Xunyu Zhu
Improving Mathematical Reasoning Capabilities of Small Language Models via Feedback-Driven Distillation
Nov 22, 2024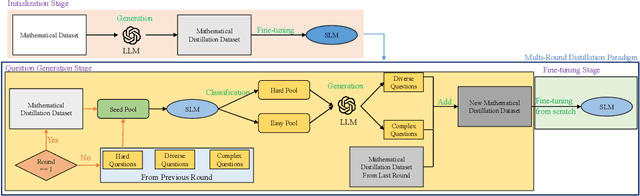



Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) demonstrate exceptional reasoning capabilities, often achieving state-of-the-art performance in various tasks. However, their substantial computational and memory demands, due to billions of parameters, hinder deployment in resource-constrained environments. A promising solution is knowledge distillation, where LLMs transfer reasoning capabilities to Small Language Models (SLMs, $\le$ 1B parameters), enabling wider deployment on low-resource devices. Existing methods primarily focus on generating high-quality reasoning rationales for distillation datasets but often neglect the critical role of data quantity and quality. To address these challenges, we propose a Feedback-Driven Distillation (FDD) framework to enhance SLMs' mathematical reasoning capabilities. In the initialization stage, a distillation dataset is constructed by prompting LLMs to pair mathematical problems with corresponding reasoning rationales. We classify problems into easy and hard categories based on SLM performance. For easy problems, LLMs generate more complex variations, while for hard problems, new questions of similar complexity are synthesized. In addition, we propose a multi-round distillation paradigm to iteratively enrich the distillation datasets, thereby progressively improving the mathematical reasoning abilities of SLMs. Experimental results demonstrate that our method can make SLMs achieve SOTA mathematical reasoning performance.
Key-Point-Driven Mathematical Reasoning Distillation of Large Language Model
Jul 14, 2024
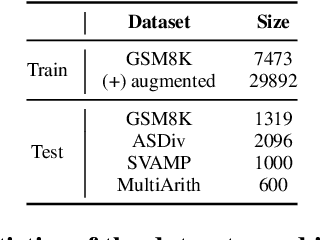
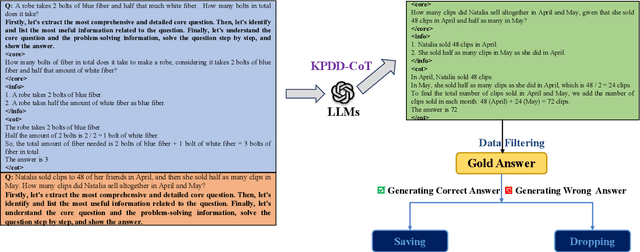
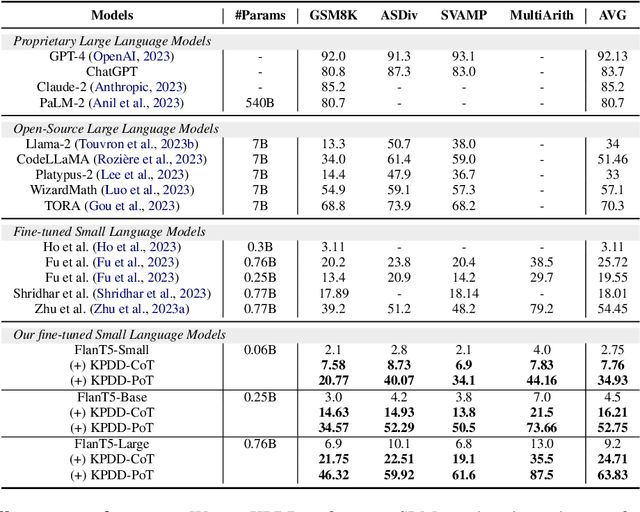
Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have demonstrated exceptional proficiency in mathematical reasoning tasks due to their extensive parameter counts and training on vast datasets. Despite these capabilities, deploying LLMs is hindered by their computational demands. Distilling LLM mathematical reasoning into Smaller Language Models (SLMs) has emerged as a solution to this challenge, although these smaller models often suffer from errors in calculation and semantic understanding. Prior work has proposed Program-of-Thought Distillation (PoTD) to avoid calculation error. To further address semantic understanding errors, we propose Key-Point-Driven Mathematical Reasoning Distillation (KPDD). KPDD enhances the reasoning performance of SLMs by breaking down the problem-solving process into three stages: Core Question Extraction, Problem-Solving Information Extraction, and Step-by-Step Solution. This method is further divided into KPDD-CoT, which generates Chain-of-Thought rationales, and KPDD-PoT, which creates Program-of-Thought rationales. The experiment results show that KPDD-CoT significantly improves reasoning abilities, while KPDD-PoT achieves state-of-the-art performance in mathematical reasoning tasks. Our approach effectively mitigates misunderstanding errors, advancing the deployment of efficient and capable SLMs.
Distilling Mathematical Reasoning Capabilities into Small Language Models
Feb 01, 2024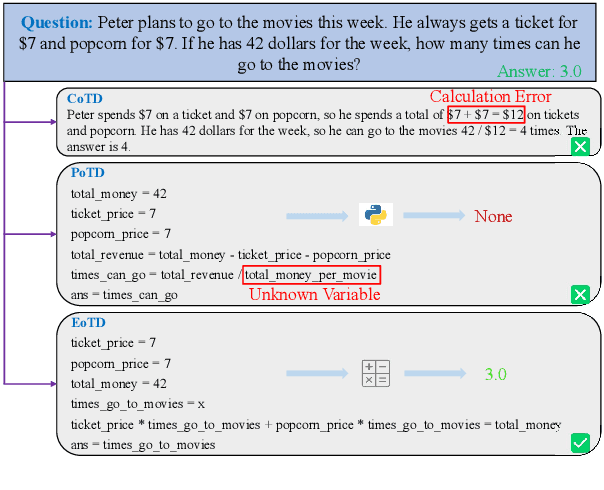
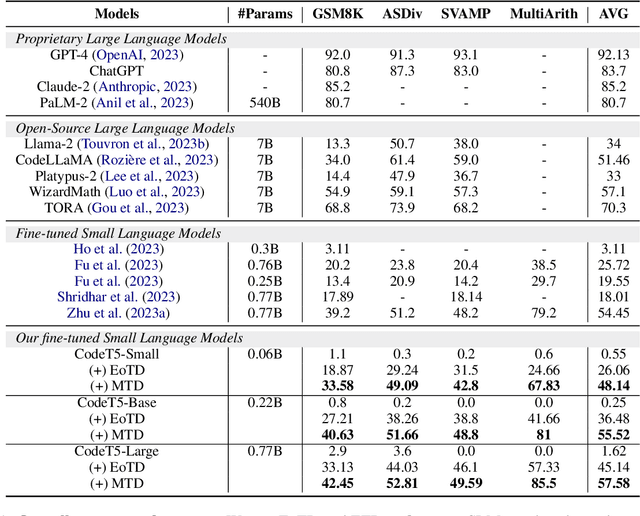
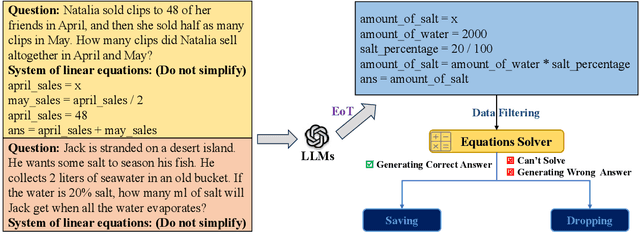
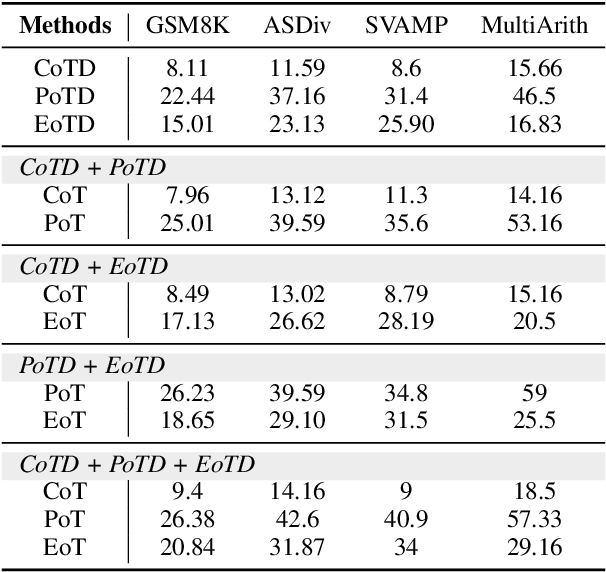
Abstract:This work addresses the challenge of democratizing advanced Large Language Models (LLMs) by compressing their mathematical reasoning capabilities into sub-billion parameter Small Language Models (SLMs) without compromising performance. We introduce Equation-of-Thought Distillation (EoTD), a novel technique that encapsulates the reasoning process into equation-based representations to construct an EoTD dataset for fine-tuning SLMs. Additionally, we propose the Ensemble Thoughts Distillation (ETD) framework to enhance the reasoning performance of SLMs. This involves creating a reasoning dataset with multiple thought processes, including Chain-of-Thought (CoT), Program-of-Thought (PoT), and Equation-of-Thought (EoT), and using it for fine-tuning. Our experimental findings demonstrate that EoTD significantly boosts the reasoning abilities of SLMs, while ETD enables these models to achieve state-of-the-art reasoning performance.
A Survey on Model Compression for Large Language Models
Aug 17, 2023Abstract:Large Language Models (LLMs) have revolutionized natural language processing tasks with remarkable success. However, their formidable size and computational demands present significant challenges for practical deployment, especially in resource-constrained environments. As these challenges become increasingly pertinent, the field of model compression has emerged as a pivotal research area to alleviate these limitations. This paper presents a comprehensive survey that navigates the landscape of model compression techniques tailored specifically for LLMs. Addressing the imperative need for efficient deployment, we delve into various methodologies, encompassing quantization, pruning, knowledge distillation, and more. Within each of these techniques, we highlight recent advancements and innovative approaches that contribute to the evolving landscape of LLM research. Furthermore, we explore benchmarking strategies and evaluation metrics that are essential for assessing the effectiveness of compressed LLMs. By providing insights into the latest developments and practical implications, this survey serves as an invaluable resource for both researchers and practitioners. As LLMs continue to evolve, this survey aims to facilitate enhanced efficiency and real-world applicability, establishing a foundation for future advancements in the field.
Robust Neural Architecture Search
Apr 10, 2023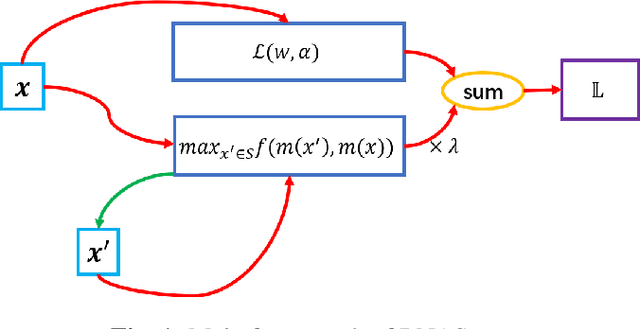
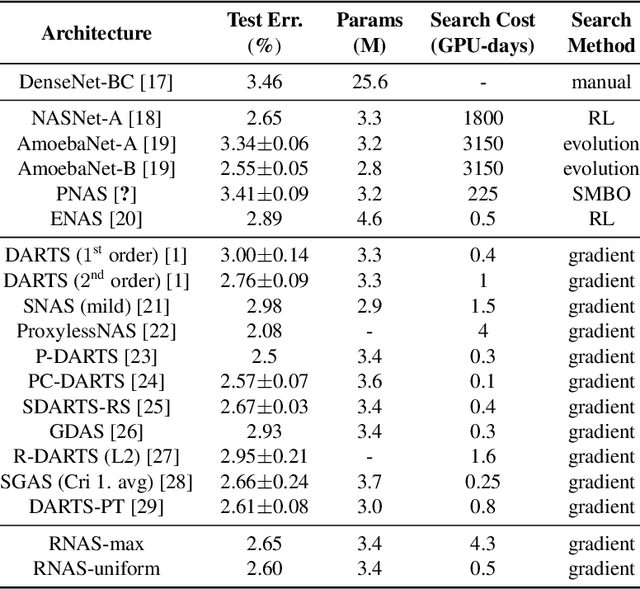
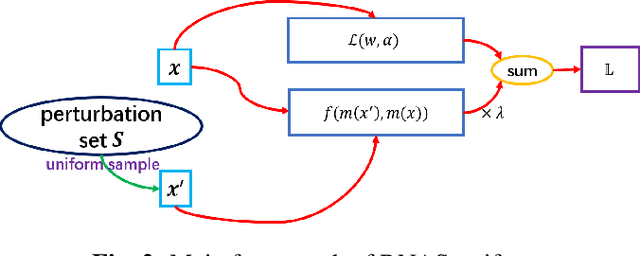
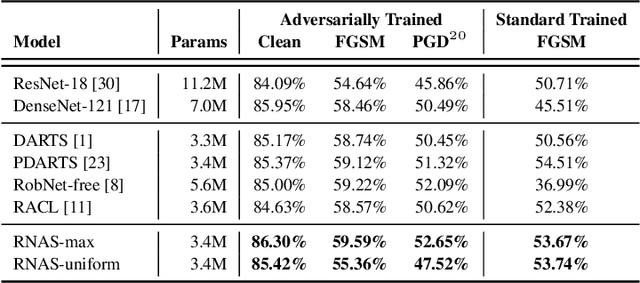
Abstract:Neural Architectures Search (NAS) becomes more and more popular over these years. However, NAS-generated models tends to suffer greater vulnerability to various malicious attacks. Lots of robust NAS methods leverage adversarial training to enhance the robustness of NAS-generated models, however, they neglected the nature accuracy of NAS-generated models. In our paper, we propose a novel NAS method, Robust Neural Architecture Search (RNAS). To design a regularization term to balance accuracy and robustness, RNAS generates architectures with both high accuracy and good robustness. To reduce search cost, we further propose to use noise examples instead adversarial examples as input to search architectures. Extensive experiments show that RNAS achieves state-of-the-art (SOTA) performance on both image classification and adversarial attacks, which illustrates the proposed RNAS achieves a good tradeoff between robustness and accuracy.
Improving Differentiable Architecture Search via Self-Distillation
Feb 11, 2023Abstract:Differentiable Architecture Search (DARTS) is a simple yet efficient Neural Architecture Search (NAS) method. During the search stage, DARTS trains a supernet by jointly optimizing architecture parameters and network parameters. During the evaluation stage, DARTS derives the optimal architecture based on architecture parameters. However, the loss landscape of the supernet is not smooth, and it results in a performance gap between the supernet and the optimal architecture. In the paper, we propose Self-Distillation Differentiable Neural Architecture Search (SD-DARTS) by utilizing self-distillation to transfer knowledge of the supernet in previous steps to guide the training of the supernet in the current steps. SD-DARTS can minimize the loss difference for the two consecutive iterations so that minimize the sharpness of the supernet's loss to bridge the performance gap between the supernet and the optimal architecture. Furthermore, we propose voted teachers, which select multiple previous supernets as teachers and vote teacher output probabilities as the final teacher prediction. The knowledge of several teachers is more abundant than a single teacher, thus, voted teachers can be more suitable to lead the training of the supernet. Experimental results on real datasets illustrate the advantages of our novel self-distillation-based NAS method compared to state-of-the-art alternatives.
Operation-level Progressive Differentiable Architecture Search
Feb 11, 2023Abstract:Differentiable Neural Architecture Search (DARTS) is becoming more and more popular among Neural Architecture Search (NAS) methods because of its high search efficiency and low compute cost. However, the stability of DARTS is very inferior, especially skip connections aggregation that leads to performance collapse. Though existing methods leverage Hessian eigenvalues to alleviate skip connections aggregation, they make DARTS unable to explore architectures with better performance. In the paper, we propose operation-level progressive differentiable neural architecture search (OPP-DARTS) to avoid skip connections aggregation and explore better architectures simultaneously. We first divide the search process into several stages during the search phase and increase candidate operations into the search space progressively at the beginning of each stage. It can effectively alleviate the unfair competition between operations during the search phase of DARTS by offsetting the inherent unfair advantage of the skip connection over other operations. Besides, to keep the competition between operations relatively fair and select the operation from the candidate operations set that makes training loss of the supernet largest. The experiment results indicate that our method is effective and efficient. Our method's performance on CIFAR-10 is superior to the architecture found by standard DARTS, and the transferability of our method also surpasses standard DARTS. We further demonstrate the robustness of our method on three simple search spaces, i.e., S2, S3, S4, and the results show us that our method is more robust than standard DARTS. Our code is available at https://github.com/zxunyu/OPP-DARTS.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge