Yilei Xiong
Deformable Siamese Attention Networks for Visual Object Tracking
Apr 14, 2020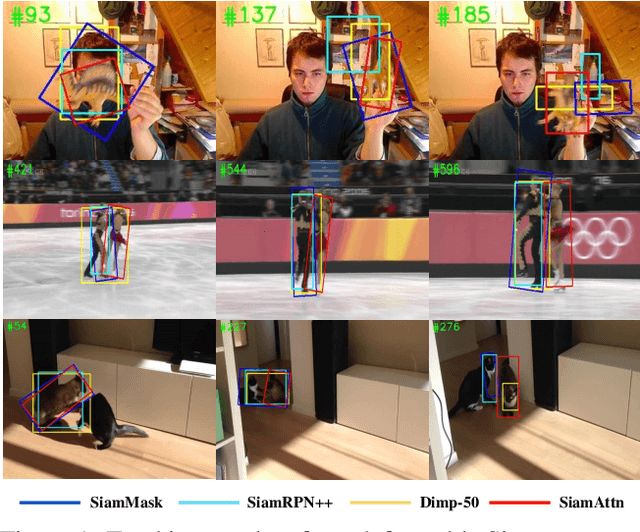
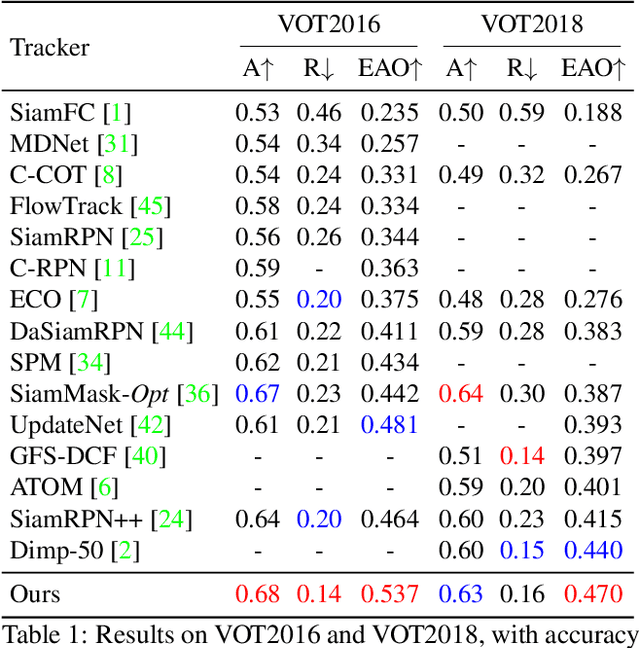
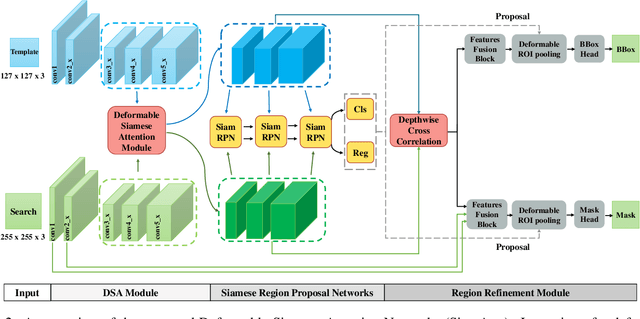
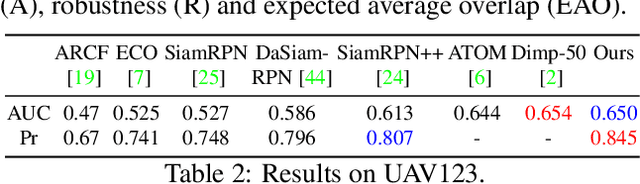
Abstract:Siamese-based trackers have achieved excellent performance on visual object tracking. However, the target template is not updated online, and the features of the target template and search image are computed independently in a Siamese architecture. In this paper, we propose Deformable Siamese Attention Networks, referred to as SiamAttn, by introducing a new Siamese attention mechanism that computes deformable self-attention and cross-attention. The self attention learns strong context information via spatial attention, and selectively emphasizes interdependent channel-wise features with channel attention. The cross-attention is capable of aggregating rich contextual inter-dependencies between the target template and the search image, providing an implicit manner to adaptively update the target template. In addition, we design a region refinement module that computes depth-wise cross correlations between the attentional features for more accurate tracking. We conduct experiments on six benchmarks, where our method achieves new state of-the-art results, outperforming the strong baseline, SiamRPN++ [24], by 0.464->0.537 and 0.415->0.470 EAO on VOT 2016 and 2018.
Move Forward and Tell: A Progressive Generator of Video Descriptions
Jul 26, 2018



Abstract:We present an efficient framework that can generate a coherent paragraph to describe a given video. Previous works on video captioning usually focus on video clips. They typically treat an entire video as a whole and generate the caption conditioned on a single embedding. On the contrary, we consider videos with rich temporal structures and aim to generate paragraph descriptions that can preserve the story flow while being coherent and concise. Towards this goal, we propose a new approach, which produces a descriptive paragraph by assembling temporally localized descriptions. Given a video, it selects a sequence of distinctive clips and generates sentences thereon in a coherent manner. Particularly, the selection of clips and the production of sentences are done jointly and progressively driven by a recurrent network -- what to describe next depends on what have been said before. Here, the recurrent network is learned via self-critical sequence training with both sentence-level and paragraph-level rewards. On the ActivityNet Captions dataset, our method demonstrated the capability of generating high-quality paragraph descriptions for videos. Compared to those by other methods, the descriptions produced by our method are often more relevant, more coherent, and more concise.
* Accepted by ECCV 2018
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge