Yeganeh Bahoo
Inverse k-visibility for RSSI-based Indoor Geometric Mapping
Aug 14, 2024Abstract:In recent years, the increased availability of WiFi in indoor environments has gained an interest in the robotics community to leverage WiFi signals for enhancing indoor SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) systems. SLAM technology is widely used, especially for the navigation and control of autonomous robots. This paper discusses various works in developing WiFi-based localization and challenges in achieving high-accuracy geometric maps. This paper introduces the concept of inverse k-visibility developed from the k-visibility algorithm to identify the free space in an unknown environment for planning, navigation, and obstacle avoidance. Comprehensive experiments, including those utilizing single and multiple RSSI signals, were conducted in both simulated and real-world environments to demonstrate the robustness of the proposed algorithm. Additionally, a detailed analysis comparing the resulting maps with ground-truth Lidar-based maps is provided to highlight the algorithm's accuracy and reliability.
DPPE: Dense Pose Estimation in a Plenoxels Environment using Gradient Approximation
Mar 16, 2024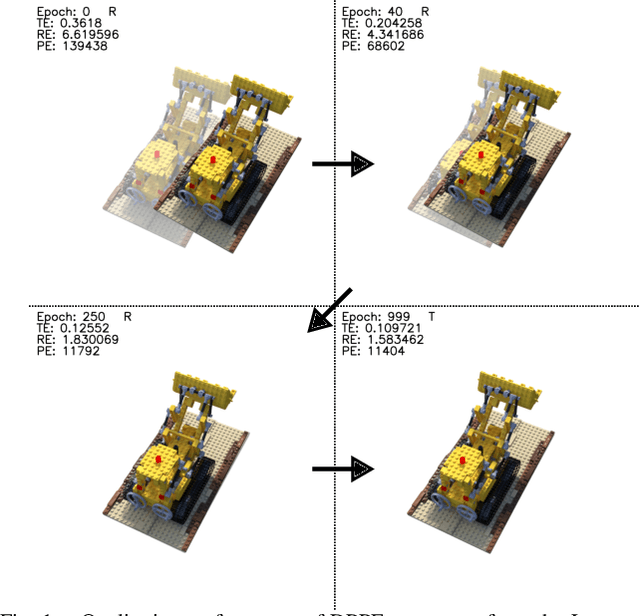
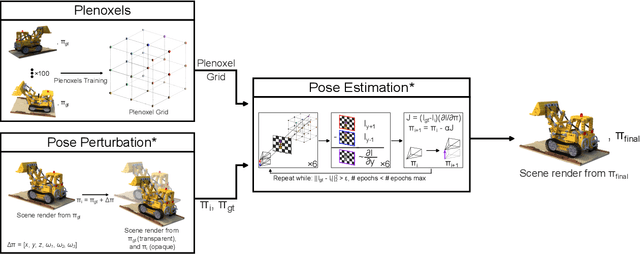
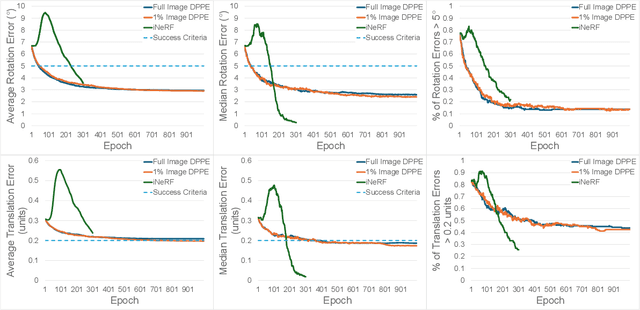

Abstract:We present DPPE, a dense pose estimation algorithm that functions over a Plenoxels environment. Recent advances in neural radiance field techniques have shown that it is a powerful tool for environment representation. More recent neural rendering algorithms have significantly improved both training duration and rendering speed. Plenoxels introduced a fully-differentiable radiance field technique that uses Plenoptic volume elements contained in voxels for rendering, offering reduced training times and better rendering accuracy, while also eliminating the neural net component. In this work, we introduce a 6-DoF monocular RGB-only pose estimation procedure for Plenoxels, which seeks to recover the ground truth camera pose after a perturbation. We employ a variation on classical template matching techniques, using stochastic gradient descent to optimize the pose by minimizing errors in re-rendering. In particular, we examine an approach that takes advantage of the rapid rendering speed of Plenoxels to numerically approximate part of the pose gradient, using a central differencing technique. We show that such methods are effective in pose estimation. Finally, we perform ablations over key components of the problem space, with a particular focus on image subsampling and Plenoxel grid resolution. Project website: https://sites.google.com/view/dppe
Structure from WiFi (SfW): RSSI-based Geometric Mapping of Indoor Environments
Mar 04, 2024Abstract:With the rising prominence of WiFi in common spaces, efforts have been made in the robotics community to take advantage of this fact by incorporating WiFi signal measurements in indoor SLAM (Simultaneous Localization and Mapping) systems. SLAM is essential in a wide range of applications, especially in the control of autonomous robots. This paper describes recent work in the development of WiFi-based localization and addresses the challenges currently faced in achieving WiFi-based geometric mapping. Inspired by the field of research into k-visibility, this paper presents the concept of inverse k-visibility and proposes a novel algorithm that allows robots to build a map of the free space of an unknown environment, essential for planning, navigation, and avoiding obstacles. Experiments performed in simulated and real-world environments demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge