Yejiang Yang
Efficient Neural Hybrid System Learning and Transition System Abstraction for Dynamical Systems
Nov 15, 2024


Abstract:This paper proposes a neural network hybrid modeling framework for dynamics learning to promote an interpretable, computationally efficient way of dynamics learning and system identification. First, a low-level model will be trained to learn the system dynamics, which utilizes multiple simple neural networks to approximate the local dynamics generated from data-driven partitions. Then, based on the low-level model, a high-level model will be trained to abstract the low-level neural hybrid system model into a transition system that allows Computational Tree Logic Verification to promote the model's ability with human interaction and verification efficiency.
Compression Repair for Feedforward Neural Networks Based on Model Equivalence Evaluation
Feb 18, 2024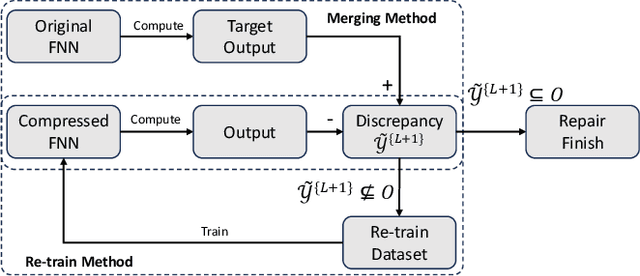
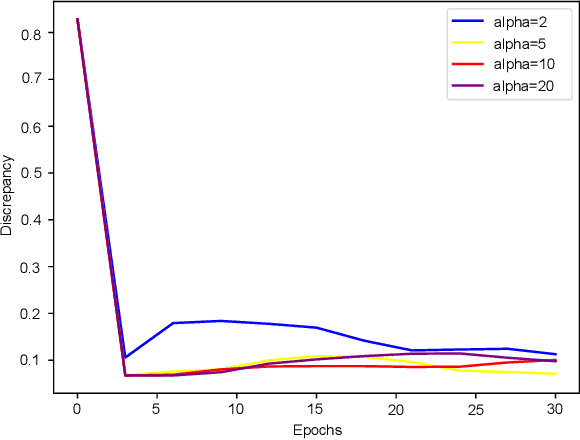
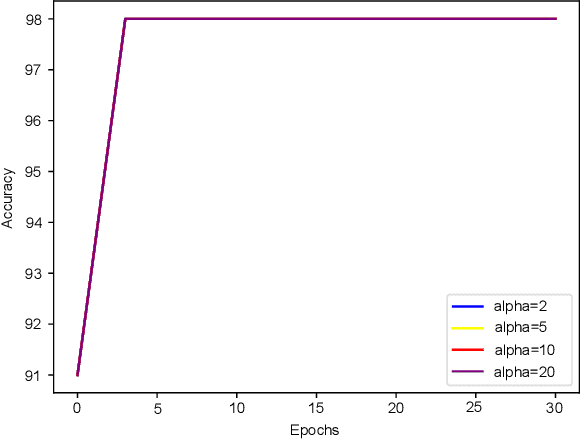
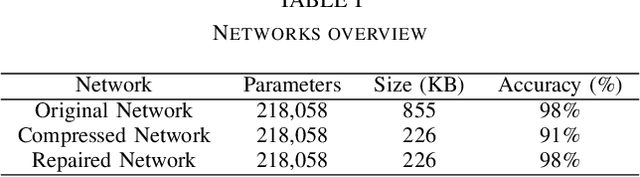
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a method of repairing compressed Feedforward Neural Networks (FNNs) based on equivalence evaluation of two neural networks. In the repairing framework, a novel neural network equivalence evaluation method is developed to compute the output discrepancy between two neural networks. The output discrepancy can quantitatively characterize the output difference produced by compression procedures. Based on the computed output discrepancy, the repairing method first initializes a new training set for the compressed networks to narrow down the discrepancy between the two neural networks and improve the performance of the compressed network. Then, we repair the compressed FNN by re-training based on the training set. We apply our developed method to the MNIST dataset to demonstrate the effectiveness and advantages of our proposed repair method.
A Transition System Abstraction Framework for Neural Network Dynamical System Models
Feb 18, 2024


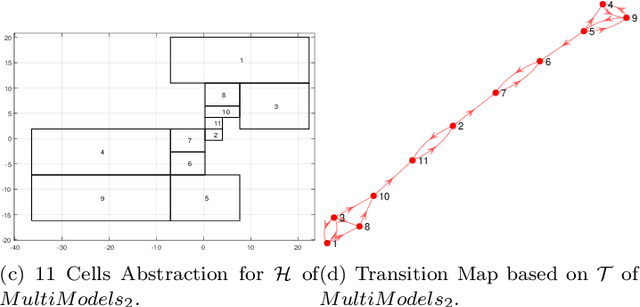
Abstract:This paper proposes a transition system abstraction framework for neural network dynamical system models to enhance the model interpretability, with applications to complex dynamical systems such as human behavior learning and verification. To begin with, the localized working zone will be segmented into multiple localized partitions under the data-driven Maximum Entropy (ME) partitioning method. Then, the transition matrix will be obtained based on the set-valued reachability analysis of neural networks. Finally, applications to human handwriting dynamics learning and verification are given to validate our proposed abstraction framework, which demonstrates the advantages of enhancing the interpretability of the black-box model, i.e., our proposed framework is able to abstract a data-driven neural network model into a transition system, making the neural network model interpretable through verifying specifications described in Computational Tree Logic (CTL) languages.
A Data-Driven Hybrid Automaton Framework to Modeling Complex Dynamical Systems
Apr 26, 2023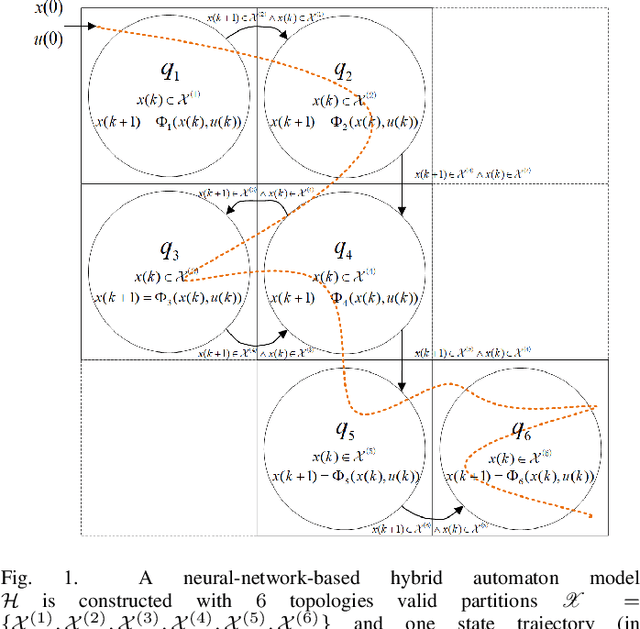
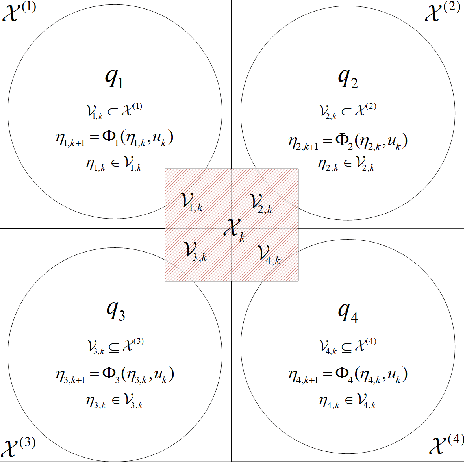
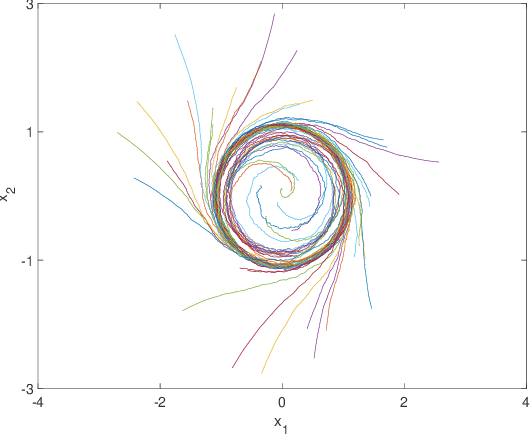
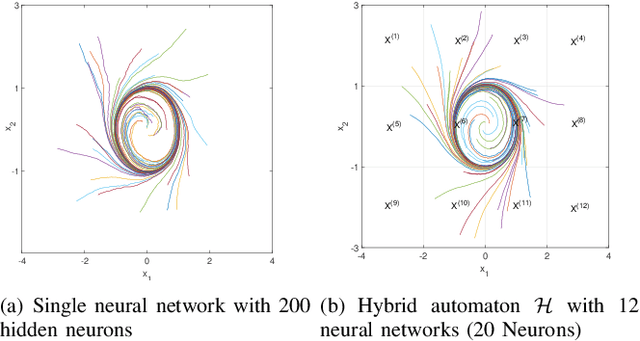
Abstract:In this paper, a computationally efficient data-driven hybrid automaton model is proposed to capture unknown complex dynamical system behaviors using multiple neural networks. The sampled data of the system is divided by valid partitions into groups corresponding to their topologies and based on which, transition guards are defined. Then, a collection of small-scale neural networks that are computationally efficient are trained as the local dynamical description for their corresponding topologies. After modeling the system with a neural-network-based hybrid automaton, the set-valued reachability analysis with low computation cost is provided based on interval analysis and a split and combined process. At last, a numerical example of the limit cycle is presented to illustrate that the developed models can significantly reduce the computational cost in reachable set computation without sacrificing any modeling precision.
Robust Optimization Framework for Training Shallow Neural Networks Using Reachability Method
Jul 27, 2021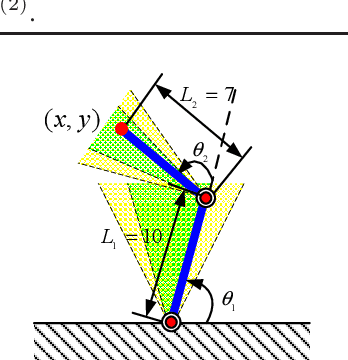
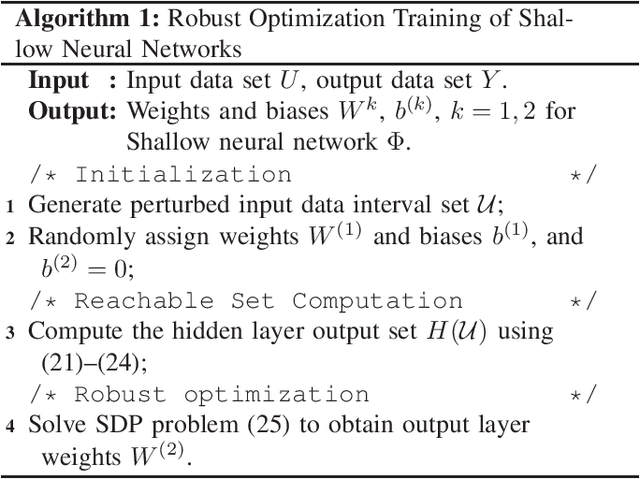
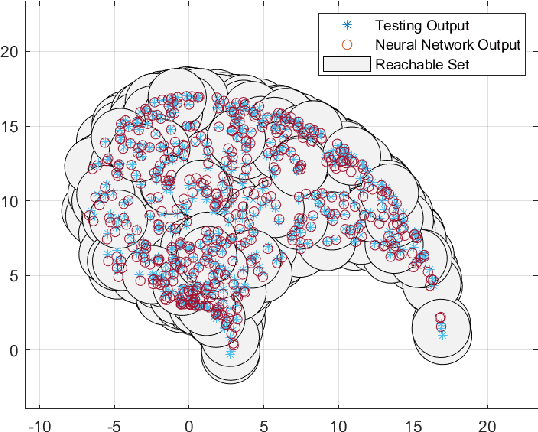
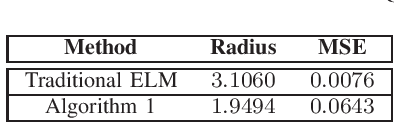
Abstract:In this paper, a robust optimization framework is developed to train shallow neural networks based on reachability analysis of neural networks. To characterize noises of input data, the input training data is disturbed in the description of interval sets. Interval-based reachability analysis is then performed for the hidden layer. With the reachability analysis results, a robust optimization training method is developed in the framework of robust least-square problems. Then, the developed robust least-square problem is relaxed to a semidefinite programming problem. It has been shown that the developed robust learning method can provide better robustness against perturbations at the price of loss of training accuracy to some extent. At last, the proposed method is evaluated on a robot arm model learning example.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge