Xu-Lu Zhang
Cardiac Evidence Backtracking for Eating Behavior Monitoring using Collocative Electrocardiogram Imagining
Feb 20, 2025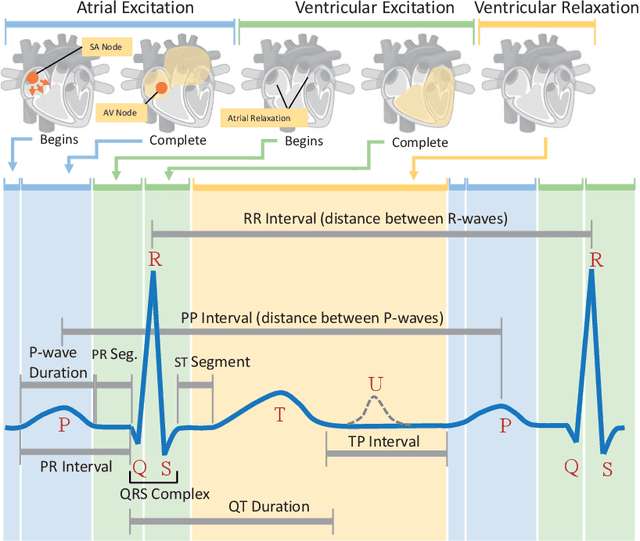
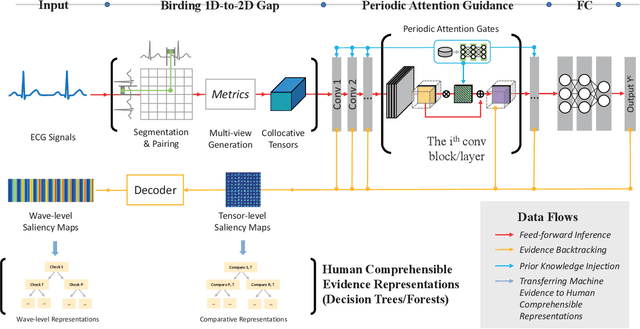
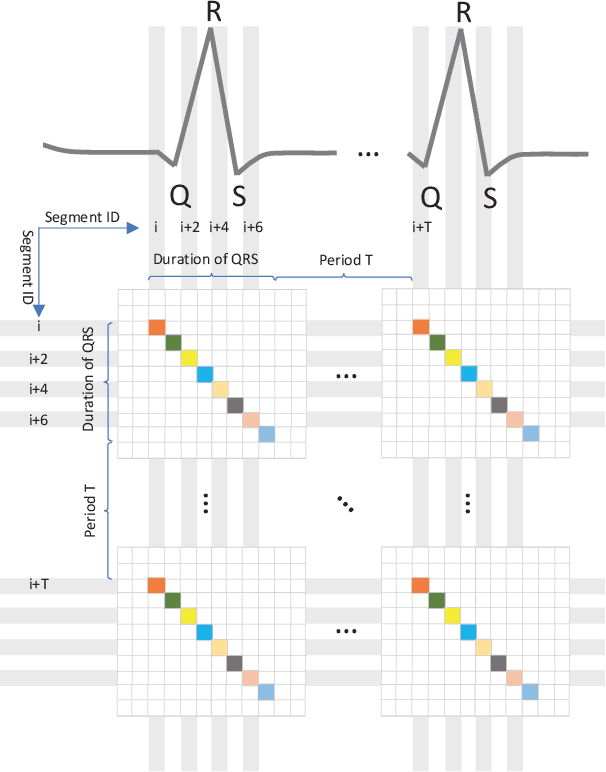
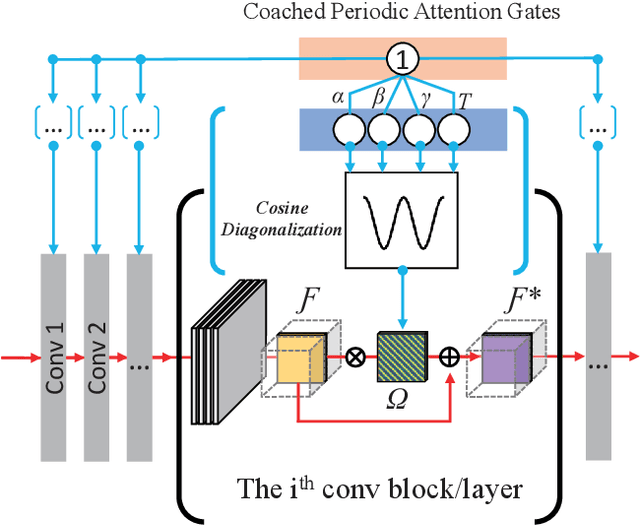
Abstract:Eating monitoring has remained an open challenge in medical research for years due to the lack of non-invasive sensors for continuous monitoring and the reliable methods for automatic behavior detection. In this paper, we present a pilot study using the wearable 24-hour ECG for sensing and tailoring the sophisticated deep learning for ad-hoc and interpretable detection. This is accomplished using a collocative learning framework in which 1) we construct collocative tensors as pseudo-images from 1D ECG signals to improve the feasibility of 2D image-based deep models; 2) we formulate the cardiac logic of analyzing the ECG data in a comparative way as periodic attention regulators so as to guide the deep inference to collect evidence in a human comprehensible manner; and 3) we improve the interpretability of the framework by enabling the backtracking of evidence with a set of methods designed for Class Activation Mapping (CAM) decoding and decision tree/forest generation. The effectiveness of the proposed framework has been validated on the largest ECG dataset of eating behavior with superior performance over conventional models, and its capacity of cardiac evidence mining has also been verified through the consistency of the evidence it backtracked and that of the previous medical studies.
Compositional Inversion for Stable Diffusion Models
Dec 14, 2023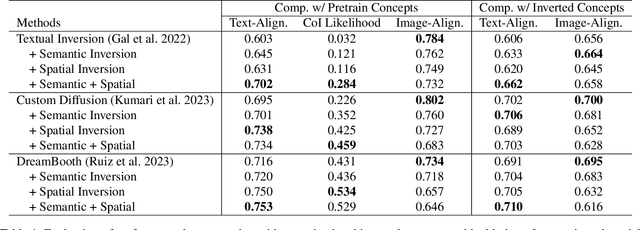
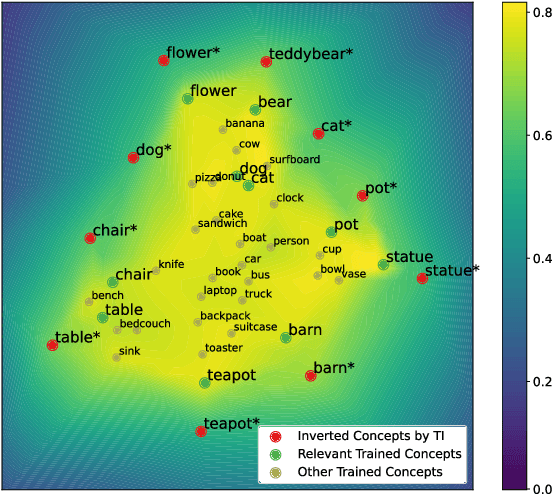
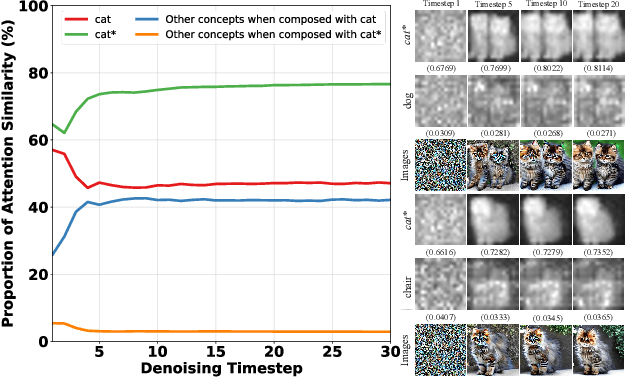
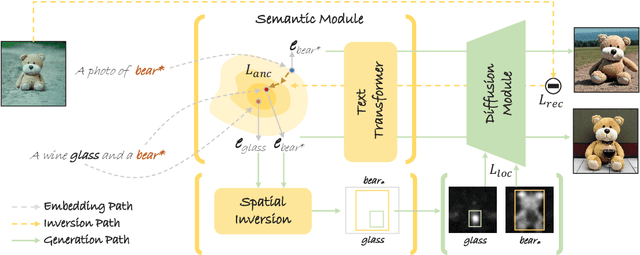
Abstract:Inversion methods, such as Textual Inversion, generate personalized images by incorporating concepts of interest provided by user images. However, existing methods often suffer from overfitting issues, where the dominant presence of inverted concepts leads to the absence of other desired concepts. It stems from the fact that during inversion, the irrelevant semantics in the user images are also encoded, forcing the inverted concepts to occupy locations far from the core distribution in the embedding space. To address this issue, we propose a method that guides the inversion process towards the core distribution for compositional embeddings. Additionally, we introduce a spatial regularization approach to balance the attention on the concepts being composed. Our method is designed as a post-training approach and can be seamlessly integrated with other inversion methods. Experimental results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed approach in mitigating the overfitting problem and generating more diverse and balanced compositions of concepts in the synthesized images. The source code is available at https://github.com/zhangxulu1996/Compositional-Inversion.
Conceptor Learning for Class Activation Mapping
Jan 21, 2022Abstract:Class Activation Mapping (CAM) has been widely adopted to generate saliency maps which provides visual explanations for deep neural networks (DNNs). The saliency maps are conventionally generated by fusing the channels of the target feature map using a weighted average scheme. It is a weak model for the inter-channel relation, in the sense that it only models the relation among channels in a contrastive way (i.e., channels that play key roles in the prediction are given higher weights for them to stand out in the fusion). The collaborative relation, which makes the channels work together to provide cross reference, has been ignored. Furthermore, the model has neglected the intra-channel relation thoroughly.In this paper, we address this problem by introducing Conceptor learning into CAM generation. Conceptor leaning has been originally proposed to model the patterns of state changes in recurrent neural networks (RNNs). By relaxing the dependency of Conceptor learning to RNNs, we make Conceptor-CAM not only generalizable to more DNN architectures but also able to learn both the inter- and intra-channel relations for better saliency map generation. Moreover, we have enabled the use of Boolean operations to combine the positive and pseudo-negative evidences, which has made the CAM inference more robust and comprehensive. The effectiveness of Conceptor-CAM has been validated with both formal verifications and experiments on the dataset of the largest scale in literature. The experimental results show that Conceptor-CAM is compatible with and can bring significant improvement to all well recognized CAM-based methods, and has outperformed the state-of-the-art methods by 43.14%~72.79% (88.39%~168.15%) on ILSVRC2012 in Average Increase (Drop), 15.42%~42.55% (47.09%~372.09%) on VOC, and 17.43%~31.32% (47.54%~206.45%) on COCO, respectively.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge