Yesh Godse
Sim-to-Real Learning of All Common Bipedal Gaits via Periodic Reward Composition
Nov 02, 2020



Abstract:We study the problem of realizing the full spectrum of bipedal locomotion on a real robot with sim-to-real reinforcement learning (RL). A key challenge of learning legged locomotion is describing different gaits, via reward functions, in a way that is intuitive for the designer and specific enough to reliably learn the gait across different initial random seeds or hyperparameters. A common approach is to use reference motions (e.g. trajectories of joint positions) to guide learning. However, finding high-quality reference motions can be difficult and the trajectories themselves narrowly constrain the space of learned motion. At the other extreme, reference-free reward functions are often underspecified (e.g. move forward) leading to massive variance in policy behavior, or are the product of significant reward-shaping via trial-and-error, making them exclusive to specific gaits. In this work, we propose a reward-specification framework based on composing simple probabilistic periodic costs on basic forces and velocities. We instantiate this framework to define a parametric reward function with intuitive settings for all common bipedal gaits - standing, walking, hopping, running, and skipping. Using this function we demonstrate successful sim-to-real transfer of the learned gaits to the bipedal robot Cassie, as well as a generic policy that can transition between all of the two-beat gaits.
Learning Spring Mass Locomotion: Guiding Policies with a Reduced-Order Model
Oct 21, 2020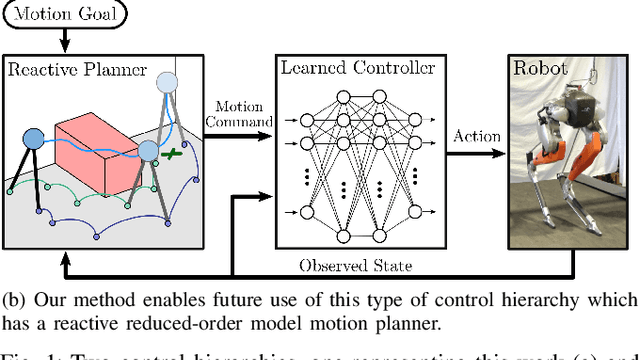
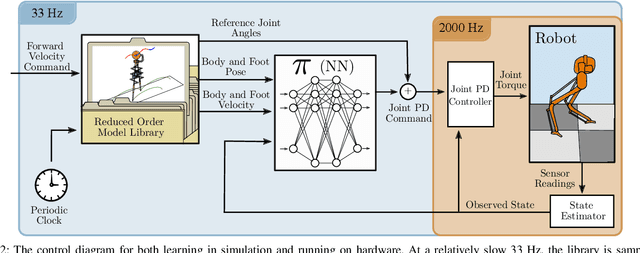
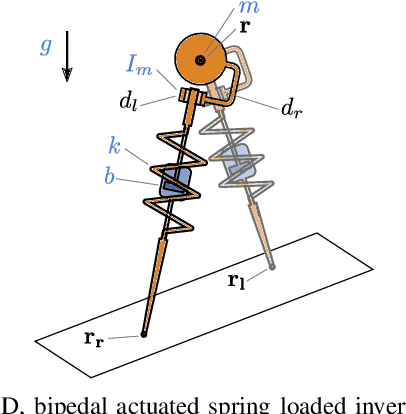
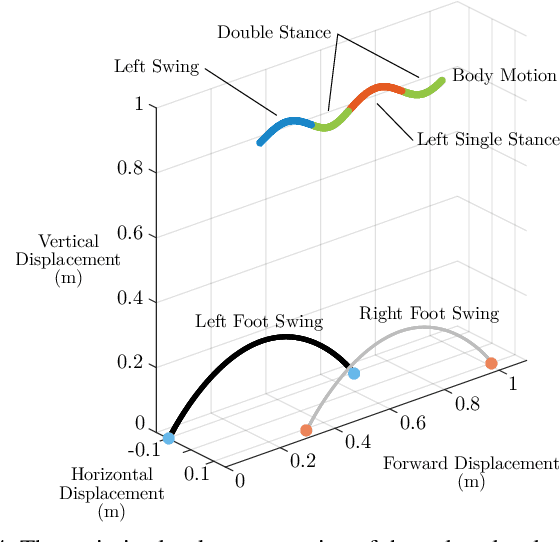
Abstract:In this paper, we describe an approach to achieve dynamic legged locomotion on physical robots which combines existing methods for control with reinforcement learning. Specifically, our goal is a control hierarchy in which highest-level behaviors are planned through reduced-order models, which describe the fundamental physics of legged locomotion, and lower level controllers utilize a learned policy that can bridge the gap between the idealized, simple model and the complex, full order robot. The high-level planner can use a model of the environment and be task specific, while the low-level learned controller can execute a wide range of motions so that it applies to many different tasks. In this letter we describe this learned dynamic walking controller and show that a range of walking motions from reduced-order models can be used as the command and primary training signal for learned policies. The resulting policies do not attempt to naively track the motion (as a traditional trajectory tracking controller would) but instead balance immediate motion tracking with long term stability. The resulting controller is demonstrated on a human scale, unconstrained, untethered bipedal robot at speeds up to 1.2 m/s. This letter builds the foundation of a generic, dynamic learned walking controller that can be applied to many different tasks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge