Yingqi Lin
Distinguish Any Fake Videos: Unleashing the Power of Large-scale Data and Motion Features
May 24, 2024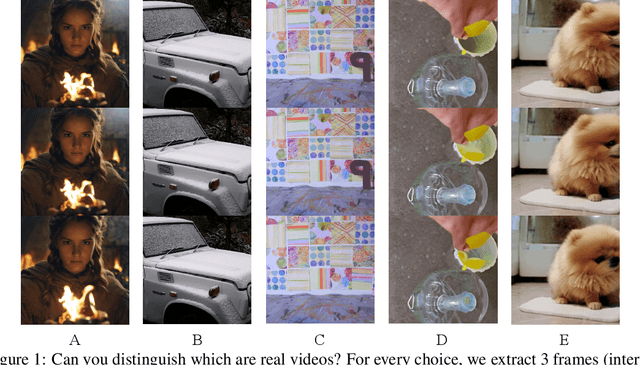
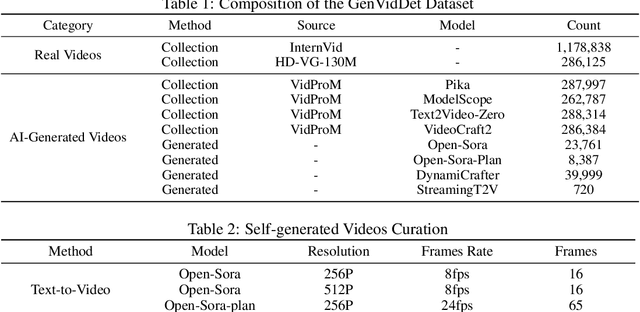

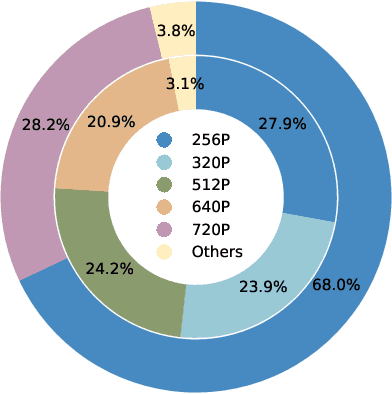
Abstract:The development of AI-Generated Content (AIGC) has empowered the creation of remarkably realistic AI-generated videos, such as those involving Sora. However, the widespread adoption of these models raises concerns regarding potential misuse, including face video scams and copyright disputes. Addressing these concerns requires the development of robust tools capable of accurately determining video authenticity. The main challenges lie in the dataset and neural classifier for training. Current datasets lack a varied and comprehensive repository of real and generated content for effective discrimination. In this paper, we first introduce an extensive video dataset designed specifically for AI-Generated Video Detection (GenVidDet). It includes over 2.66 M instances of both real and generated videos, varying in categories, frames per second, resolutions, and lengths. The comprehensiveness of GenVidDet enables the training of a generalizable video detector. We also present the Dual-Branch 3D Transformer (DuB3D), an innovative and effective method for distinguishing between real and generated videos, enhanced by incorporating motion information alongside visual appearance. DuB3D utilizes a dual-branch architecture that adaptively leverages and fuses raw spatio-temporal data and optical flow. We systematically explore the critical factors affecting detection performance, achieving the optimal configuration for DuB3D. Trained on GenVidDet, DuB3D can distinguish between real and generated video content with 96.77% accuracy, and strong generalization capability even for unseen types.
Video Frame Interpolation with Region-Distinguishable Priors from SAM
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:In existing Video Frame Interpolation (VFI) approaches, the motion estimation between neighboring frames plays a crucial role. However, the estimation accuracy in existing methods remains a challenge, primarily due to the inherent ambiguity in identifying corresponding areas in adjacent frames for interpolation. Therefore, enhancing accuracy by distinguishing different regions before motion estimation is of utmost importance. In this paper, we introduce a novel solution involving the utilization of open-world segmentation models, e.g., SAM (Segment Anything Model), to derive Region-Distinguishable Priors (RDPs) in different frames. These RDPs are represented as spatial-varying Gaussian mixtures, distinguishing an arbitrary number of areas with a unified modality. RDPs can be integrated into existing motion-based VFI methods to enhance features for motion estimation, facilitated by our designed play-and-plug Hierarchical Region-aware Feature Fusion Module (HRFFM). HRFFM incorporates RDP into various hierarchical stages of VFI's encoder, using RDP-guided Feature Normalization (RDPFN) in a residual learning manner. With HRFFM and RDP, the features within VFI's encoder exhibit similar representations for matched regions in neighboring frames, thus improving the synthesis of intermediate frames. Extensive experiments demonstrate that HRFFM consistently enhances VFI performance across various scenes.
Geometric-Aware Low-Light Image and Video Enhancement via Depth Guidance
Dec 26, 2023Abstract:Low-Light Enhancement (LLE) is aimed at improving the quality of photos/videos captured under low-light conditions. It is worth noting that most existing LLE methods do not take advantage of geometric modeling. We believe that incorporating geometric information can enhance LLE performance, as it provides insights into the physical structure of the scene that influences illumination conditions. To address this, we propose a Geometry-Guided Low-Light Enhancement Refine Framework (GG-LLERF) designed to assist low-light enhancement models in learning improved features for LLE by integrating geometric priors into the feature representation space. In this paper, we employ depth priors as the geometric representation. Our approach focuses on the integration of depth priors into various LLE frameworks using a unified methodology. This methodology comprises two key novel modules. First, a depth-aware feature extraction module is designed to inject depth priors into the image representation. Then, Hierarchical Depth-Guided Feature Fusion Module (HDGFFM) is formulated with a cross-domain attention mechanism, which combines depth-aware features with the original image features within the LLE model. We conducted extensive experiments on public low-light image and video enhancement benchmarks. The results illustrate that our designed framework significantly enhances existing LLE methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge