Yanchong Zheng
SATS: Self-Attention Transfer for Continual Semantic Segmentation
Mar 15, 2022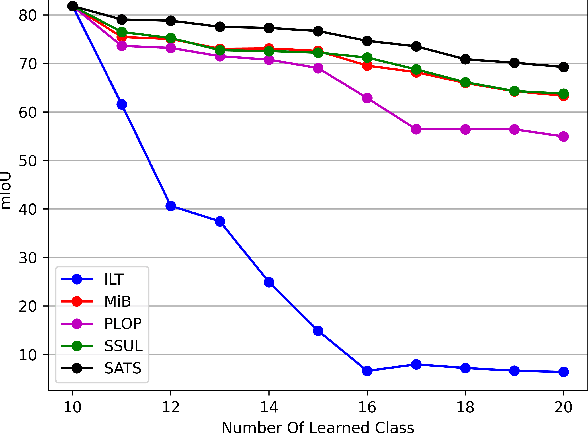
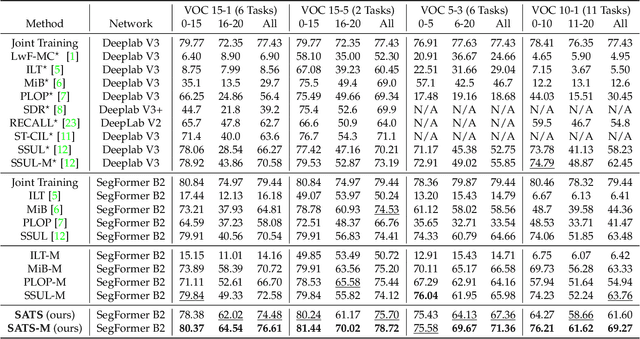
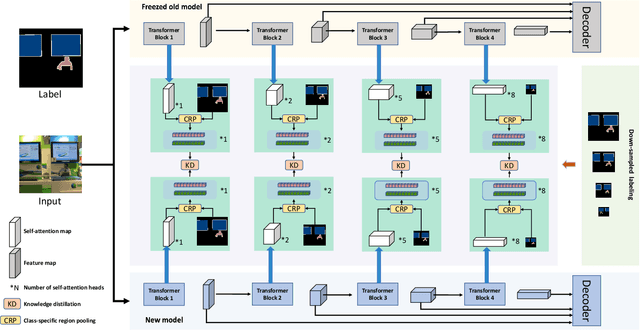
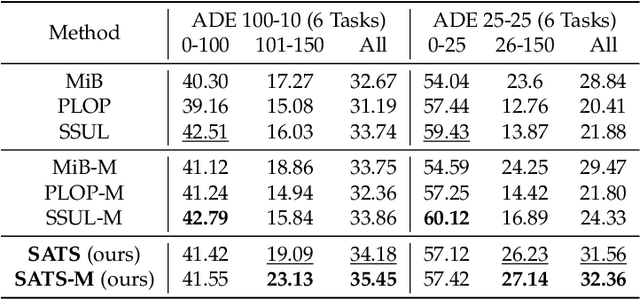
Abstract:Continually learning to segment more and more types of image regions is a desired capability for many intelligent systems. However, such continual semantic segmentation suffers from the same catastrophic forgetting issue as in continual classification learning. While multiple knowledge distillation strategies originally for continual classification have been well adapted to continual semantic segmentation, they only consider transferring old knowledge based on the outputs from one or more layers of deep fully convolutional networks. Different from existing solutions, this study proposes to transfer a new type of information relevant to knowledge, i.e. the relationships between elements (Eg. pixels or small local regions) within each image which can capture both within-class and between-class knowledge. The relationship information can be effectively obtained from the self-attention maps in a Transformer-style segmentation model. Considering that pixels belonging to the same class in each image often share similar visual properties, a class-specific region pooling is applied to provide more efficient relationship information for knowledge transfer. Extensive evaluations on multiple public benchmarks support that the proposed self-attention transfer method can further effectively alleviate the catastrophic forgetting issue, and its flexible combination with one or more widely adopted strategies significantly outperforms state-of-the-art solu
Dropout against Deep Leakage from Gradients
Aug 25, 2021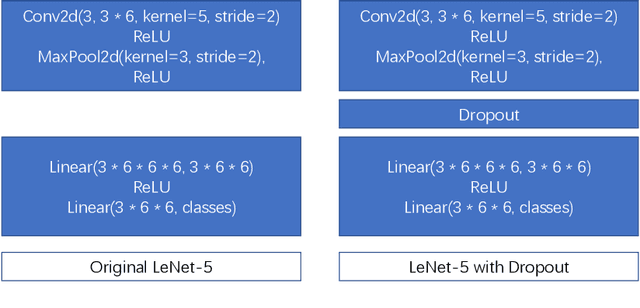
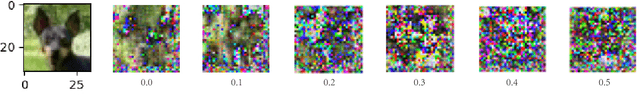
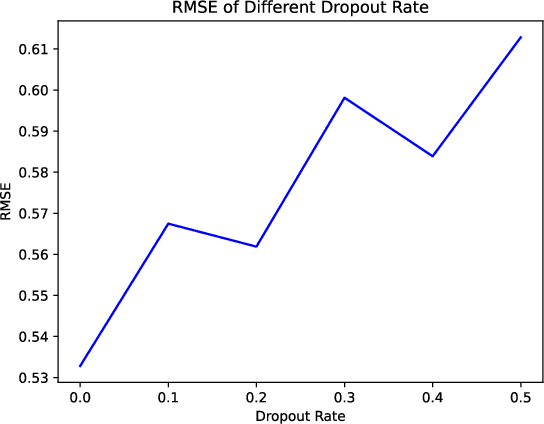
Abstract:As the scale and size of the data increases significantly nowadays, federal learning (Bonawitz et al. [2019]) for high performance computing and machine learning has been much more important than ever beforeAbadi et al. [2016]. People used to believe that sharing gradients seems to be safe to conceal the local training data during the training stage. However, Zhu et al. [2019] demonstrated that it was possible to recover raw data from the model training data by detecting gradients. They use generated random dummy data and minimise the distance between them and real data. Zhao et al. [2020] pushes the convergence algorithm even further. By replacing the original loss function with cross entropy loss, they achieve better fidelity threshold. In this paper, we propose using an additional dropout (Srivastava et al. [2014]) layer before feeding the data to the classifier. It is very effective in preventing leakage of raw data, as the training data cannot converge to a small RMSE even after 5,800 epochs with dropout rate set to 0.5.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge