Xionglin Luo
Multi-View Non-negative Matrix Factorization Discriminant Learning via Cross Entropy Loss
Jan 08, 2022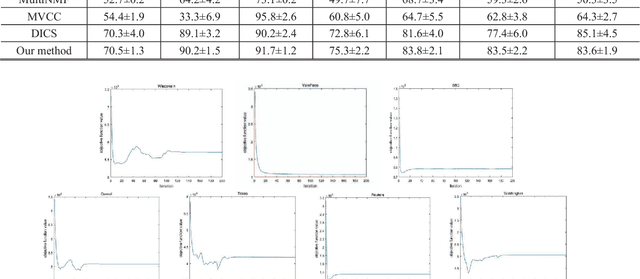
Abstract:Multi-view learning accomplishes the task objectives of classification by leverag-ing the relationships between different views of the same object. Most existing methods usually focus on consistency and complementarity between multiple views. But not all of this information is useful for classification tasks. Instead, it is the specific discriminating information that plays an important role. Zhong Zhang et al. explore the discriminative and non-discriminative information exist-ing in common and view-specific parts among different views via joint non-negative matrix factorization. In this paper, we improve this algorithm on this ba-sis by using the cross entropy loss function to constrain the objective function better. At last, we implement better classification effect than original on the same data sets and show its superiority over many state-of-the-art algorithms.
Self-attention Multi-view Representation Learning with Diversity-promoting Complementarity
Jan 01, 2022
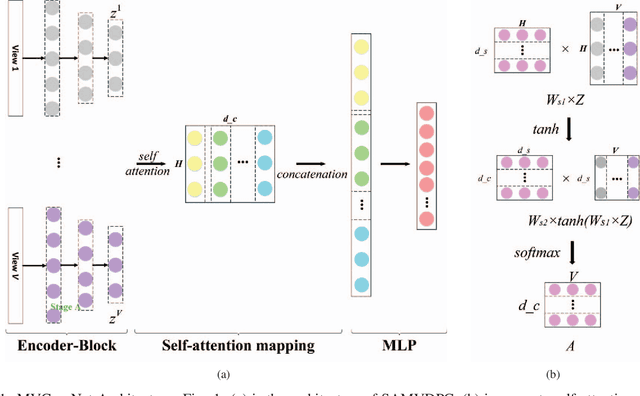
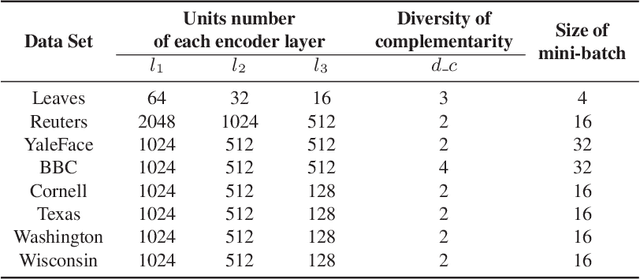
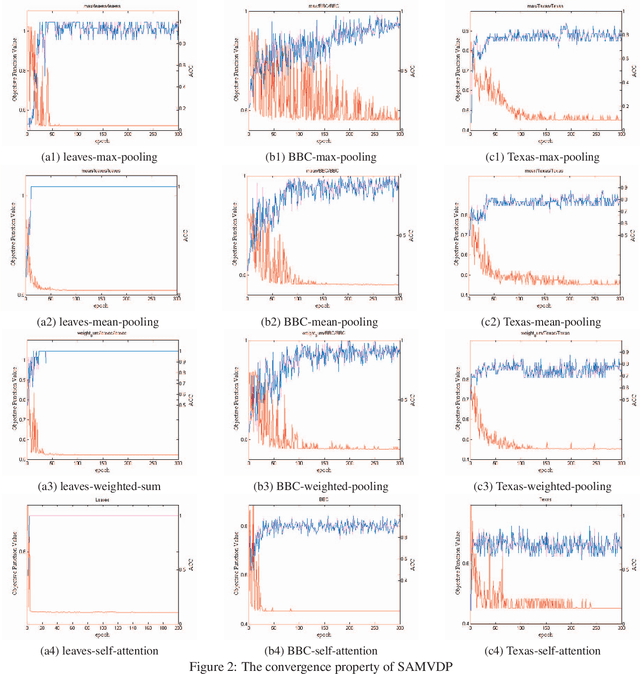
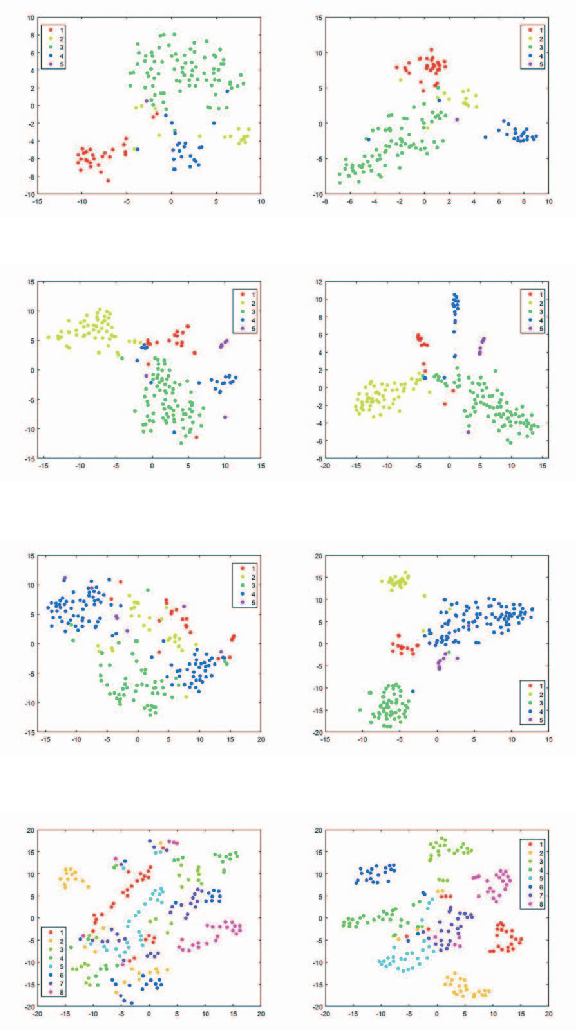
Abstract:Multi-view learning attempts to generate a model with a better performance by exploiting the consensus and/or complementarity among multi-view data. However, in terms of complementarity, most existing approaches only can find representations with single complementarity rather than complementary information with diversity. In this paper, to utilize both complementarity and consistency simultaneously, give free rein to the potential of deep learning in grasping diversity-promoting complementarity for multi-view representation learning, we propose a novel supervised multi-view representation learning algorithm, called Self-Attention Multi-View network with Diversity-Promoting Complementarity (SAMVDPC), which exploits the consistency by a group of encoders, uses self-attention to find complementary information entailing diversity. Extensive experiments conducted on eight real-world datasets have demonstrated the effectiveness of our proposed method, and show its superiority over several baseline methods, which only consider single complementary information.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge