Yaniv Leviathan
Prompt Repetition Improves Non-Reasoning LLMs
Dec 17, 2025Abstract:When not using reasoning, repeating the input prompt improves performance for popular models (Gemini, GPT, Claude, and Deepseek) without increasing the number of generated tokens or latency.
Selective Attention Improves Transformer
Oct 03, 2024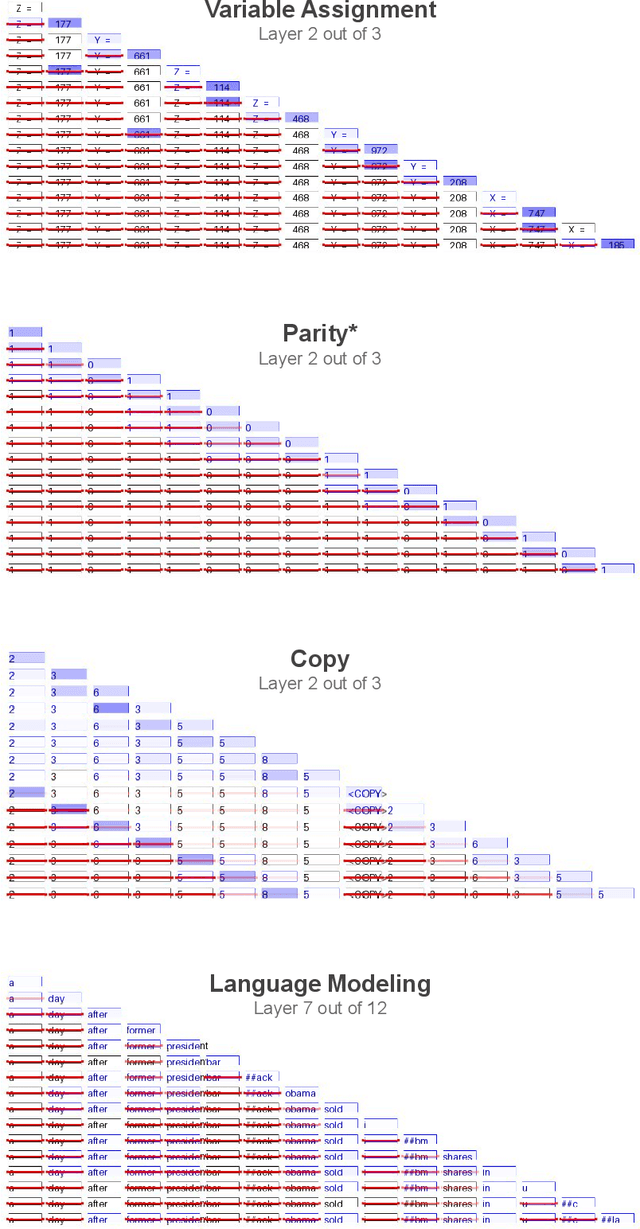
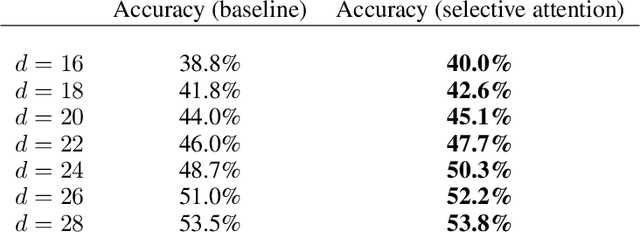


Abstract:Unneeded elements in the attention's context degrade performance. We introduce Selective Attention, a simple parameter-free change to the standard attention mechanism which reduces attention to unneeded elements. Selective attention improves language modeling performance in a variety of model sizes and context lengths. For example, a range of transformers trained with the language modeling objective on C4 with selective attention perform equivalently to standard transformers with ~2X more heads and parameters in their attention modules. Selective attention also allows decreasing the size of the attention's context buffer, leading to meaningful reductions in the memory and compute requirements during inference. For example, transformers with 100M parameters trained on C4 with context sizes of 512, 1,024, and 2,048 need 16X, 25X, and 47X less memory for their attention module, respectively, when equipped with selective attention, as those without selective attention, with the same validation perplexity.
Diffusion Models Are Real-Time Game Engines
Aug 27, 2024Abstract:We present GameNGen, the first game engine powered entirely by a neural model that enables real-time interaction with a complex environment over long trajectories at high quality. GameNGen can interactively simulate the classic game DOOM at over 20 frames per second on a single TPU. Next frame prediction achieves a PSNR of 29.4, comparable to lossy JPEG compression. Human raters are only slightly better than random chance at distinguishing short clips of the game from clips of the simulation. GameNGen is trained in two phases: (1) an RL-agent learns to play the game and the training sessions are recorded, and (2) a diffusion model is trained to produce the next frame, conditioned on the sequence of past frames and actions. Conditioning augmentations enable stable auto-regressive generation over long trajectories.
A Picture is Worth a Thousand Words: Principled Recaptioning Improves Image Generation
Oct 25, 2023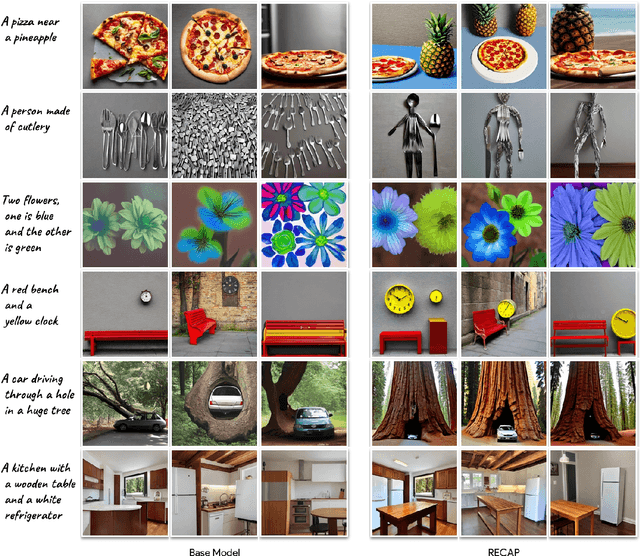
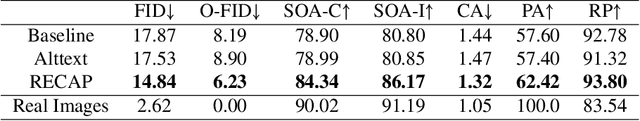
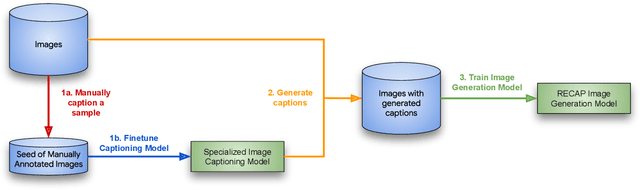
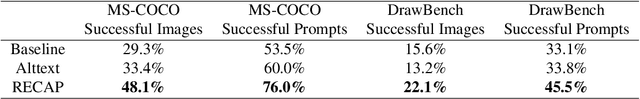
Abstract:Text-to-image diffusion models achieved a remarkable leap in capabilities over the last few years, enabling high-quality and diverse synthesis of images from a textual prompt. However, even the most advanced models often struggle to precisely follow all of the directions in their prompts. The vast majority of these models are trained on datasets consisting of (image, caption) pairs where the images often come from the web, and the captions are their HTML alternate text. A notable example is the LAION dataset, used by Stable Diffusion and other models. In this work we observe that these captions are often of low quality, and argue that this significantly affects the model's capability to understand nuanced semantics in the textual prompts. We show that by relabeling the corpus with a specialized automatic captioning model and training a text-to-image model on the recaptioned dataset, the model benefits substantially across the board. First, in overall image quality: e.g. FID 14.84 vs. the baseline of 17.87, and 64.3% improvement in faithful image generation according to human evaluation. Second, in semantic alignment, e.g. semantic object accuracy 84.34 vs. 78.90, counting alignment errors 1.32 vs. 1.44 and positional alignment 62.42 vs. 57.60. We analyze various ways to relabel the corpus and provide evidence that this technique, which we call RECAP, both reduces the train-inference discrepancy and provides the model with more information per example, increasing sample efficiency and allowing the model to better understand the relations between captions and images.
Face0: Instantaneously Conditioning a Text-to-Image Model on a Face
Jun 11, 2023Abstract:We present Face0, a novel way to instantaneously condition a text-to-image generation model on a face, in sample time, without any optimization procedures such as fine-tuning or inversions. We augment a dataset of annotated images with embeddings of the included faces and train an image generation model, on the augmented dataset. Once trained, our system is practically identical at inference time to the underlying base model, and is therefore able to generate images, given a user-supplied face image and a prompt, in just a couple of seconds. Our method achieves pleasing results, is remarkably simple, extremely fast, and equips the underlying model with new capabilities, like controlling the generated images both via text or via direct manipulation of the input face embeddings. In addition, when using a fixed random vector instead of a face embedding from a user supplied image, our method essentially solves the problem of consistent character generation across images. Finally, while requiring further research, we hope that our method, which decouples the model's textual biases from its biases on faces, might be a step towards some mitigation of biases in future text-to-image models.
Dreamix: Video Diffusion Models are General Video Editors
Feb 02, 2023
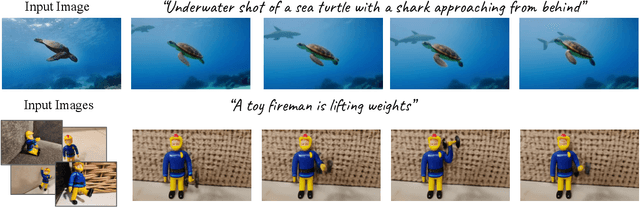
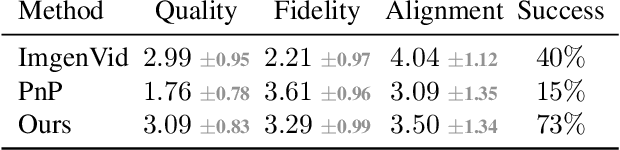
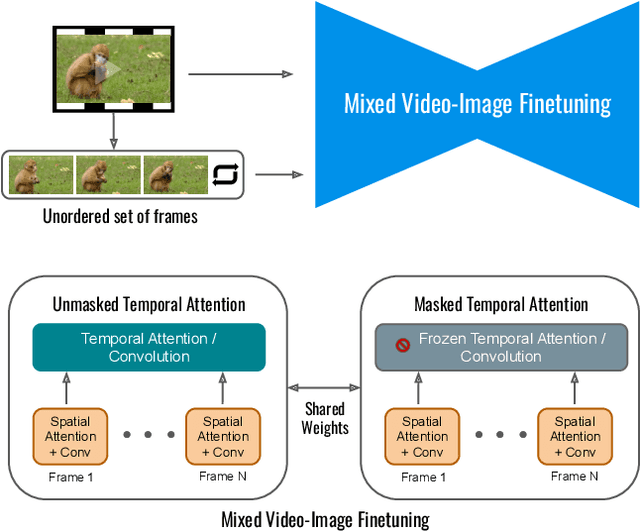
Abstract:Text-driven image and video diffusion models have recently achieved unprecedented generation realism. While diffusion models have been successfully applied for image editing, very few works have done so for video editing. We present the first diffusion-based method that is able to perform text-based motion and appearance editing of general videos. Our approach uses a video diffusion model to combine, at inference time, the low-resolution spatio-temporal information from the original video with new, high resolution information that it synthesized to align with the guiding text prompt. As obtaining high-fidelity to the original video requires retaining some of its high-resolution information, we add a preliminary stage of finetuning the model on the original video, significantly boosting fidelity. We propose to improve motion editability by a new, mixed objective that jointly finetunes with full temporal attention and with temporal attention masking. We further introduce a new framework for image animation. We first transform the image into a coarse video by simple image processing operations such as replication and perspective geometric projections, and then use our general video editor to animate it. As a further application, we can use our method for subject-driven video generation. Extensive qualitative and numerical experiments showcase the remarkable editing ability of our method and establish its superior performance compared to baseline methods.
Fast Inference from Transformers via Speculative Decoding
Nov 30, 2022Abstract:Inference from large autoregressive models like Transformers is slow - decoding K tokens takes K serial runs of the model. In this work we introduce speculative decoding - an algorithm to sample from autoregressive models faster without any changes to the outputs, by computing several tokens in parallel. At the heart of our approach lie the observations that (1) hard language-modeling tasks often include easier subtasks that can be approximated well by more efficient models, and (2) using speculative execution and a novel sampling method, we can make exact decoding from the large models faster, by running them in parallel on the outputs of the approximation models, potentially generating several tokens concurrently, and without changing the distribution. Our method supports existing off-the-shelf models without retraining or architecture changes. We demonstrate it on T5-XXL and show a 2X-3X acceleration compared to the standard T5X implementation, with identical outputs.
UniTune: Text-Driven Image Editing by Fine Tuning an Image Generation Model on a Single Image
Oct 20, 2022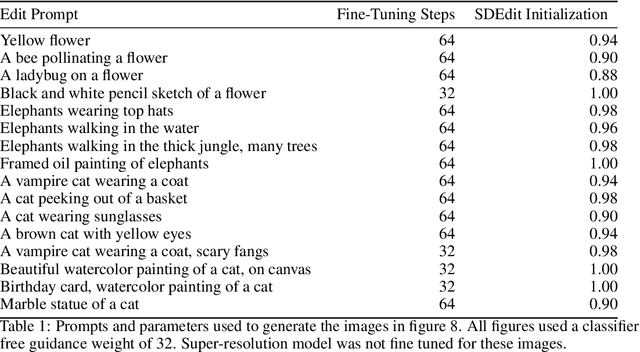
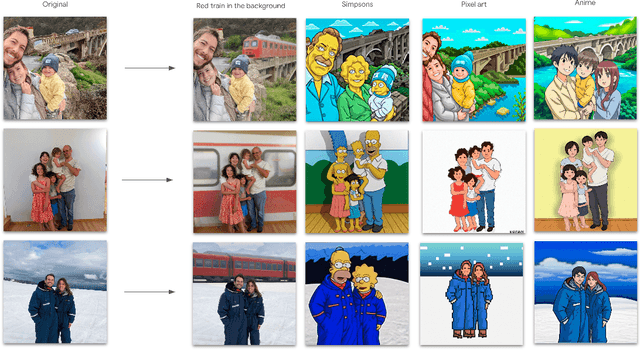


Abstract:We present UniTune, a simple and novel method for general text-driven image editing. UniTune gets as input an arbitrary image and a textual edit description, and carries out the edit while maintaining high semantic and visual fidelity to the input image. UniTune uses text, an intuitive interface for art-direction, and does not require additional inputs, like masks or sketches. At the core of our method is the observation that with the right choice of parameters, we can fine-tune a large text-to-image diffusion model on a single image, encouraging the model to maintain fidelity to the input image while still allowing expressive manipulations. We used Imagen as our text-to-image model, but we expect UniTune to work with other large-scale models as well. We test our method in a range of different use cases, and demonstrate its wide applicability.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge