Yang Ming
Two-timescale Beamforming Optimization for Downlink Multi-user Holographic MIMO Surfaces
Nov 07, 2025Abstract:Benefiting from the rapid development of metamaterials and metasurfaces, the holographic multiple-input and multiple-output surface (HMIMOS) has been regarded as a promising solution for future wireless networks recently. By densely packing numerous radiation elements together, HMIMOS is capable of realizing accurate beamforming with low hardware complexity. However, enormous radiation elements on the HMIMOS lead to high computational complexity and signaling overhead when applying traditional beamforming schemes relying on instantaneous channel state information (CSI). To tackle this problem, we propose a two-timescale optimization scheme to minimize the required transmission power under the constraint of all users' quality-of-service (QoS). Specifically, the beampatterns at the base station (BS) and the user equippment (UE) are optimized over the slowly changing statistical CSI based on the constrained stochastic successive convex approximation (CSSCA) algorithm. Then, the instantaneous CSI is utilized to design the precoding matrix in order to ensure the system performance without significant increase in computational cost, due to the small number of feeds on the HMIMOS. Simulation results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method compared to other baselines.
* This manuscript has been accepted by IEEE Transactions on Vehicular Technology (IEEE TVT)
TypeII-CsiNet: CSI Feedback with TypeII Codebook
May 21, 2024



Abstract:The latest TypeII codebook selects partial strongest angular-delay ports for the feedback of downlink channel state information (CSI), whereas its performance is limited due to the deficiency of utilizing the correlations among the port coefficients. To tackle this issue, we propose a tailored autoencoder named TypeII-CsiNet to effectively integrate the TypeII codebook with deep learning, wherein three novel designs are developed for sufficiently boosting the sum rate performance. Firstly, a dedicated pre-processing module is designed to sort the selected ports for reserving the correlations of their corresponding coefficients. Secondly, a position-filling layer is developed in the decoder to fill the feedback coefficients into their ports in the recovered CSI matrix, so that the corresponding angular-delay-domain structure is adequately leveraged to enhance the reconstruction accuracy. Thirdly, a two-stage loss function is proposed to improve the sum rate performance while avoiding the trapping in local optimums during model training. Simulation results verify that our proposed TypeII-CsiNet outperforms the TypeII codebook and existing deep learning benchmarks.
Deep Learning Empowered Type-II Codebook: New Perspectives for Enhancing CSI Feedback
May 14, 2023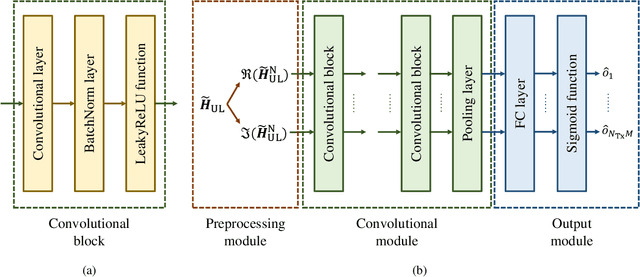
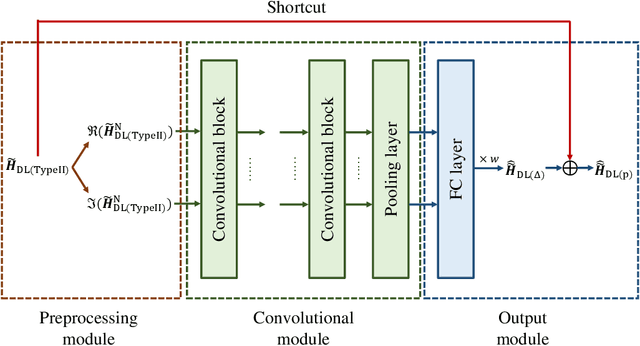
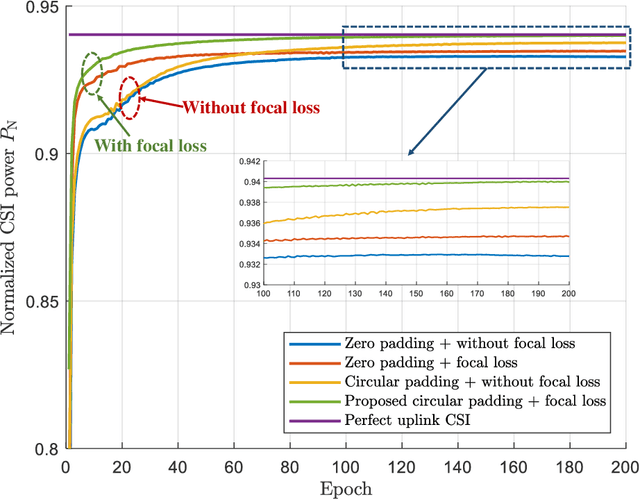
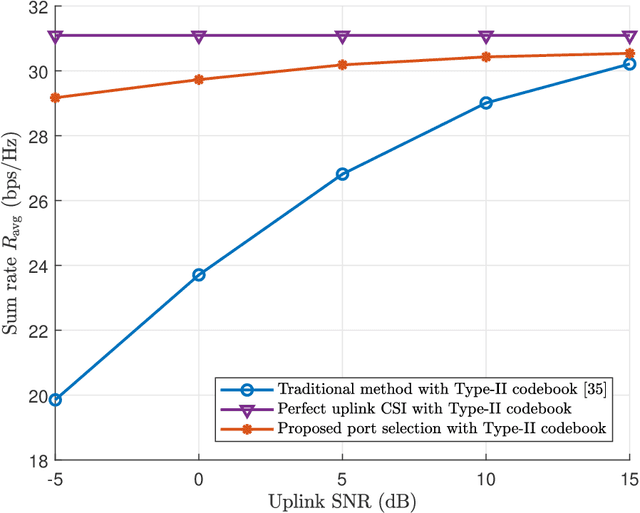
Abstract:Deep learning based channel state information (CSI) feedback in frequency division duplex systems has drawn widespread attention in both academia and industry. In this paper, we focus on integrating the Type-II codebook in the wireless communication standards with deep learning to enhance the performance of CSI feedback. In contrast to the existing deep learning based studies on the Release 16 Type-II codebook, the Type-II codebook in Release 17 (R17) exploits the angular-delay-domain partial reciprocity between uplink and downlink channels to select part of angular-delay-domain ports for measuring and feeding back the downlink CSI, where the performance of deep learning based conventional methods is limited due to the deficiency of sparse structures. To address this issue, we propose two new perspectives of adopting deep learning to improve the R17 Type-II codebook. Firstly, considering the low signal-to-noise ratio of uplink channels, deep learning is utilized to accurately select the dominant angular-delay-domain ports, where the focal loss is harnessed to solve the class imbalance problem. Secondly, we propose to adopt deep learning to reconstruct the downlink CSI based on the feedback of the R17 Type-II codebook at the base station, where the information of sparse structures can be effectively leveraged. Furthermore, a weighted shortcut module is designed to facilitate the accurate reconstruction, and a two-stage loss function that combines the mean squared error and sum rate is proposed for adapting to practical multi-user scenarios. Simulation results demonstrate that our proposed deep learning based port selection and CSI reconstruction methods can improve the sum rate performance compared with the traditional R17 Type-II codebook and deep learning benchmarks.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge