Yang Min
Edge-Enabled Real-time Railway Track Segmentation
Jan 21, 2024Abstract:Accurate and rapid railway track segmentation can assist automatic train driving and is a key step in early warning to fixed or moving obstacles on the railway track. However, certain existing algorithms tailored for track segmentation often struggle to meet the requirements of real-time and efficiency on resource-constrained edge devices. Considering this challenge, we propose an edge-enabled real-time railway track segmentation algorithm, which is optimized to be suitable for edge applications by optimizing the network structure and quantizing the model after training. Initially, Ghost convolution is introduced to reduce the complexity of the backbone, thereby achieving the extraction of key information of the interested region at a lower cost. To further reduce the model complexity and calculation, a new lightweight detection head is proposed to achieve the best balance between accuracy and efficiency. Subsequently, we introduce quantization techniques to map the model's floating-point weights and activation values into lower bit-width fixed-point representations, reducing computational demands and memory footprint, ultimately accelerating the model's inference. Finally, we draw inspiration from GPU parallel programming principles to expedite the pre-processing and post-processing stages of the algorithm by doing parallel processing. The approach is evaluated with public and challenging dataset RailSem19 and tested on Jetson Nano. Experimental results demonstrate that our enhanced algorithm achieves an accuracy level of 83.3% while achieving a real-time inference rate of 25 frames per second when the input size is 480x480, thereby effectively meeting the requirements for real-time and high-efficiency operation.
Efficient Metropolitan Traffic Prediction Based on Graph Recurrent Neural Network
Nov 02, 2018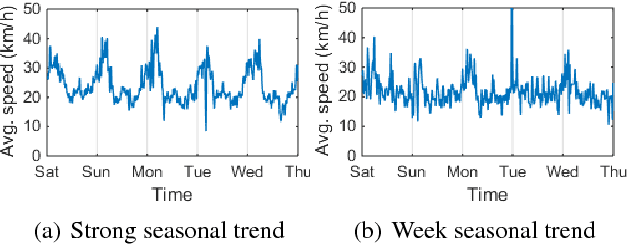
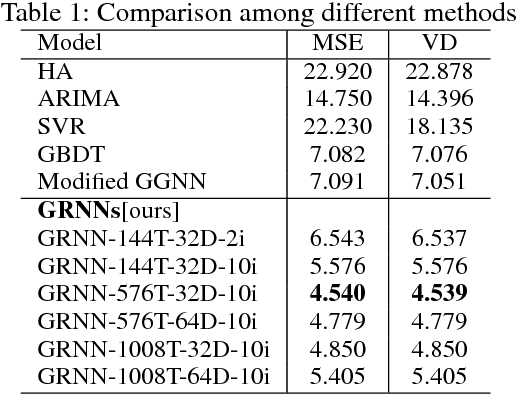
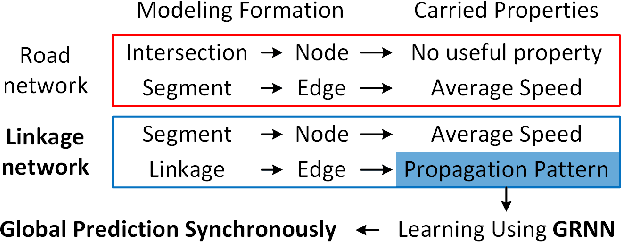
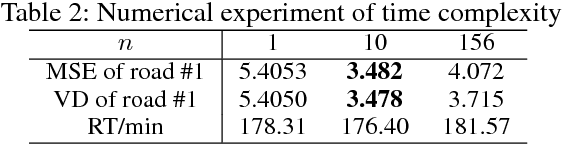
Abstract:Traffic prediction is a fundamental and vital task in Intelligence Transportation System (ITS), but it is very challenging to get high accuracy while containing low computational complexity due to the spatiotemporal characteristics of traffic flow, especially under the metropolitan circumstances. In this work, a new topological framework, called Linkage Network, is proposed to model the road networks and present the propagation patterns of traffic flow. Based on the Linkage Network model, a novel online predictor, named Graph Recurrent Neural Network (GRNN), is designed to learn the propagation patterns in the graph. It could simultaneously predict traffic flow for all road segments based on the information gathered from the whole graph, which thus reduces the computational complexity significantly from O(nm) to O(n+m), while keeping the high accuracy. Moreover, it can also predict the variations of traffic trends. Experiments based on real-world data demonstrate that the proposed method outperforms the existing prediction methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge