Christopher Kolios
Morphological Detection and Classification of Microplastics and Nanoplastics Emerged from Consumer Products by Deep Learning
Sep 20, 2024



Abstract:Plastic pollution presents an escalating global issue, impacting health and environmental systems, with micro- and nanoplastics found across mediums from potable water to air. Traditional methods for studying these contaminants are labor-intensive and time-consuming, necessitating a shift towards more efficient technologies. In response, this paper introduces micro- and nanoplastics (MiNa), a novel and open-source dataset engineered for the automatic detection and classification of micro and nanoplastics using object detection algorithms. The dataset, comprising scanning electron microscopy images simulated under realistic aquatic conditions, categorizes plastics by polymer type across a broad size spectrum. We demonstrate the application of state-of-the-art detection algorithms on MiNa, assessing their effectiveness and identifying the unique challenges and potential of each method. The dataset not only fills a critical gap in available resources for microplastic research but also provides a robust foundation for future advancements in the field.
DPPE: Dense Pose Estimation in a Plenoxels Environment using Gradient Approximation
Mar 16, 2024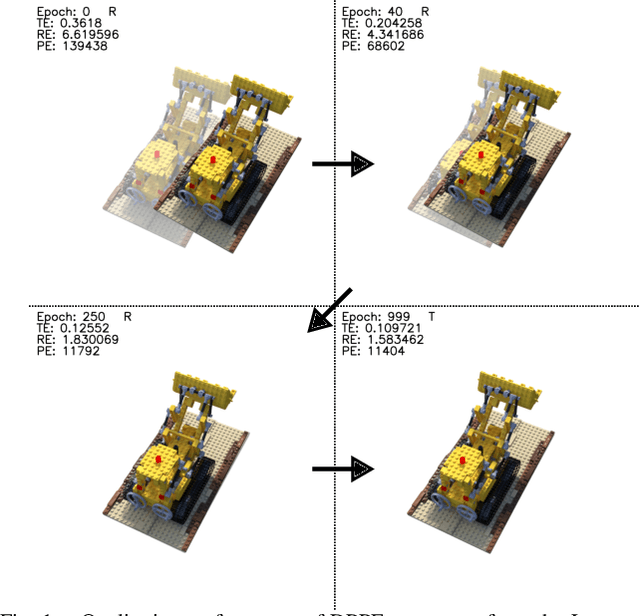
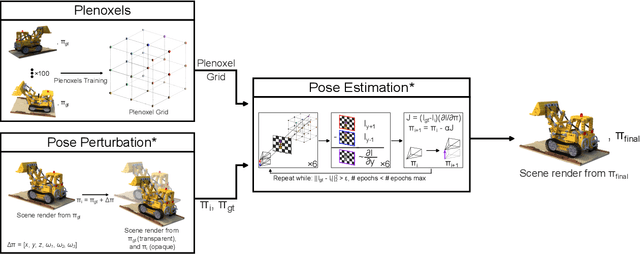
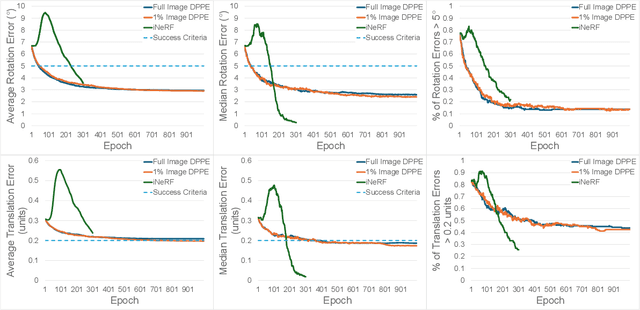

Abstract:We present DPPE, a dense pose estimation algorithm that functions over a Plenoxels environment. Recent advances in neural radiance field techniques have shown that it is a powerful tool for environment representation. More recent neural rendering algorithms have significantly improved both training duration and rendering speed. Plenoxels introduced a fully-differentiable radiance field technique that uses Plenoptic volume elements contained in voxels for rendering, offering reduced training times and better rendering accuracy, while also eliminating the neural net component. In this work, we introduce a 6-DoF monocular RGB-only pose estimation procedure for Plenoxels, which seeks to recover the ground truth camera pose after a perturbation. We employ a variation on classical template matching techniques, using stochastic gradient descent to optimize the pose by minimizing errors in re-rendering. In particular, we examine an approach that takes advantage of the rapid rendering speed of Plenoxels to numerically approximate part of the pose gradient, using a central differencing technique. We show that such methods are effective in pose estimation. Finally, we perform ablations over key components of the problem space, with a particular focus on image subsampling and Plenoxel grid resolution. Project website: https://sites.google.com/view/dppe
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge