Yiannis Gkoufas
IBM Research -- Ireland
Towards Real-time Customer Experience Prediction for Telecommunication Operators
Sep 24, 2015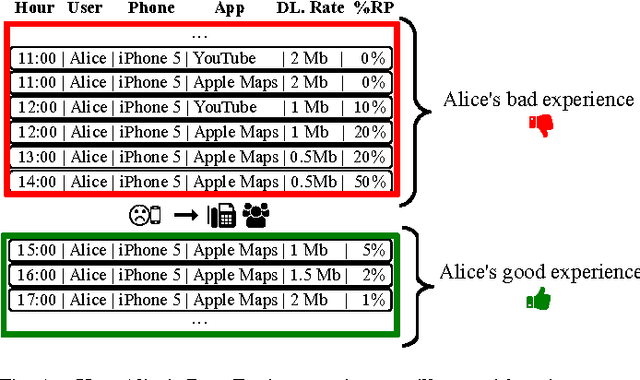
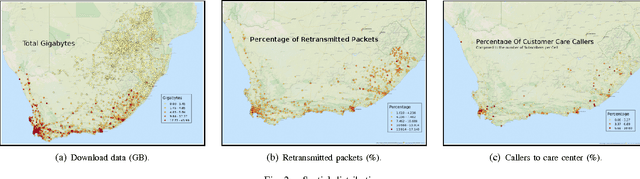
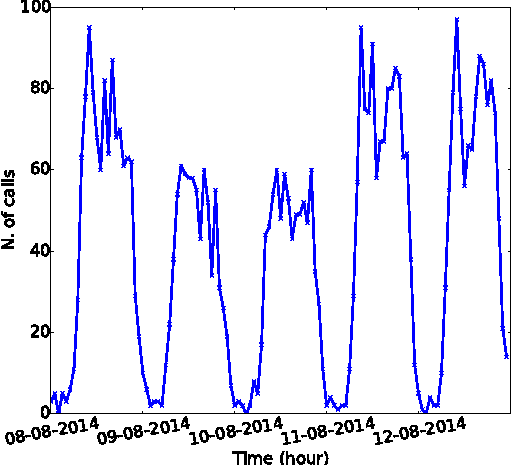
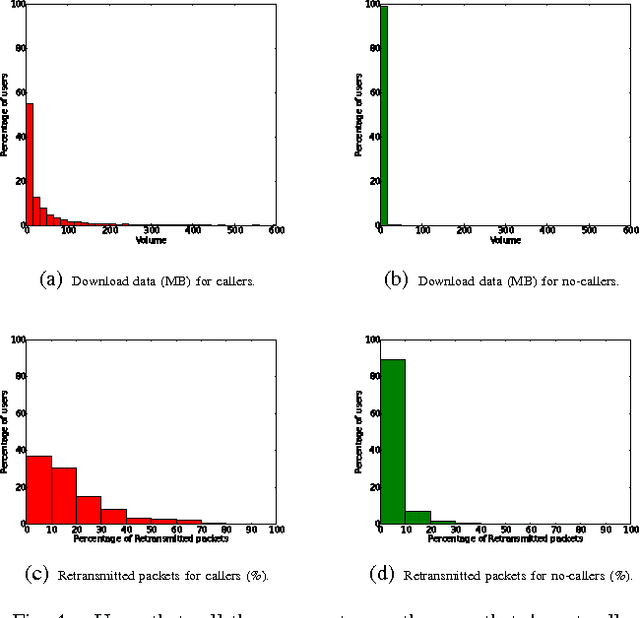
Abstract:Telecommunications operators (telcos) traditional sources of income, voice and SMS, are shrinking due to customers using over-the-top (OTT) applications such as WhatsApp or Viber. In this challenging environment it is critical for telcos to maintain or grow their market share, by providing users with as good an experience as possible on their network. But the task of extracting customer insights from the vast amounts of data collected by telcos is growing in complexity and scale everey day. How can we measure and predict the quality of a user's experience on a telco network in real-time? That is the problem that we address in this paper. We present an approach to capture, in (near) real-time, the mobile customer experience in order to assess which conditions lead the user to place a call to a telco's customer care center. To this end, we follow a supervised learning approach for prediction and train our 'Restricted Random Forest' model using, as a proxy for bad experience, the observed customer transactions in the telco data feed before the user places a call to a customer care center. We evaluate our approach using a rich dataset provided by a major African telecommunication's company and a novel big data architecture for both the training and scoring of predictive models. Our empirical study shows our solution to be effective at predicting user experience by inferring if a customer will place a call based on his current context. These promising results open new possibilities for improved customer service, which will help telcos to reduce churn rates and improve customer experience, both factors that directly impact their revenue growth.
(Blue) Taxi Destination and Trip Time Prediction from Partial Trajectories
Sep 17, 2015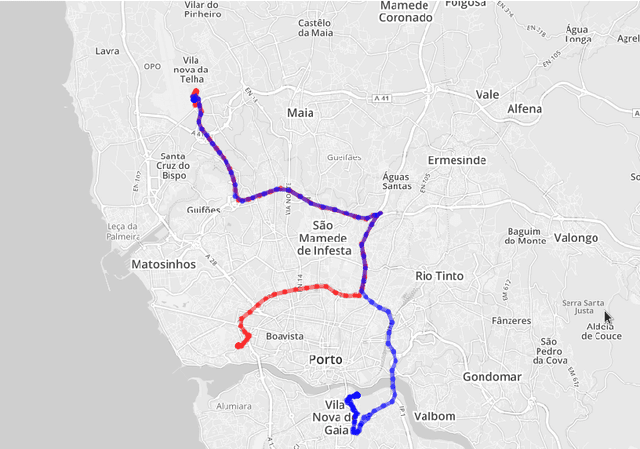
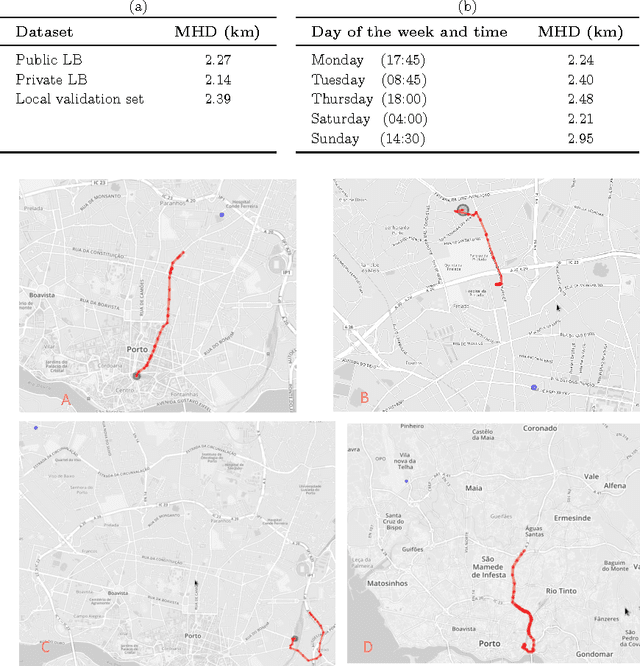
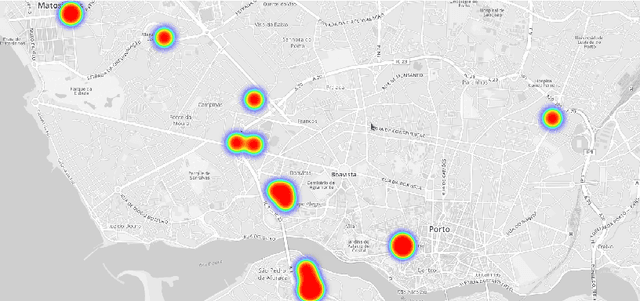
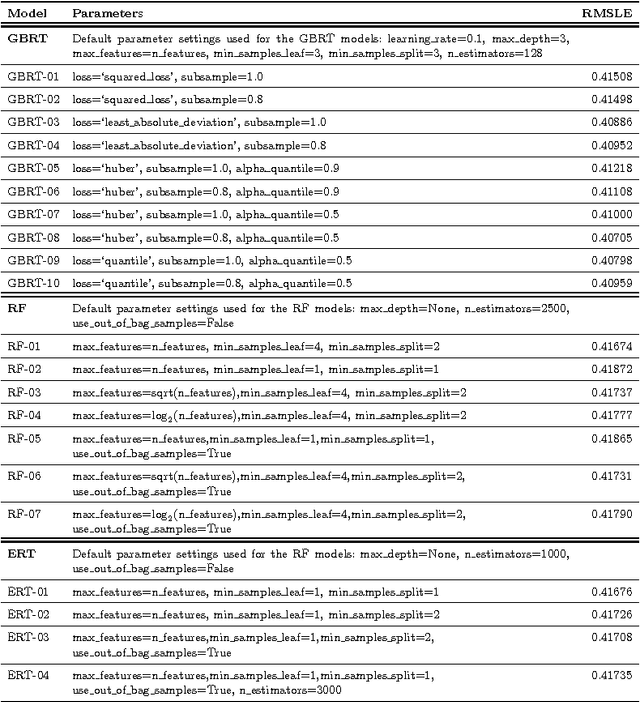
Abstract:Real-time estimation of destination and travel time for taxis is of great importance for existing electronic dispatch systems. We present an approach based on trip matching and ensemble learning, in which we leverage the patterns observed in a dataset of roughly 1.7 million taxi journeys to predict the corresponding final destination and travel time for ongoing taxi trips, as a solution for the ECML/PKDD Discovery Challenge 2015 competition. The results of our empirical evaluation show that our approach is effective and very robust, which led our team -- BlueTaxi -- to the 3rd and 7th position of the final rankings for the trip time and destination prediction tasks, respectively. Given the fact that the final rankings were computed using a very small test set (with only 320 trips) we believe that our approach is one of the most robust solutions for the challenge based on the consistency of our good results across the test sets.
Predicting User Engagement in Twitter with Collaborative Ranking
Dec 26, 2014
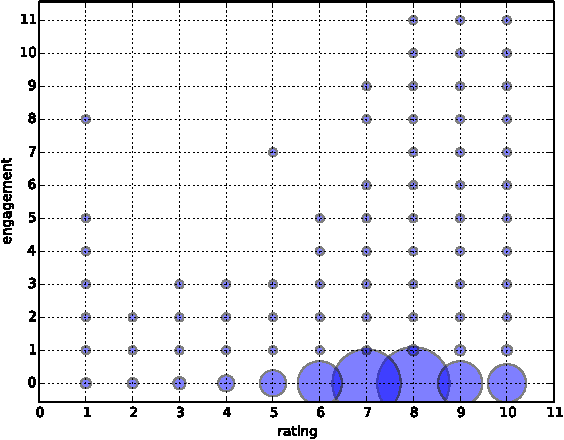

Abstract:Collaborative Filtering (CF) is a core component of popular web-based services such as Amazon, YouTube, Netflix, and Twitter. Most applications use CF to recommend a small set of items to the user. For instance, YouTube presents to a user a list of top-n videos she would likely watch next based on her rating and viewing history. Current methods of CF evaluation have been focused on assessing the quality of a predicted rating or the ranking performance for top-n recommended items. However, restricting the recommender system evaluation to these two aspects is rather limiting and neglects other dimensions that could better characterize a well-perceived recommendation. In this paper, instead of optimizing rating or top-n recommendation, we focus on the task of predicting which items generate the highest user engagement. In particular, we use Twitter as our testbed and cast the problem as a Collaborative Ranking task where the rich features extracted from the metadata of the tweets help to complement the transaction information limited to user ids, item ids, ratings and timestamps. We learn a scoring function that directly optimizes the user engagement in terms of nDCG@10 on the predicted ranking. Experiments conducted on an extended version of the MovieTweetings dataset, released as part of the RecSys Challenge 2014, show the effectiveness of our approach.
* RecSysChallenge'14 at RecSys 2014, October 10, 2014, Foster City, CA, USA
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge