Yingying Hu
FourierPET: Deep Fourier-based Unrolled Network for Low-count PET Reconstruction
Jan 16, 2026Abstract:Low-count positron emission tomography (PET) reconstruction is a challenging inverse problem due to severe degradations arising from Poisson noise, photon scarcity, and attenuation correction errors. Existing deep learning methods typically address these in the spatial domain with an undifferentiated optimization objective, making it difficult to disentangle overlapping artifacts and limiting correction effectiveness. In this work, we perform a Fourier-domain analysis and reveal that these degradations are spectrally separable: Poisson noise and photon scarcity cause high-frequency phase perturbations, while attenuation errors suppress low-frequency amplitude components. Leveraging this insight, we propose FourierPET, a Fourier-based unrolled reconstruction framework grounded in the Alternating Direction Method of Multipliers. It consists of three tailored modules: a spectral consistency module that enforces global frequency alignment to maintain data fidelity, an amplitude-phase correction module that decouples and compensates for high-frequency phase distortions and low-frequency amplitude suppression, and a dual adjustment module that accelerates convergence during iterative reconstruction. Extensive experiments demonstrate that FourierPET achieves state-of-the-art performance with significantly fewer parameters, while offering enhanced interpretability through frequency-aware correction.
CliniChat: A Multi-Source Knowledge-Driven Framework for Clinical Interview Dialogue Reconstruction and Evaluation
Apr 14, 2025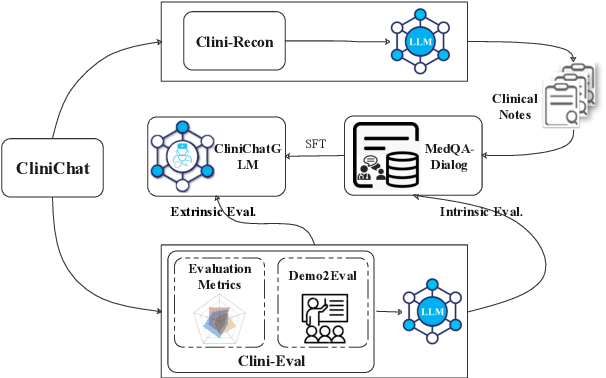
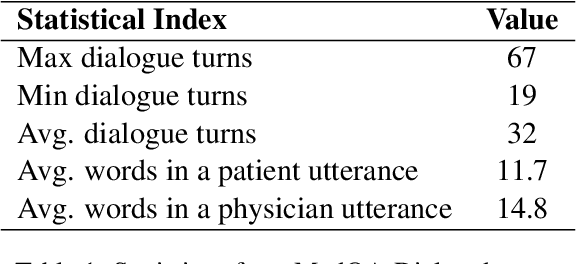
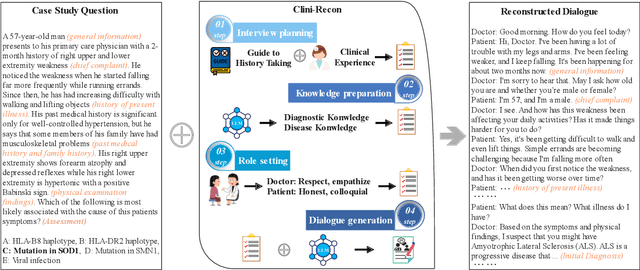
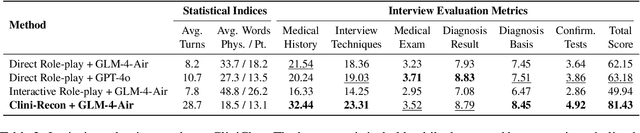
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) hold great promise for assisting clinical interviews due to their fluent interactive capabilities and extensive medical knowledge. However, the lack of high-quality interview dialogue data and widely accepted evaluation methods has significantly impeded this process. So we propose CliniChat, a framework that integrates multi-source knowledge to enable LLMs to simulate real-world clinical interviews. It consists of two modules: Clini-Recon and Clini-Eval, each responsible for reconstructing and evaluating interview dialogues, respectively. By incorporating three sources of knowledge, Clini-Recon transforms clinical notes into systematic, professional, and empathetic interview dialogues. Clini-Eval combines a comprehensive evaluation metric system with a two-phase automatic evaluation approach, enabling LLMs to assess interview performance like experts. We contribute MedQA-Dialog, a high-quality synthetic interview dialogue dataset, and CliniChatGLM, a model specialized for clinical interviews. Experimental results demonstrate that CliniChatGLM's interview capabilities undergo a comprehensive upgrade, particularly in history-taking, achieving state-of-the-art performance.
Implementation and Evaluation of Physical Layer Key Generation on SDR based LoRa Platform
Aug 30, 2023



Abstract:Physical layer key generation technology which leverages channel randomness to generate secret keys has attracted extensive attentions in long range (LoRa)-based networks recently. We in this paper develop a software-defined radio (SDR) based LoRa communications platform using GNU Radio on universal software radio peripheral (USRP) to implement and evaluate typical physical layer key generation schemes. Thanks to the flexibility and configurability of GNU Radio to extract LoRa packets, we are able to obtain the fine-grained channel frequency response (CFR) through LoRa preamble based channel estimation for key generation. Besides, we propose a lowcomplexity preprocessing method to enhance the randomness of quantization while reducing the secret key disagreement ratio. The results indicate that we can achieve 367 key bits with a high level of randomness through just a single effective channel probing in an indoor environment at a distance of 2 meters under the circumstance of a spreading factor (SF) of 7, a preamble length of 8, a signal bandwidth of 250 kHz, and a sampling rate of 1 MHz.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge