Yanxia Wu
Curriculum-style Data Augmentation for LLM-based Metaphor Detection
Dec 04, 2024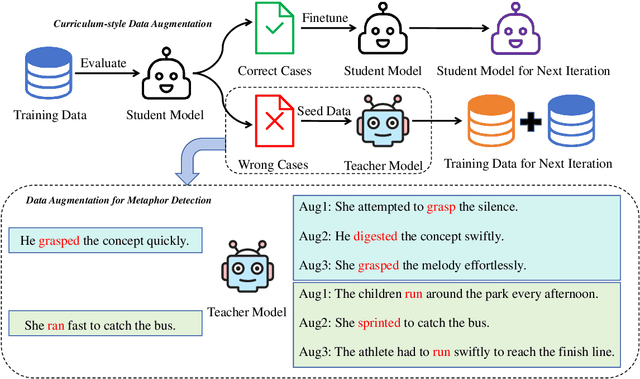

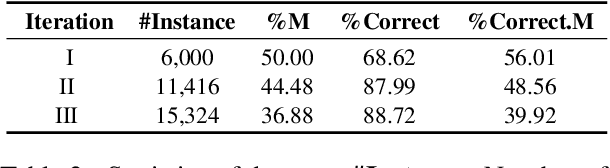
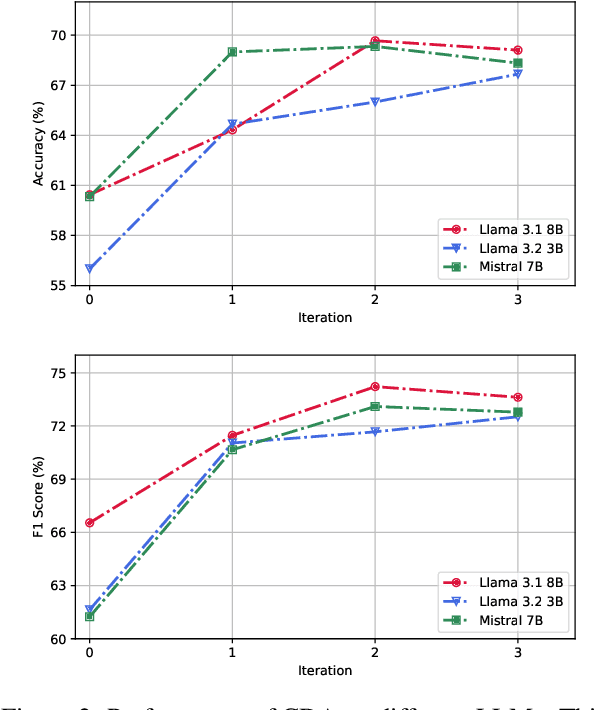
Abstract:Recently, utilizing large language models (LLMs) for metaphor detection has achieved promising results. However, these methods heavily rely on the capabilities of closed-source LLMs, which come with relatively high inference costs and latency. To address this, we propose a method for metaphor detection by fine-tuning open-source LLMs, effectively reducing inference costs and latency with a single inference step. Furthermore, metaphor detection suffers from a severe data scarcity problem, which hinders effective fine-tuning of LLMs. To tackle this, we introduce Curriculum-style Data Augmentation (CDA). Specifically, before fine-tuning, we evaluate the training data to identify correctly predicted instances for fine-tuning, while incorrectly predicted instances are used as seed data for data augmentation. This approach enables the model to quickly learn simpler knowledge and progressively acquire more complex knowledge, thereby improving performance incrementally. Experimental results demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across all baselines. Additionally, we provide detailed ablation studies to validate the effectiveness of CDA.
A Practical Solution for SAR Despeckling with Only Single Speckled Images
Dec 13, 2019



Abstract:In this letter, we aim to address synthetic aperture radar (SAR) despeckling problem with the necessity of neither clean (speckle-free) SAR images nor independent speckled image pairs from the same scene, a practical solution for SAR despeckling (PSD) is proposed. Firstly, to generate speckled-to-speckled (S2S) image pairs from the same scene in the situation of only single speckled SAR images are available, an adversarial learning framework is designed. Then, the S2S SAR image pairs are employed to train a modified despeckling Nested-UNet model using the Noise2Noise (N2N) strategy. Moreover, an iterative version of the PSD method (PSDi) is also proposed. The performance of the proposed methods is demonstrated by both synthetic speckled and real SAR data. SAR block-matching 3-D algorithm (SAR-BM3D) and SAR dilated residual network (SAR-DRN) are used in the visual and quantitative comparison. Experimental results show that the proposed methods can reach a good tradeoff between speckle suppression and edge preservation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge