Ying Bian
Learning Multiple Explainable and Generalizable Cues for Face Anti-spoofing
Feb 21, 2022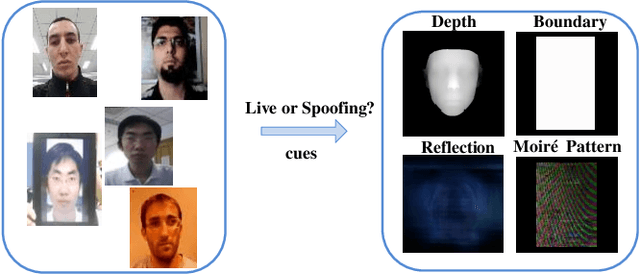
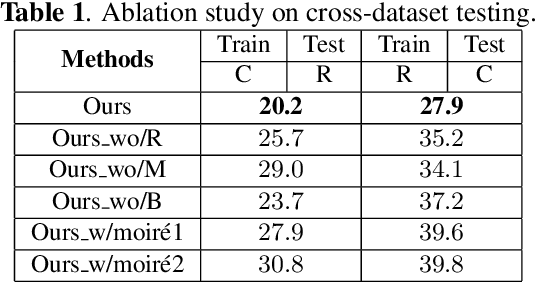
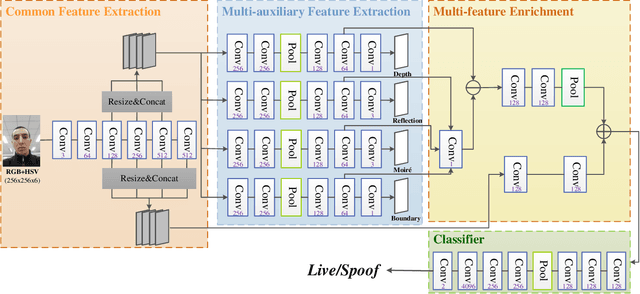
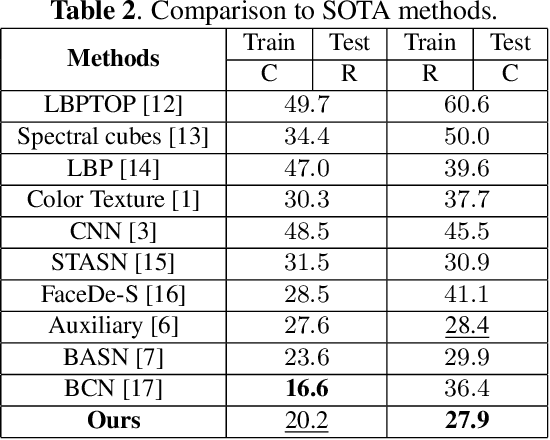
Abstract:Although previous CNN based face anti-spoofing methods have achieved promising performance under intra-dataset testing, they suffer from poor generalization under cross-dataset testing. The main reason is that they learn the network with only binary supervision, which may learn arbitrary cues overfitting on the training dataset. To make the learned feature explainable and more generalizable, some researchers introduce facial depth and reflection map as the auxiliary supervision. However, many other generalizable cues are unexplored for face anti-spoofing, which limits their performance under cross-dataset testing. To this end, we propose a novel framework to learn multiple explainable and generalizable cues (MEGC) for face anti-spoofing. Specifically, inspired by the process of human decision, four mainly used cues by humans are introduced as auxiliary supervision including the boundary of spoof medium, moir\'e pattern, reflection artifacts and facial depth in addition to the binary supervision. To avoid extra labelling cost, corresponding synthetic methods are proposed to generate these auxiliary supervision maps. Extensive experiments on public datasets validate the effectiveness of these cues, and state-of-the-art performances are achieved by our proposed method.
Self-Domain Adaptation for Face Anti-Spoofing
Feb 24, 2021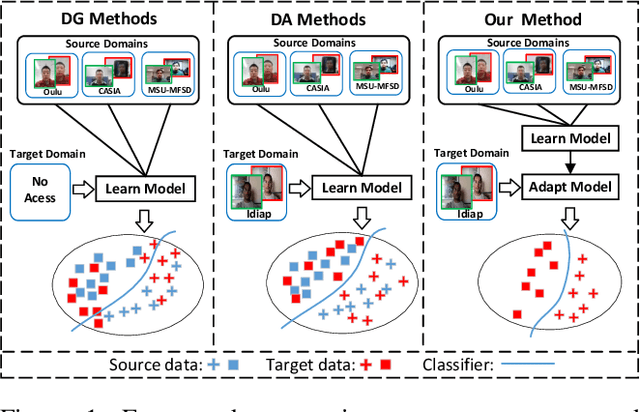
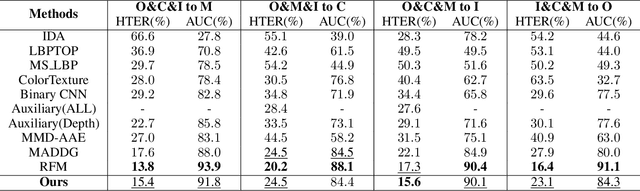
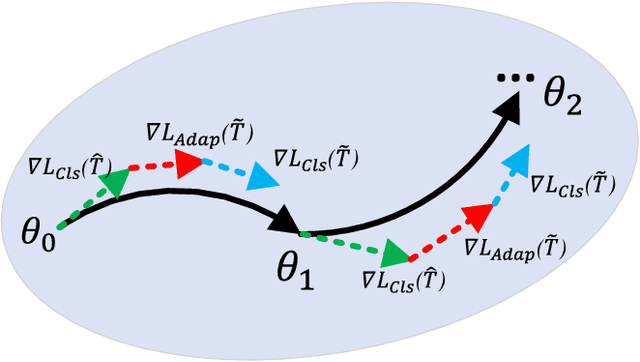
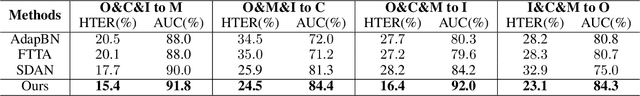
Abstract:Although current face anti-spoofing methods achieve promising results under intra-dataset testing, they suffer from poor generalization to unseen attacks. Most existing works adopt domain adaptation (DA) or domain generalization (DG) techniques to address this problem. However, the target domain is often unknown during training which limits the utilization of DA methods. DG methods can conquer this by learning domain invariant features without seeing any target data. However, they fail in utilizing the information of target data. In this paper, we propose a self-domain adaptation framework to leverage the unlabeled test domain data at inference. Specifically, a domain adaptor is designed to adapt the model for test domain. In order to learn a better adaptor, a meta-learning based adaptor learning algorithm is proposed using the data of multiple source domains at the training step. At test time, the adaptor is updated using only the test domain data according to the proposed unsupervised adaptor loss to further improve the performance. Extensive experiments on four public datasets validate the effectiveness of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge