Yihuan Liao
Generalizable Collaborative Search-and-Capture in Cluttered Environments via Path-Guided MAPPO and Directional Frontier Allocation
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Collaborative pursuit-evasion in cluttered environments presents significant challenges due to sparse rewards and constrained Fields of View (FOV). Standard Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning (MARL) often suffers from inefficient exploration and fails to scale to large scenarios. We propose PGF-MAPPO (Path-Guided Frontier MAPPO), a hierarchical framework bridging topological planning with reactive control. To resolve local minima and sparse rewards, we integrate an A*-based potential field for dense reward shaping. Furthermore, we introduce Directional Frontier Allocation, combining Farthest Point Sampling (FPS) with geometric angle suppression to enforce spatial dispersion and accelerate coverage. The architecture employs a parameter-shared decentralized critic, maintaining O(1) model complexity suitable for robotic swarms. Experiments demonstrate that PGF-MAPPO achieves superior capture efficiency against faster evaders. Policies trained on 10x10 maps exhibit robust zero-shot generalization to unseen 20x20 environments, significantly outperforming rule-based and learning-based baselines.
Sum-Rate Maximization for Pinching Antenna-assisted NOMA Systems with Multiple Dielectric Waveguides
Mar 13, 2025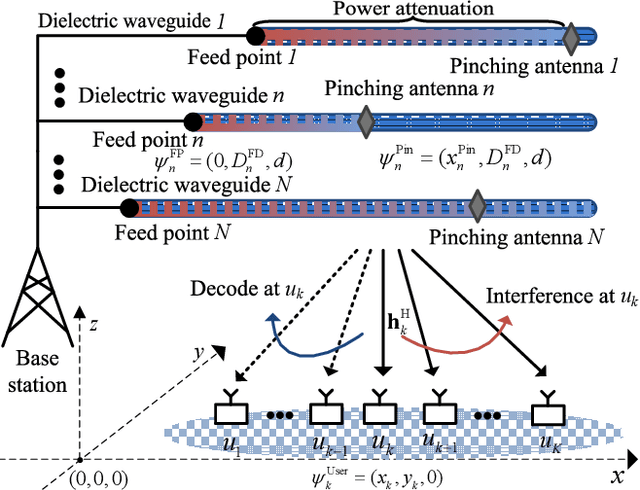
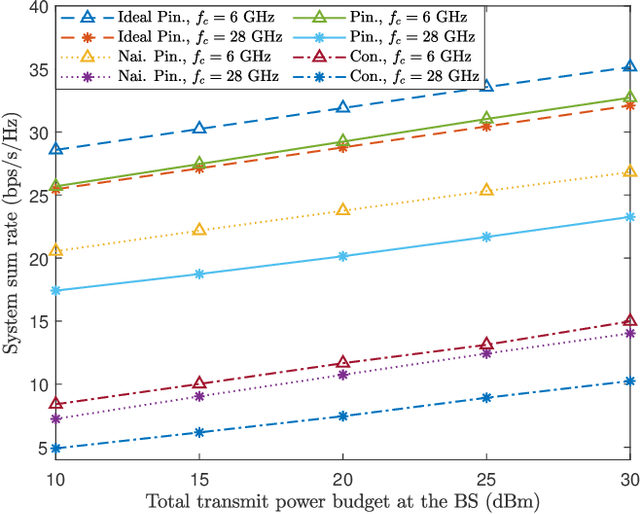
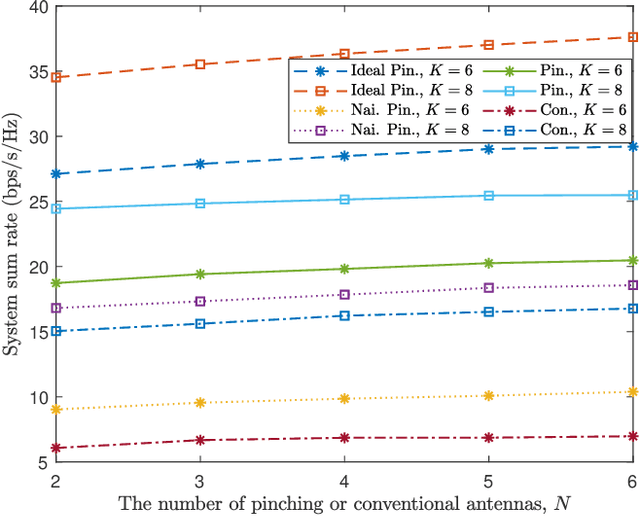
Abstract:This paper investigates the resource allocation design for a pinching antenna (PA)-assisted multiuser multiple-input single-output (MISO) non-orthogonal multiple access (NOMA) system featuring multiple dielectric waveguides. To enhance model accuracy, we propose a novel frequency-dependent power attenuation model for dielectric waveguides in PA-assisted systems. By jointly optimizing the precoder vector and the PA placement, we aim to maximize the system's sum-rate while accounting for the power attenuation across dielectric waveguides. The design is formulated as a non-convex optimization problem. To effectively address the problem at hand, we introduce an alternating optimization-based algorithm to obtain a suboptimal solution in polynomial time. Our results demonstrate that the proposed PA-assisted system not only significantly outperforms the conventional system but also surpasses a naive PA-assisted system that disregards power attenuation. The performance gain compared to the naive PA-assisted system becomes more pronounced at high carrier frequencies, emphasizing the importance of considering power attenuation in system design.
Self-Connected Spatially Coupled LDPC Codes with Improved Termination
Jun 30, 2023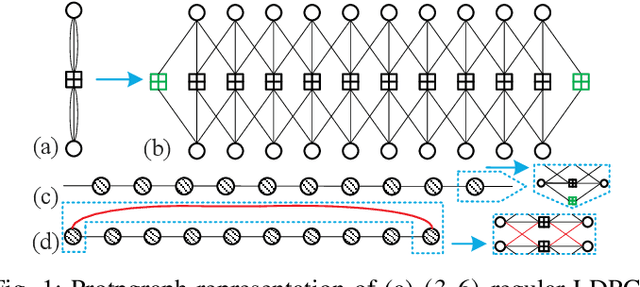
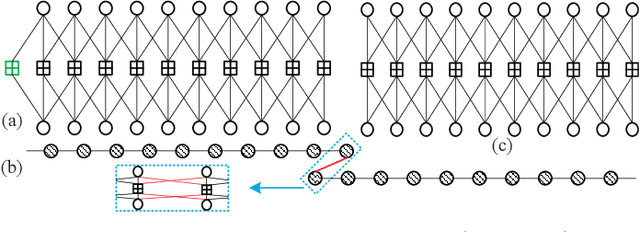
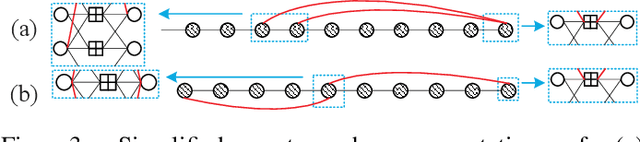
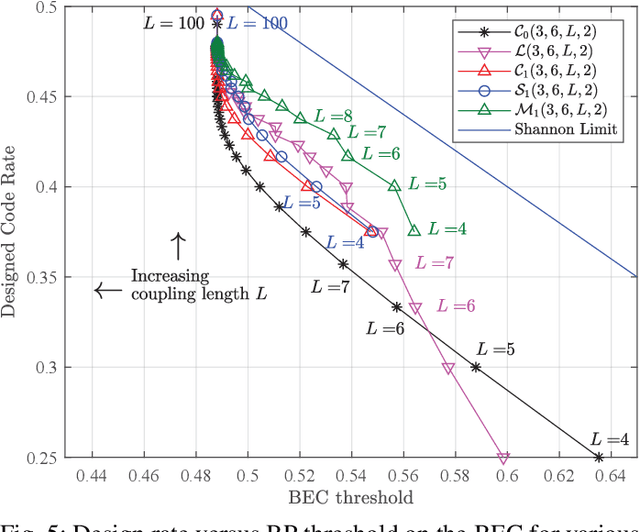
Abstract:This paper investigates the design of self-connected spatially coupled low-density parity-check (SC-LDPC) codes. First, a termination method is proposed to reduce rate loss. Particularly, a single-side open SC-LDPC ensemble is introduced, which halves the rate loss of a conventional terminated SC-LDPC by reducing the number of check nodes. We further propose a self-connection method that allows reliable information to propagate from several directions to improve the decoding threshold. We demonstrate that the proposed ensembles not only achieve a better trade-off between rate loss and gap to capacity than several existing protograph SC-LDPC codes with short chain lengths but also exhibit threshold saturation behavior. Finite blocklength error performance is provided to exemplify the superiority of the proposed codes over conventional protograph SC-LDPC codes.
Windowed Decoding for Delayed Bit-Interleaved Coded Modulation
Aug 15, 2021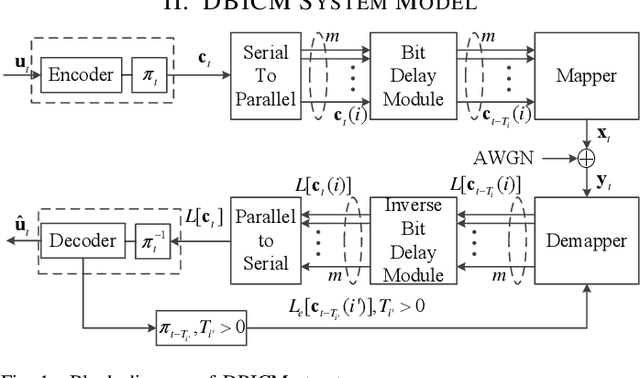
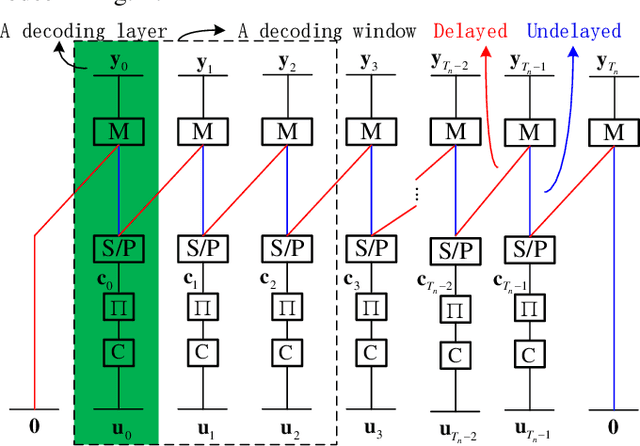
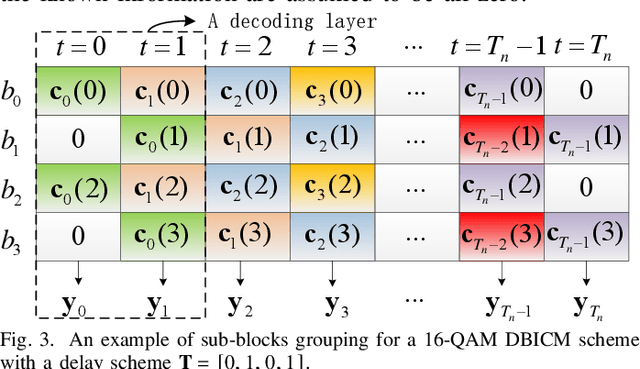
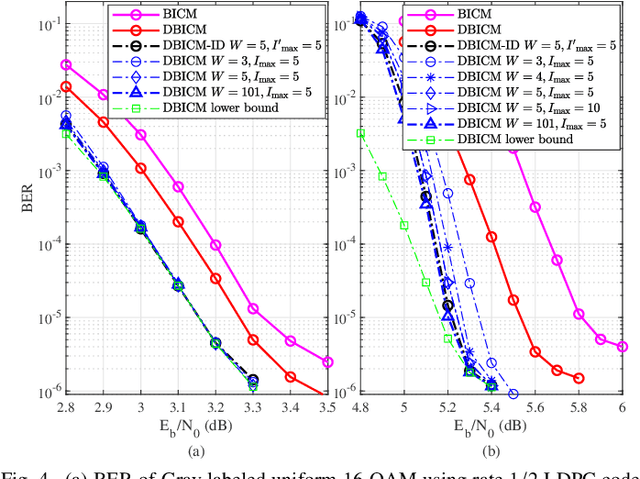
Abstract:Delayed bit-interleaved coded modulation (DBICM) generalizes bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) by modulating differently delayed sub-blocks of codewords onto the same signals. DBICM improves transmission reliability over BICM due to its capability of detecting undelayed sub-blocks with the extrinsic information of the decoded delayed sub-blocks. In this work, we propose a novel windowed decoding algorithm for DBICM, which uses the extrinsic information of both the decoded delayed and undelayed sub-blocks, to improve the detection on all sub-blocks. Numerical results show that the proposed windowed decoding significantly outperforms the original decoding.
Connecting Spatially Coupled LDPC Code Chains for Bit-Interleaved Coded Modulation
Jul 07, 2021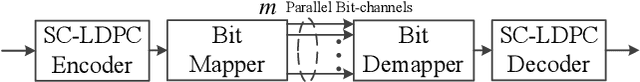
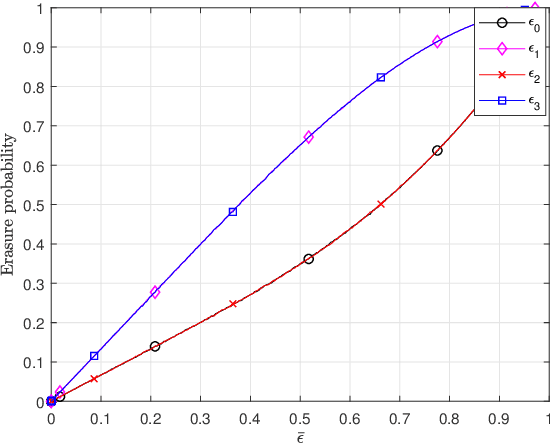
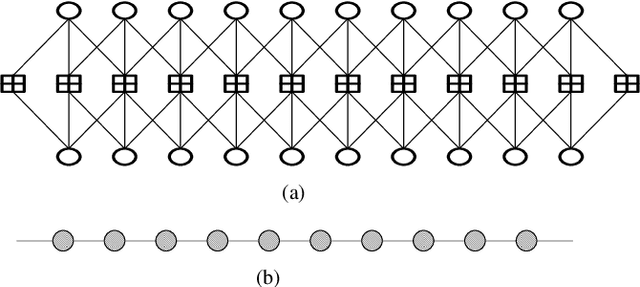
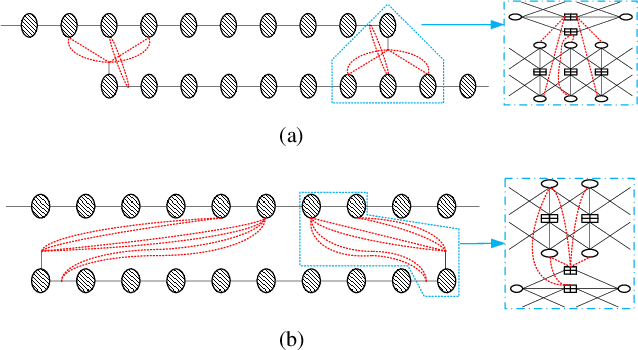
Abstract:This paper investigates the design of spatially coupled low-density parity-check (SC-LDPC) codes constructed from connected-chain ensembles for bit-interleaved coded modulation (BICM) schemes. For short coupling lengths, connecting multiple SC-LDPC chains can improve decoding performance over single-chains and impose structured unequal error protection (UEP). A joint design of connected-chain ensembles and bit mapping to further exploit the UEP from codes and high-order modulations is proposed. Numerical results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed design over existing connected-chain ensembles and over single-chain ensembles with existing bit mapping design.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge