Yashvardhan Sharma
Distributed and Decentralised Training: Technical Governance Challenges in a Shifting AI Landscape
Jul 10, 2025Abstract:Advances in low-communication training algorithms are enabling a shift from centralised model training to compute setups that are either distributed across multiple clusters or decentralised via community-driven contributions. This paper distinguishes these two scenarios - distributed and decentralised training - which are little understood and often conflated in policy discourse. We discuss how they could impact technical AI governance through an increased risk of compute structuring, capability proliferation, and the erosion of detectability and shutdownability. While these trends foreshadow a possible new paradigm that could challenge key assumptions of compute governance, we emphasise that certain policy levers, like export controls, remain relevant. We also acknowledge potential benefits of decentralised AI, including privacy-preserving training runs that could unlock access to more data, and mitigating harmful power concentration. Our goal is to support more precise policymaking around compute, capability proliferation, and decentralised AI development.
Impact of Decoding Methods on Human Alignment of Conversational LLMs
Jul 28, 2024



Abstract:To be included into chatbot systems, Large language models (LLMs) must be aligned with human conversational conventions. However, being trained mainly on web-scraped data gives existing LLMs a voice closer to informational text than actual human speech. In this paper, we examine the effect of decoding methods on the alignment between LLM-generated and human conversations, including Beam Search, Top K Sampling, and Nucleus Sampling. We present new measures of alignment in substance, style, and psychometric orientation, and experiment with two conversation datasets. Our results provide subtle insights: better alignment is attributed to fewer beams in Beam Search and lower values of P in Nucleus Sampling. We also find that task-oriented and open-ended datasets perform differently in terms of alignment, indicating the significance of taking into account the context of the interaction.
Rhetorical Role Labeling of Legal Documents using Transformers and Graph Neural Networks
May 06, 2023Abstract:A legal document is usually long and dense requiring human effort to parse it. It also contains significant amounts of jargon which make deriving insights from it using existing models a poor approach. This paper presents the approaches undertaken to perform the task of rhetorical role labelling on Indian Court Judgements as part of SemEval Task 6: understanding legal texts, shared subtask A. We experiment with graph based approaches like Graph Convolutional Networks and Label Propagation Algorithm, and transformer-based approaches including variants of BERT to improve accuracy scores on text classification of complex legal documents.
BITS Pilani at HinglishEval: Quality Evaluation for Code-Mixed Hinglish Text Using Transformers
Jun 17, 2022



Abstract:Code-Mixed text data consists of sentences having words or phrases from more than one language. Most multi-lingual communities worldwide communicate using multiple languages, with English usually one of them. Hinglish is a Code-Mixed text composed of Hindi and English but written in Roman script. This paper aims to determine the factors influencing the quality of Code-Mixed text data generated by the system. For the HinglishEval task, the proposed model uses multi-lingual BERT to find the similarity between synthetically generated and human-generated sentences to predict the quality of synthetically generated Hinglish sentences.
Fake News Detection: Experiments and Approaches beyond Linguistic Features
Sep 27, 2021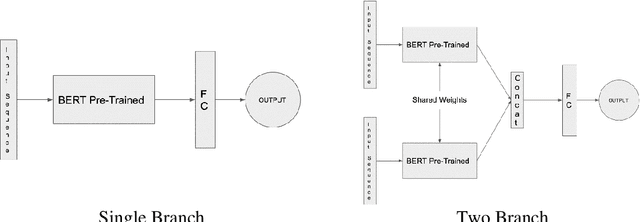
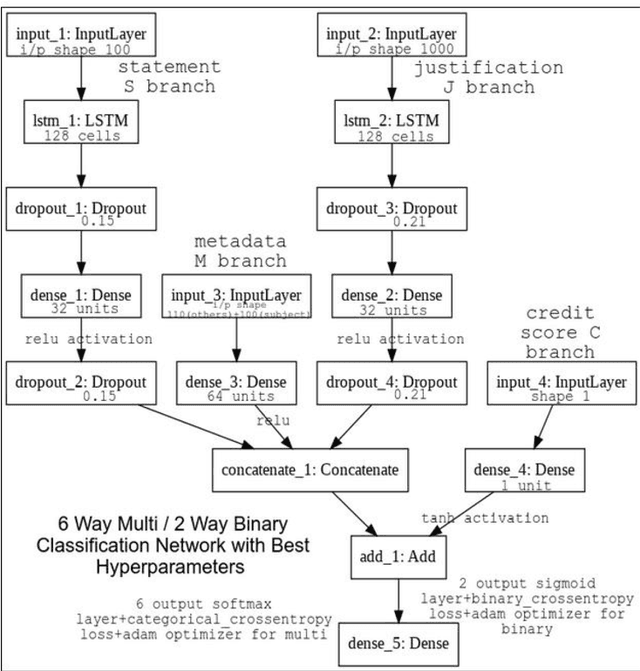
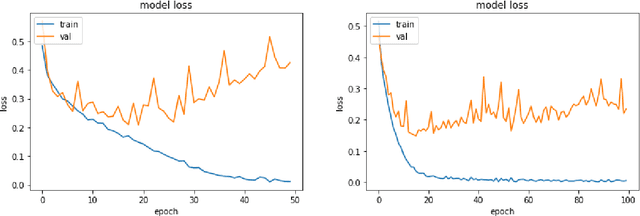

Abstract:Easier access to the internet and social media has made disseminating information through online sources very easy. Sources like Facebook, Twitter, online news sites and personal blogs of self-proclaimed journalists have become significant players in providing news content. The sheer amount of information and the speed at which it is generated online makes it practically beyond the scope of human verification. There is, hence, a pressing need to develop technologies that can assist humans with automatic fact-checking and reliable identification of fake news. This paper summarizes the multiple approaches that were undertaken and the experiments that were carried out for the task. Credibility information and metadata associated with the news article have been used for improved results. The experiments also show how modelling justification or evidence can lead to improved results. Additionally, the use of visual features in addition to linguistic features is demonstrated. A detailed comparison of the results showing that our models perform significantly well when compared to robust baselines as well as state-of-the-art models are presented.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge