Yazhong Si
AOSR-Net: All-in-One Sandstorm Removal Network
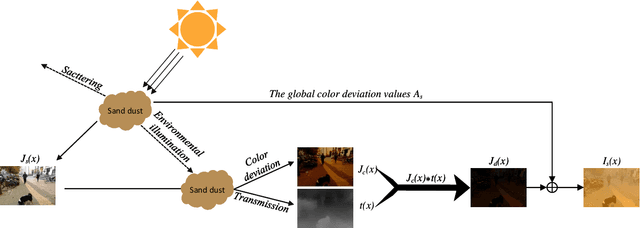
Sep 16, 2023Abstract:Most existing sandstorm image enhancement methods are based on traditional theory and prior knowledge, which often restrict their applicability in real-world scenarios. In addition, these approaches often adopt a strategy of color correction followed by dust removal, which makes the algorithm structure too complex. To solve the issue, we introduce a novel image restoration model, named all-in-one sandstorm removal network (AOSR-Net). This model is developed based on a re-formulated sandstorm scattering model, which directly establishes the image mapping relationship by integrating intermediate parameters. Such integration scheme effectively addresses the problems of over-enhancement and weak generalization in the field of sand dust image enhancement. Experimental results on synthetic and real-world sandstorm images demonstrate the superiority of the proposed AOSR-Net over state-of-the-art (SOTA) algorithms.
A comprehensive benchmark analysis for sand dust image reconstruction
Feb 07, 2022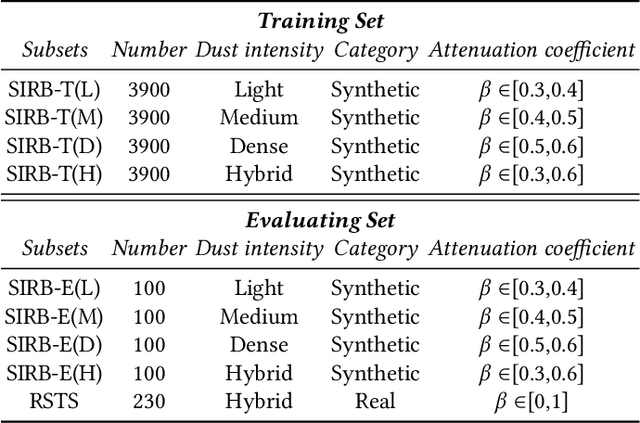
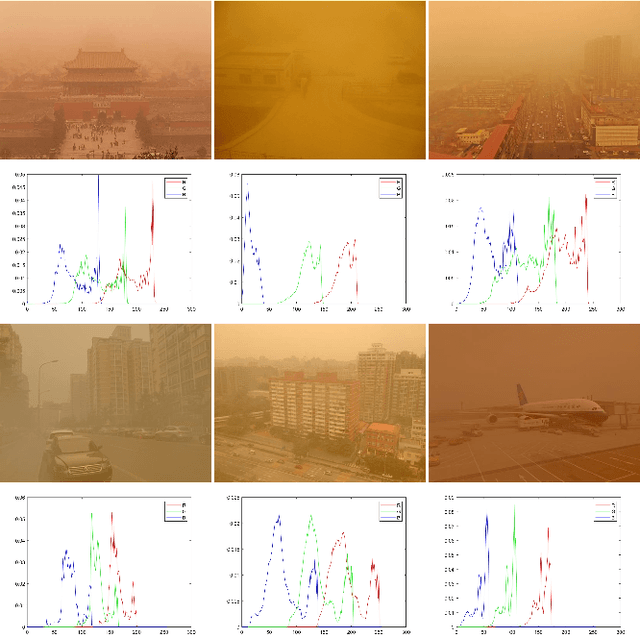
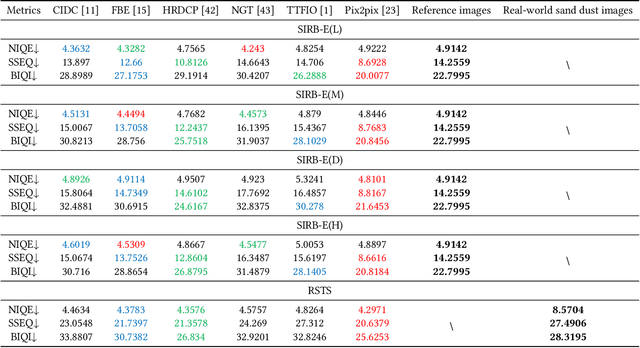
Abstract:Numerous sand dust image enhancement algorithms have been proposed in recent years. To our best acknowledge, however, most methods evaluated their performance with no-reference way using few selected real-world images from internet. It is unclear how to quantitatively analysis the performance of the algorithms in a supervised way and how we could gauge the progress in the field. Moreover, due to the absence of large-scale benchmark datasets, there are no well-known reports of data-driven based method for sand dust image enhancement up till now. To advance the development of deep learning-based algorithms for sand dust image reconstruction, while enabling supervised objective evaluation of algorithm performance. In this paper, we presented a comprehensive perceptual study and analysis of real-world sand dust images, then constructed a Sand-dust Image Reconstruction Benchmark (SIRB) for training Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) and evaluating algorithms performance. In addition, we adopted the existing image transformation neural network trained on SIRB as baseline to illustrate the generalization of SIRB for training CNNs. Finally, we conducted the qualitative and quantitative evaluation to demonstrate the performance and limitations of the state-of-the-arts (SOTA), which shed light on future research in sand dust image reconstruction.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge