabling a structured approach to risk assessment. In conclusion, the framework incorporates scalability with long-term memory and enhances decision-making through explanation and interpretation, enabling comprehensive risk assessments for logistic hub deployment in hyperconnected supply chain networks.
Efficient Retrieval of Temporal Event Sequences from Textual Descriptions
Oct 17, 2024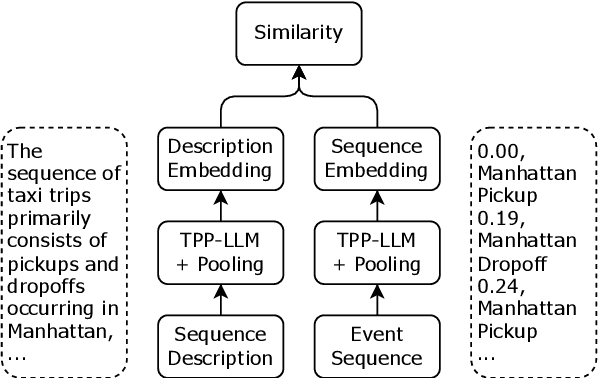
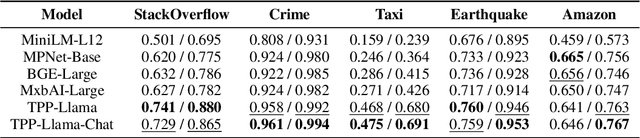
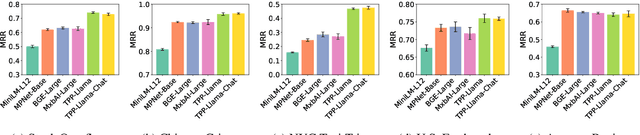
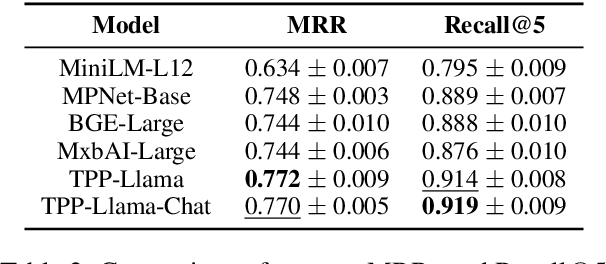
Abstract:Retrieving temporal event sequences from textual descriptions is essential for applications such as analyzing e-commerce behavior, monitoring social media activities, and tracking criminal incidents. In this paper, we introduce TPP-LLM-Embedding, a unified model for efficiently embedding and retrieving event sequences based on natural language descriptions. Built on the TPP-LLM framework, which integrates large language models with temporal point processes, our model encodes both event types and times, generating a sequence-level representation through pooling. Textual descriptions are embedded using the same architecture, ensuring a shared embedding space for both sequences and descriptions. We optimize a contrastive loss based on similarity between these embeddings, bringing matching pairs closer and separating non-matching ones. TPP-LLM-Embedding enables efficient retrieval and demonstrates superior performance compared to baseline models across diverse datasets.
TPP-LLM: Modeling Temporal Point Processes by Efficiently Fine-Tuning Large Language Models
Oct 02, 2024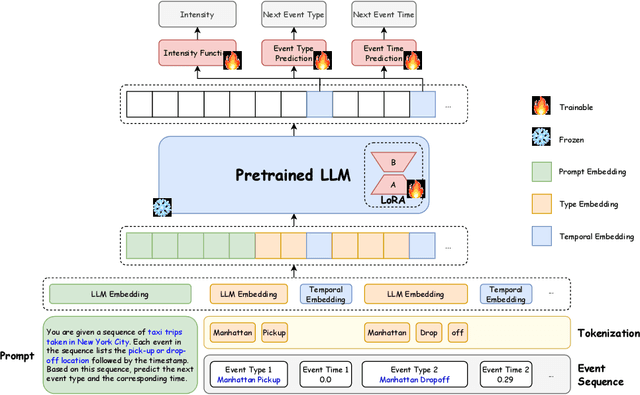
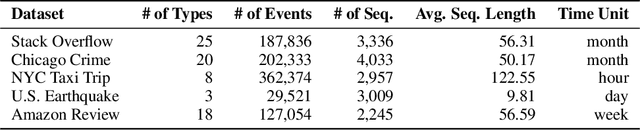
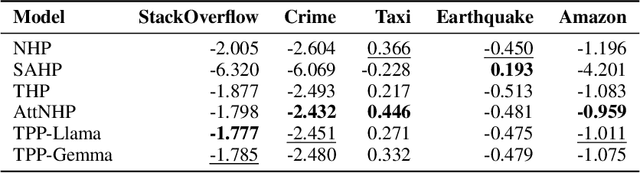
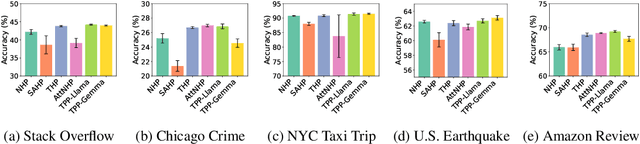
Abstract:Temporal point processes (TPPs) are widely used to model the timing and occurrence of events in domains such as social networks, transportation systems, and e-commerce. In this paper, we introduce TPP-LLM, a novel framework that integrates large language models (LLMs) with TPPs to capture both the semantic and temporal aspects of event sequences. Unlike traditional methods that rely on categorical event type representations, TPP-LLM directly utilizes the textual descriptions of event types, enabling the model to capture rich semantic information embedded in the text. While LLMs excel at understanding event semantics, they are less adept at capturing temporal patterns. To address this, TPP-LLM incorporates temporal embeddings and employs parameter-efficient fine-tuning (PEFT) methods to effectively learn temporal dynamics without extensive retraining. This approach improves both predictive accuracy and computational efficiency. Experimental results across diverse real-world datasets demonstrate that TPP-LLM outperforms state-of-the-art baselines in sequence modeling and event prediction, highlighting the benefits of combining LLMs with TPPs.
InvAgent: A Large Language Model based Multi-Agent System for Inventory Management in Supply Chains
Jul 16, 2024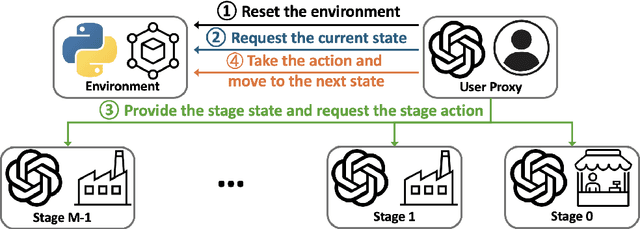
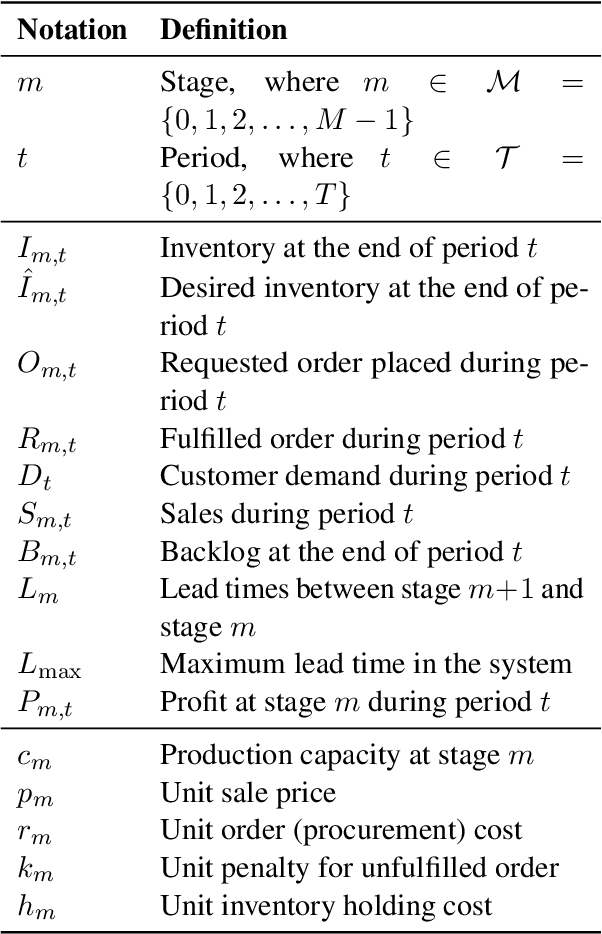
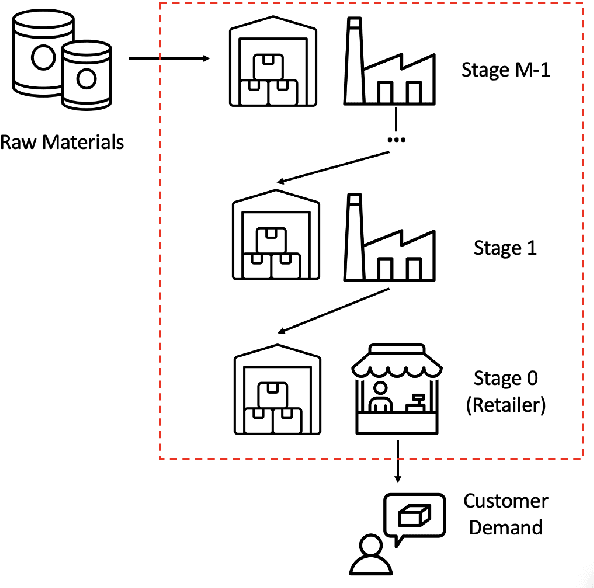
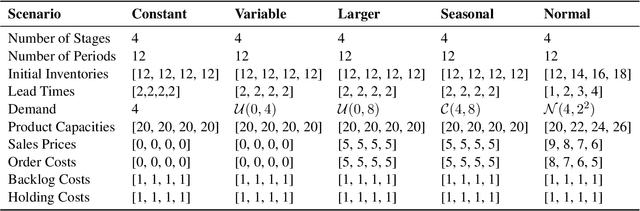
Abstract:Supply chain management (SCM) involves coordinating the flow of goods, information, and finances across various entities to deliver products efficiently. Effective inventory management is crucial in today's volatile, uncertain, complex, and ambiguous (VUCA) world. Previous research has demonstrated the superiority of heuristic methods and reinforcement learning applications in inventory management. However, the application of large language models (LLMs) as autonomous agents in multi-agent systems for inventory management remains underexplored. This study introduces a novel approach using LLMs to manage multi-agent inventory systems. Leveraging their zero-shot learning capabilities, our model, InvAgent, enhances resilience and improves efficiency across the supply chain network. Our contributions include utilizing LLMs for zero-shot learning to enable adaptive and informed decision-making without prior training, providing significant explainability and clarity through Chain-of-Thought (CoT), and demonstrating dynamic adaptability to varying demand scenarios while minimizing costs and avoiding stockouts. Extensive evaluations across different scenarios highlight the efficiency of our model in SCM.
EconLogicQA: A Question-Answering Benchmark for Evaluating Large Language Models in Economic Sequential Reasoning
May 13, 2024Abstract:In this paper, we introduce EconLogicQA, a rigorous benchmark designed to assess the sequential reasoning capabilities of large language models (LLMs) within the intricate realms of economics, business, and supply chain management. Diverging from traditional benchmarks that predict subsequent events individually, EconLogicQA poses a more challenging task: it requires models to discern and sequence multiple interconnected events, capturing the complexity of economic logics. EconLogicQA comprises an array of multi-event scenarios derived from economic articles, which necessitate an insightful understanding of both temporal and logical event relationships. Through comprehensive evaluations, we exhibit that EconLogicQA effectively gauges a LLM's proficiency in navigating the sequential complexities inherent in economic contexts. We provide a detailed description of EconLogicQA dataset and shows the outcomes from evaluating the benchmark across various leading-edge LLMs, thereby offering a thorough perspective on their sequential reasoning potential in economic contexts. Our benchmark dataset is available at https://huggingface.co/datasets/yinzhu-quan/econ_logic_qa.
Deep Reinforcement Learning based Group Recommender System
Jun 13, 2021



Abstract:Group recommender systems are widely used in current web applications. In this paper, we propose a novel group recommender system based on the deep reinforcement learning. We introduce the MovieLens data at first and generate one random group dataset, MovieLens-Rand, from it. This randomly generated dataset is described and analyzed. We also present experimental settings and two state-of-art baselines, AGREE and GroupIM. The framework of our novel model, the Deep Reinforcement learning based Group Recommender system (DRGR), is proposed. Actor-critic networks are implemented with the deep deterministic policy gradient algorithm. The DRGR model is applied on the MovieLens-Rand dataset with two baselines. Compared with baselines, we conclude that DRGR performs better than GroupIM due to long interaction histories but worse than AGREE because of the self-attention mechanism. We express advantages and shortcomings of DRGR and also give future improvement directions at the end.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge