Xuecong Hou
RPN: A Word Vector Level Data Augmentation Algorithm in Deep Learning for Language Understanding
Dec 12, 2022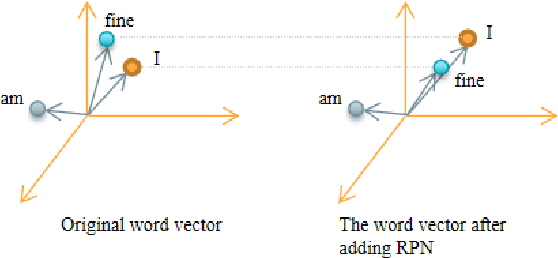
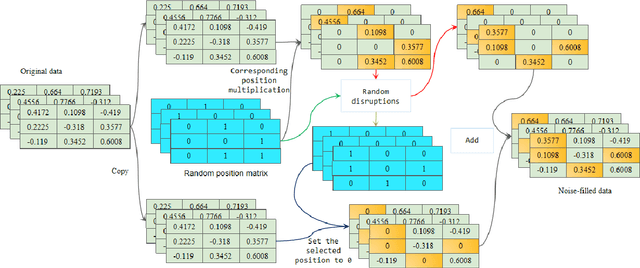
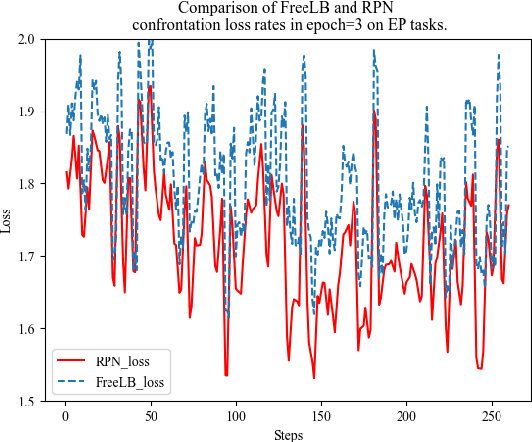
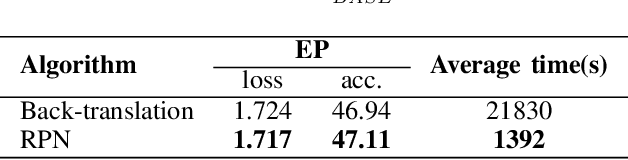
Abstract:This paper presents a new data augmentation algorithm for natural understanding tasks, called RPN:Random Position Noise algorithm.Due to the relative paucity of current text augmentation methods. Few of the extant methods apply to natural language understanding tasks for all sentence-level tasks.RPN applies the traditional augmentation on the original text to the word vector level. The RPN algorithm makes a substitution in one or several dimensions of some word vectors. As a result, the RPN can introduce a certain degree of perturbation to the sample and can adjust the range of perturbation on different tasks. The augmented samples are then used to give the model training.This makes the model more robust. In subsequent experiments, we found that adding RPN to the training or fine-tuning model resulted in a stable boost on all 8 natural language processing tasks, including TweetEval, CoLA, and SST-2 datasets, and more significant improvements than other data augmentation algorithms.The RPN algorithm applies to all sentence-level tasks for language understanding and is used in any deep learning model with a word embedding layer.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge