Xingyu Shi
Explainable Topic-Enhanced Argument Mining from Heterogeneous Sources
Jul 22, 2023Abstract:Given a controversial target such as ``nuclear energy'', argument mining aims to identify the argumentative text from heterogeneous sources. Current approaches focus on exploring better ways of integrating the target-associated semantic information with the argumentative text. Despite their empirical successes, two issues remain unsolved: (i) a target is represented by a word or a phrase, which is insufficient to cover a diverse set of target-related subtopics; (ii) the sentence-level topic information within an argument, which we believe is crucial for argument mining, is ignored. To tackle the above issues, we propose a novel explainable topic-enhanced argument mining approach. Specifically, with the use of the neural topic model and the language model, the target information is augmented by explainable topic representations. Moreover, the sentence-level topic information within the argument is captured by minimizing the distance between its latent topic distribution and its semantic representation through mutual learning. Experiments have been conducted on the benchmark dataset in both the in-target setting and the cross-target setting. Results demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model against the state-of-the-art baselines.
Topic-Aware Evidence Reasoning and Stance-Aware Aggregation for Fact Verification
Jun 02, 2021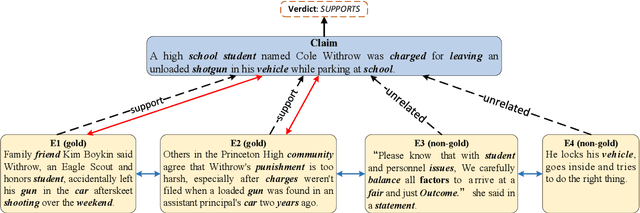

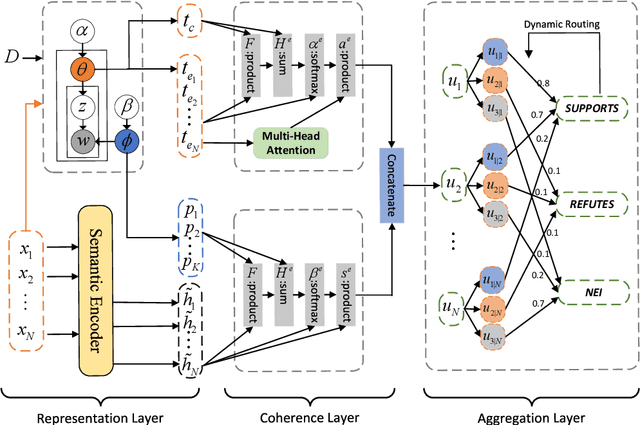
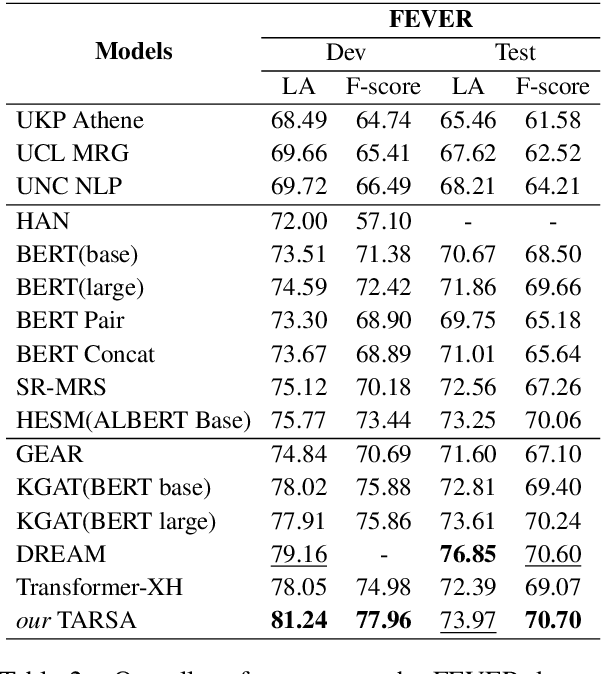
Abstract:Fact verification is a challenging task that requires simultaneously reasoning and aggregating over multiple retrieved pieces of evidence to evaluate the truthfulness of a claim. Existing approaches typically (i) explore the semantic interaction between the claim and evidence at different granularity levels but fail to capture their topical consistency during the reasoning process, which we believe is crucial for verification; (ii) aggregate multiple pieces of evidence equally without considering their implicit stances to the claim, thereby introducing spurious information. To alleviate the above issues, we propose a novel topic-aware evidence reasoning and stance-aware aggregation model for more accurate fact verification, with the following four key properties: 1) checking topical consistency between the claim and evidence; 2) maintaining topical coherence among multiple pieces of evidence; 3) ensuring semantic similarity between the global topic information and the semantic representation of evidence; 4) aggregating evidence based on their implicit stances to the claim. Extensive experiments conducted on the two benchmark datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed model over several state-of-the-art approaches for fact verification. The source code can be obtained from https://github.com/jasenchn/TARSA.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge