Xinyuan Yan
Teaching People LLM's Errors and Getting it Right
Dec 24, 2025



Abstract:People use large language models (LLMs) when they should not. This is partly because they see LLMs compose poems and answer intricate questions, so they understandably, but incorrectly, assume LLMs won't stumble on basic tasks like simple arithmetic. Prior work has tried to address this by clustering instance embeddings into regions where an LLM is likely to fail and automatically describing patterns in these regions. The found failure patterns are taught to users to mitigate their overreliance. Yet, this approach has not fully succeeded. In this analysis paper, we aim to understand why. We first examine whether the negative result stems from the absence of failure patterns. We group instances in two datasets by their meta-labels and evaluate an LLM's predictions on these groups. We then define criteria to flag groups that are sizable and where the LLM is error-prone, and find meta-label groups that meet these criteria. Their meta-labels are the LLM's failure patterns that could be taught to users, so they do exist. We next test whether prompting and embedding-based approaches can surface these known failures. Without this, users cannot be taught about them to reduce their overreliance. We find mixed results across methods, which could explain the negative result. Finally, we revisit the final metric that measures teaching effectiveness. We propose to assess a user's ability to effectively use the given failure patterns to anticipate when an LLM is error-prone. A user study shows a positive effect from teaching with this metric, unlike the human-AI team accuracy. Our findings show that teaching failure patterns could be a viable approach to mitigating overreliance, but success depends on better automated failure-discovery methods and using metrics like ours.
Visual Exploration of Feature Relationships in Sparse Autoencoders with Curated Concepts
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:Sparse autoencoders (SAEs) have emerged as a powerful tool for uncovering interpretable features in large language models (LLMs) through the sparse directions they learn. However, the sheer number of extracted directions makes comprehensive exploration intractable. While conventional embedding techniques such as UMAP can reveal global structure, they suffer from limitations including high-dimensional compression artifacts, overplotting, and misleading neighborhood distortions. In this work, we propose a focused exploration framework that prioritizes curated concepts and their corresponding SAE features over attempts to visualize all available features simultaneously. We present an interactive visualization system that combines topology-based visual encoding with dimensionality reduction to faithfully represent both local and global relationships among selected features. This hybrid approach enables users to investigate SAE behavior through targeted, interpretable subsets, facilitating deeper and more nuanced analysis of concept representation in latent space.
Explainable Mapper: Charting LLM Embedding Spaces Using Perturbation-Based Explanation and Verification Agents
Jul 24, 2025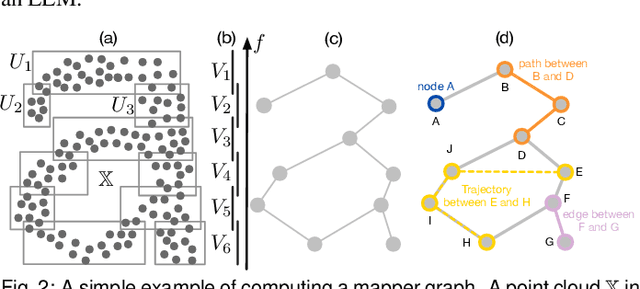
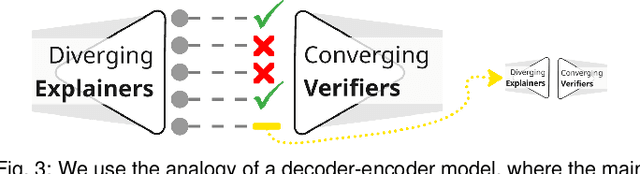
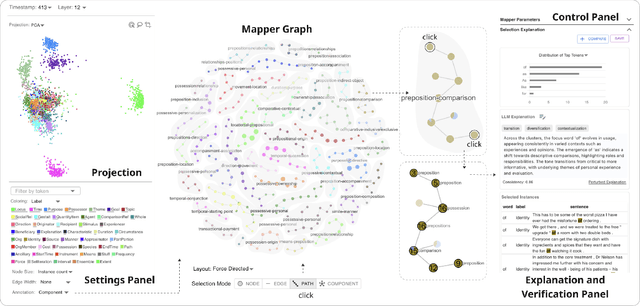
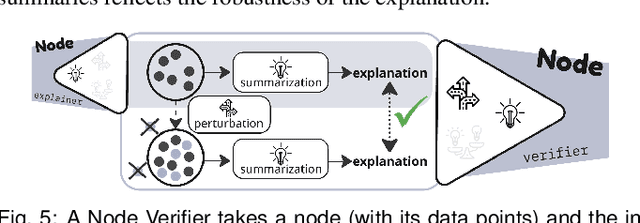
Abstract:Large language models (LLMs) produce high-dimensional embeddings that capture rich semantic and syntactic relationships between words, sentences, and concepts. Investigating the topological structures of LLM embedding spaces via mapper graphs enables us to understand their underlying structures. Specifically, a mapper graph summarizes the topological structure of the embedding space, where each node represents a topological neighborhood (containing a cluster of embeddings), and an edge connects two nodes if their corresponding neighborhoods overlap. However, manually exploring these embedding spaces to uncover encoded linguistic properties requires considerable human effort. To address this challenge, we introduce a framework for semi-automatic annotation of these embedding properties. To organize the exploration process, we first define a taxonomy of explorable elements within a mapper graph such as nodes, edges, paths, components, and trajectories. The annotation of these elements is executed through two types of customizable LLM-based agents that employ perturbation techniques for scalable and automated analysis. These agents help to explore and explain the characteristics of mapper elements and verify the robustness of the generated explanations. We instantiate the framework within a visual analytics workspace and demonstrate its effectiveness through case studies. In particular, we replicate findings from prior research on BERT's embedding properties across various layers of its architecture and provide further observations into the linguistic properties of topological neighborhoods.
VISLIX: An XAI Framework for Validating Vision Models with Slice Discovery and Analysis
May 06, 2025Abstract:Real-world machine learning models require rigorous evaluation before deployment, especially in safety-critical domains like autonomous driving and surveillance. The evaluation of machine learning models often focuses on data slices, which are subsets of the data that share a set of characteristics. Data slice finding automatically identifies conditions or data subgroups where models underperform, aiding developers in mitigating performance issues. Despite its popularity and effectiveness, data slicing for vision model validation faces several challenges. First, data slicing often needs additional image metadata or visual concepts, and falls short in certain computer vision tasks, such as object detection. Second, understanding data slices is a labor-intensive and mentally demanding process that heavily relies on the expert's domain knowledge. Third, data slicing lacks a human-in-the-loop solution that allows experts to form hypothesis and test them interactively. To overcome these limitations and better support the machine learning operations lifecycle, we introduce VISLIX, a novel visual analytics framework that employs state-of-the-art foundation models to help domain experts analyze slices in computer vision models. Our approach does not require image metadata or visual concepts, automatically generates natural language insights, and allows users to test data slice hypothesis interactively. We evaluate VISLIX with an expert study and three use cases, that demonstrate the effectiveness of our tool in providing comprehensive insights for validating object detection models.
See or Recall: A Sanity Check for the Role of Vision in Solving Visualization Question Answer Tasks with Multimodal LLMs
Apr 14, 2025Abstract:Recent developments in multimodal large language models (MLLM) have equipped language models to reason about vision and language jointly. This permits MLLMs to both perceive and answer questions about data visualization across a variety of designs and tasks. Applying MLLMs to a broad range of visualization tasks requires us to properly evaluate their capabilities, and the most common way to conduct evaluation is through measuring a model's visualization reasoning capability, analogous to how we would evaluate human understanding of visualizations (e.g., visualization literacy). However, we found that in the context of visualization question answering (VisQA), how an MLLM perceives and reasons about visualizations can be fundamentally different from how humans approach the same problem. During the evaluation, even without visualization, the model could correctly answer a substantial portion of the visualization test questions, regardless of whether any selection options were provided. We hypothesize that the vast amount of knowledge encoded in the language model permits factual recall that supersedes the need to seek information from the visual signal. It raises concerns that the current VisQA evaluation may not fully capture the models' visualization reasoning capabilities. To address this, we propose a comprehensive sanity check framework that integrates a rule-based decision tree and a sanity check table to disentangle the effects of "seeing" (visual processing) and "recall" (reliance on prior knowledge). This validates VisQA datasets for evaluation, highlighting where models are truly "seeing", positively or negatively affected by the factual recall, or relying on inductive biases for question answering. Our study underscores the need for careful consideration in designing future visualization understanding studies when utilizing MLLMs.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge