Yi-Chieh Lee
Multi-Agent Systems Shape Social Norms for Prosocial Behavior Change
Feb 07, 2026Abstract:Social norm interventions are used promote prosocial behaviors by highlighting prevalent actions, but their effectiveness is often limited in heterogeneous populations where shared understandings of desirable behaviors are lacking. This study explores whether multi-agent systems can establish "virtual social norms" to encourage donation behavior. We conducted an online experiment where participants interacted with a group of agents to discuss donation behaviors. Changes in perceived social norms, conformity, donation behavior, and user experience were measured pre- and postdiscussion. Results show that multi-agent interactions effectively increased perceived social norms and donation willingness. Notably, in-group agents led to stronger perceived social norms, higher conformity, and greater donation increases compared to out-group agents. Our findings demonstrate the potential of multi-agent systems for creating social norm interventions and offer insights into leveraging social identity dynamics to promote prosocial behavior in virtual environments.
Designing Computational Tools for Exploring Causal Relationships in Qualitative Data
Feb 06, 2026Abstract:Exploring causal relationships for qualitative data analysis in HCI and social science research enables the understanding of user needs and theory building. However, current computational tools primarily characterize and categorize qualitative data; the few systems that analyze causal relationships either inadequately consider context, lack credibility, or produce overly complex outputs. We first conducted a formative study with 15 participants interested in using computational tools for exploring causal relationships in qualitative data to understand their needs and derive design guidelines. Based on these findings, we designed and implemented QualCausal, a system that extracts and illustrates causal relationships through interactive causal network construction and multi-view visualization. A feedback study (n = 15) revealed that participants valued our system for reducing the analytical burden and providing cognitive scaffolding, yet navigated how such systems fit within their established research paradigms, practices, and habits. We discuss broader implications for designing computational tools that support qualitative data analysis.
AI-exhibited Personality Traits Can Shape Human Self-concept through Conversations
Jan 19, 2026Abstract:Recent Large Language Model (LLM) based AI can exhibit recognizable and measurable personality traits during conversations to improve user experience. However, as human understandings of their personality traits can be affected by their interaction partners' traits, a potential risk is that AI traits may shape and bias users' self-concept of their own traits. To explore the possibility, we conducted a randomized behavioral experiment. Our results indicate that after conversations about personal topics with an LLM-based AI chatbot using GPT-4o default personality traits, users' self-concepts aligned with the AI's measured personality traits. The longer the conversation, the greater the alignment. This alignment led to increased homogeneity in self-concepts among users. We also observed that the degree of self-concept alignment was positively associated with users' conversation enjoyment. Our findings uncover how AI personality traits can shape users' self-concepts through human-AI conversation, highlighting both risks and opportunities. We provide important design implications for developing more responsible and ethical AI systems.
Exploring the Effects of Chatbot Anthropomorphism and Human Empathy on Human Prosocial Behavior Toward Chatbots
Jun 25, 2025Abstract:Chatbots are increasingly integrated into people's lives and are widely used to help people. Recently, there has also been growing interest in the reverse direction-humans help chatbots-due to a wide range of benefits including better chatbot performance, human well-being, and collaborative outcomes. However, little research has explored the factors that motivate people to help chatbots. To address this gap, we draw on the Computers Are Social Actors (CASA) framework to examine how chatbot anthropomorphism-including human-like identity, emotional expression, and non-verbal expression-influences human empathy toward chatbots and their subsequent prosocial behaviors and intentions. We also explore people's own interpretations of their prosocial behaviors toward chatbots. We conducted an online experiment (N = 244) in which chatbots made mistakes in a collaborative image labeling task and explained the reasons to participants. We then measured participants' prosocial behaviors and intentions toward the chatbots. Our findings revealed that human identity and emotional expression of chatbots increased participants' prosocial behavior and intention toward chatbots, with empathy mediating these effects. Qualitative analysis further identified two motivations for participants' prosocial behaviors: empathy for the chatbot and perceiving the chatbot as human-like. We discuss the implications of these results for understanding and promoting human prosocial behaviors toward chatbots.
What is Stigma Attributed to? A Theory-Grounded, Expert-Annotated Interview Corpus for Demystifying Mental-Health Stigma
May 19, 2025Abstract:Mental-health stigma remains a pervasive social problem that hampers treatment-seeking and recovery. Existing resources for training neural models to finely classify such stigma are limited, relying primarily on social-media or synthetic data without theoretical underpinnings. To remedy this gap, we present an expert-annotated, theory-informed corpus of human-chatbot interviews, comprising 4,141 snippets from 684 participants with documented socio-cultural backgrounds. Our experiments benchmark state-of-the-art neural models and empirically unpack the challenges of stigma detection. This dataset can facilitate research on computationally detecting, neutralizing, and counteracting mental-health stigma.
Deconstructing Depression Stigma: Integrating AI-driven Data Collection and Analysis with Causal Knowledge Graphs
Feb 09, 2025Abstract:Mental-illness stigma is a persistent social problem, hampering both treatment-seeking and recovery. Accordingly, there is a pressing need to understand it more clearly, but analyzing the relevant data is highly labor-intensive. Therefore, we designed a chatbot to engage participants in conversations; coded those conversations qualitatively with AI assistance; and, based on those coding results, built causal knowledge graphs to decode stigma. The results we obtained from 1,002 participants demonstrate that conversation with our chatbot can elicit rich information about people's attitudes toward depression, while our AI-assisted coding was strongly consistent with human-expert coding. Our novel approach combining large language models (LLMs) and causal knowledge graphs uncovered patterns in individual responses and illustrated the interrelationships of psychological constructs in the dataset as a whole. The paper also discusses these findings' implications for HCI researchers in developing digital interventions, decomposing human psychological constructs, and fostering inclusive attitudes.
Wild Narratives: Exploring the Effects of Animal Chatbots on Empathy and Positive Attitudes toward Animals
Nov 09, 2024



Abstract:Rises in the number of animal abuse cases are reported around the world. While chatbots have been effective in influencing their users' perceptions and behaviors, little if any research has hitherto explored the design of chatbots that embody animal identities for the purpose of eliciting empathy toward animals. We therefore conducted a mixed-methods experiment to investigate how specific design cues in such chatbots can shape their users' perceptions of both the chatbots' identities and the type of animal they represent. Our findings indicate that such chatbots can significantly increase empathy, improve attitudes, and promote prosocial behavioral intentions toward animals, particularly when they incorporate emotional verbal expressions and authentic details of such animals' lives. These results expand our understanding of chatbots with non-human identities and highlight their potential for use in conservation initiatives, suggesting a promising avenue whereby technology could foster a more informed and empathetic society.
Multi-Agents are Social Groups: Investigating Social Influence of Multiple Agents in Human-Agent Interactions
Nov 07, 2024



Abstract:Multi-agent systems - systems with multiple independent AI agents working together to achieve a common goal - are becoming increasingly prevalent in daily life. Drawing inspiration from the phenomenon of human group social influence, we investigate whether a group of AI agents can create social pressure on users to agree with them, potentially changing their stance on a topic. We conducted a study in which participants discussed social issues with either a single or multiple AI agents, and where the agents either agreed or disagreed with the user's stance on the topic. We found that conversing with multiple agents (holding conversation content constant) increased the social pressure felt by participants, and caused a greater shift in opinion towards the agents' stances on each topic. Our study shows the potential advantages of multi-agent systems over single-agent platforms in causing opinion change. We discuss design implications for possible multi-agent systems that promote social good, as well as the potential for malicious actors to use these systems to manipulate public opinion.
Exploring the Potential of Human-LLM Synergy in Advancing Qualitative Analysis: A Case Study on Mental-Illness Stigma
May 09, 2024
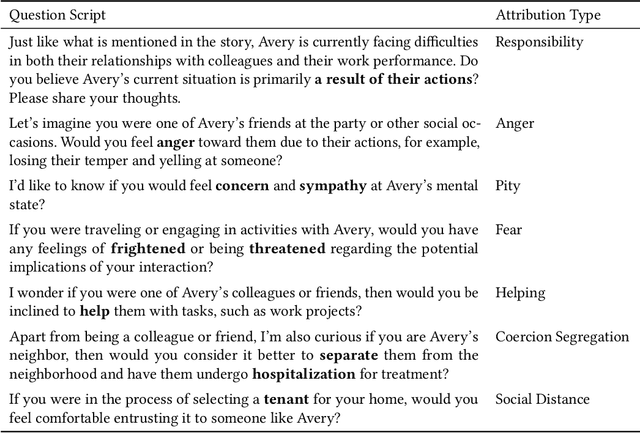
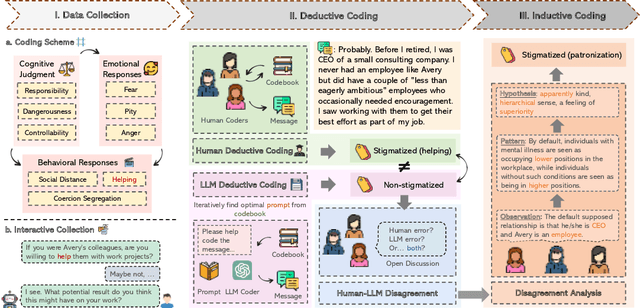
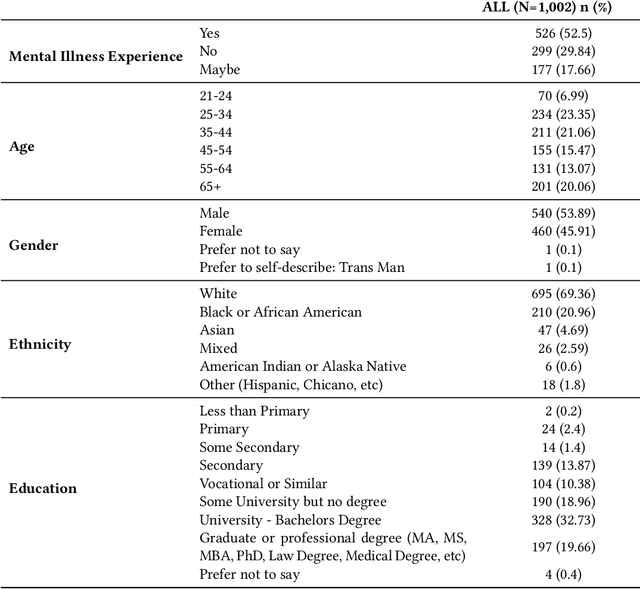
Abstract:Qualitative analysis is a challenging, yet crucial aspect of advancing research in the field of Human-Computer Interaction (HCI). Recent studies show that large language models (LLMs) can perform qualitative coding within existing schemes, but their potential for collaborative human-LLM discovery and new insight generation in qualitative analysis is still underexplored. To bridge this gap and advance qualitative analysis by harnessing the power of LLMs, we propose CHALET, a novel methodology that leverages the human-LLM collaboration paradigm to facilitate conceptualization and empower qualitative research. The CHALET approach involves LLM-supported data collection, performing both human and LLM deductive coding to identify disagreements, and performing collaborative inductive coding on these disagreement cases to derive new conceptual insights. We validated the effectiveness of CHALET through its application to the attribution model of mental-illness stigma, uncovering implicit stigmatization themes on cognitive, emotional and behavioral dimensions. We discuss the implications for future research, methodology, and the transdisciplinary opportunities CHALET presents for the HCI community and beyond.
Understanding Public Perceptions of AI Conversational Agents: A Cross-Cultural Analysis
Feb 25, 2024



Abstract:Conversational Agents (CAs) have increasingly been integrated into everyday life, sparking significant discussions on social media. While previous research has examined public perceptions of AI in general, there is a notable lack in research focused on CAs, with fewer investigations into cultural variations in CA perceptions. To address this gap, this study used computational methods to analyze about one million social media discussions surrounding CAs and compared people's discourses and perceptions of CAs in the US and China. We find Chinese participants tended to view CAs hedonically, perceived voice-based and physically embodied CAs as warmer and more competent, and generally expressed positive emotions. In contrast, US participants saw CAs more functionally, with an ambivalent attitude. Warm perception was a key driver of positive emotions toward CAs in both countries. We discussed practical implications for designing contextually sensitive and user-centric CAs to resonate with various users' preferences and needs.
* 17 pages, 4 figures, 7 tables
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge