Xingjue Liao
A bio-inspired sand-rolling robot: effect of body shape on sand rolling performance
Mar 18, 2025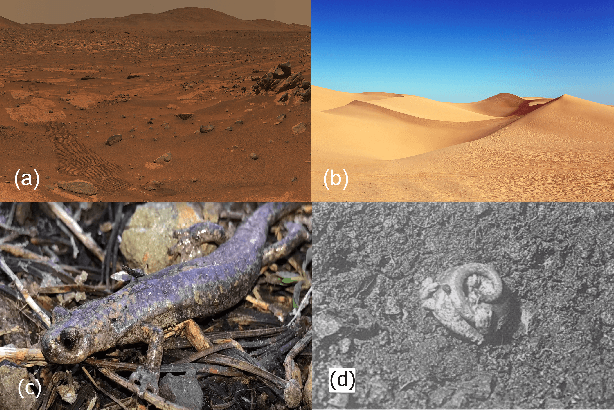
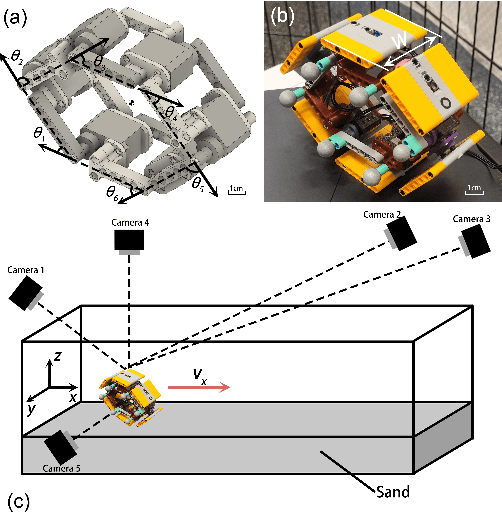
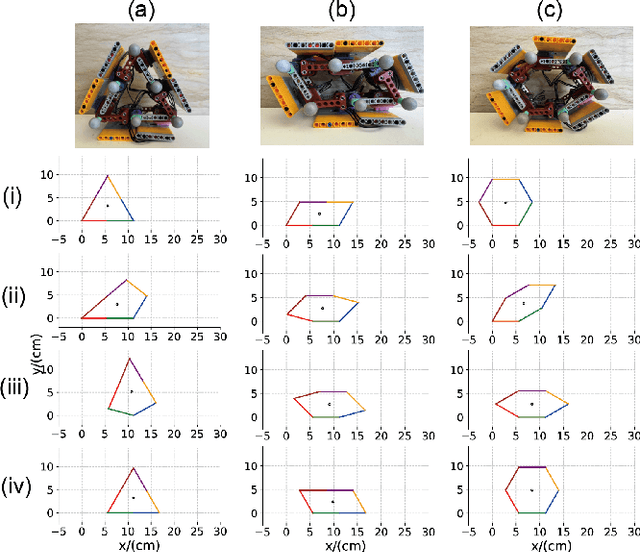
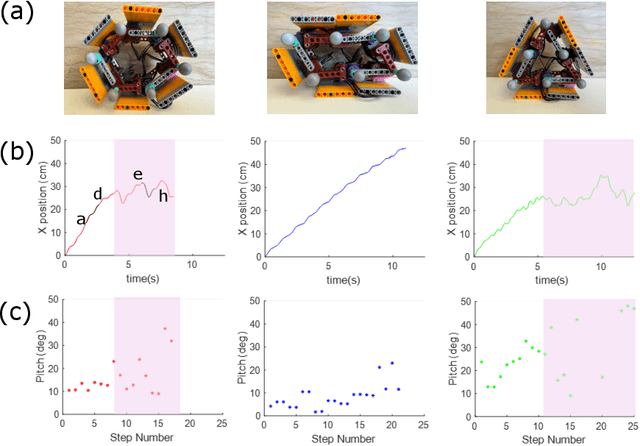
Abstract:The capability of effectively moving on complex terrains such as sand and gravel can empower our robots to robustly operate in outdoor environments, and assist with critical tasks such as environment monitoring, search-and-rescue, and supply delivery. Inspired by the Mount Lyell salamander's ability to curl its body into a loop and effectively roll down {\Revision hill slopes}, in this study we develop a sand-rolling robot and investigate how its locomotion performance is governed by the shape of its body. We experimentally tested three different body shapes: Hexagon, Quadrilateral, and Triangle. We found that Hexagon and Triangle can achieve a faster rolling speed on sand, but exhibited more frequent failures of getting stuck. Analysis of the interaction between robot and sand revealed the failure mechanism: the deformation of the sand produced a local ``sand incline'' underneath robot contact segments, increasing the effective region of supporting polygon (ERSP) and preventing the robot from shifting its center of mass (CoM) outside the ERSP to produce sustainable rolling. Based on this mechanism, a highly-simplified model successfully captured the critical body pitch for each rolling shape to produce sustained rolling on sand, and informed design adaptations that mitigated the locomotion failures and improved robot speed by more than 200$\%$. Our results provide insights into how locomotors can utilize different morphological features to achieve robust rolling motion across deformable substrates.
Multi-robot connection towards collective obstacle field traversal
Sep 18, 2024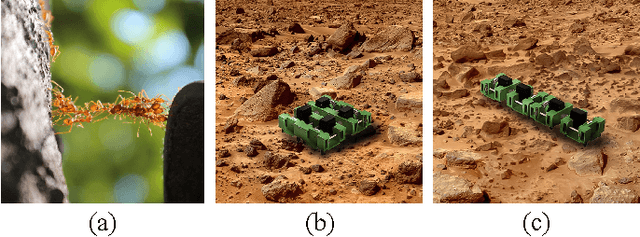
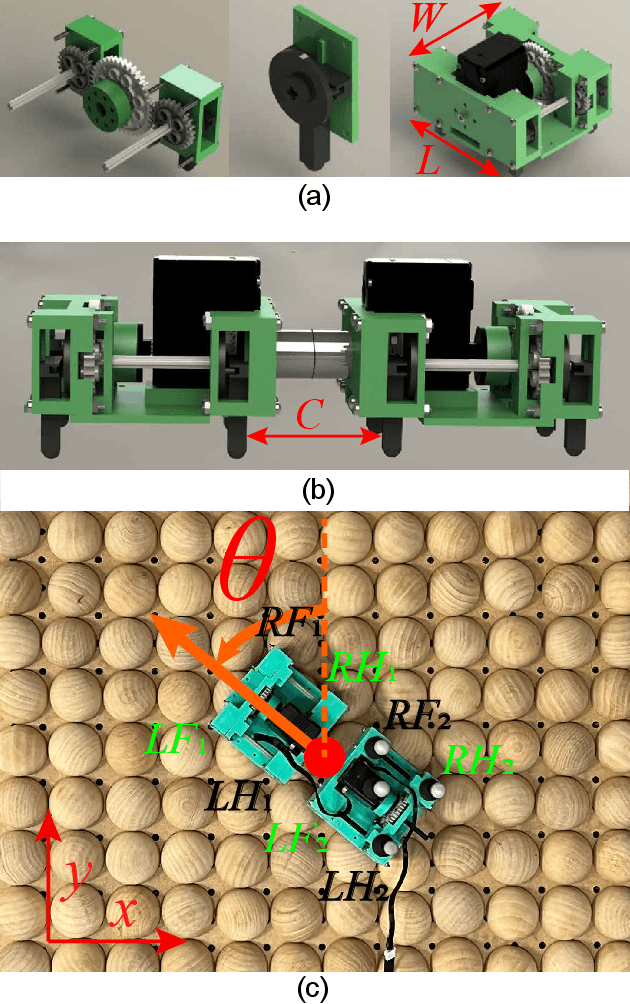
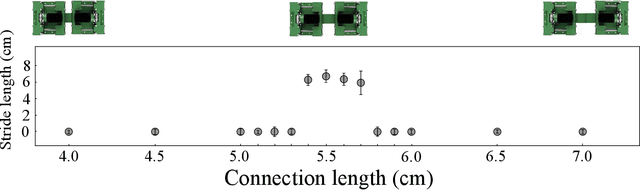
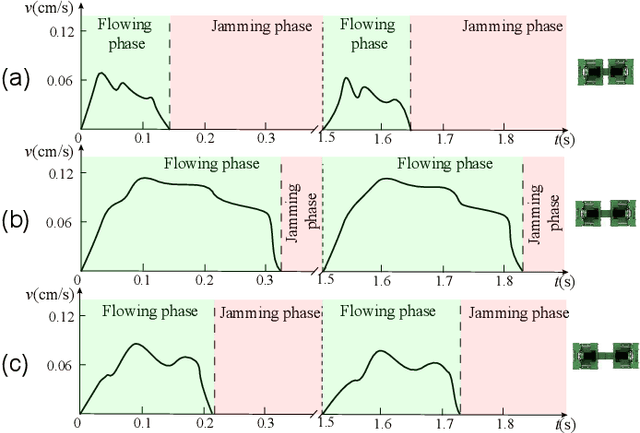
Abstract:Environments with large terrain height variations present great challenges for legged robot locomotion. Drawing inspiration from fire ants' collective assembly behavior, we study strategies that can enable two ``connectable'' robots to collectively navigate over bumpy terrains with height variations larger than robot leg length. Each robot was designed to be extremely simple, with a cubical body and one rotary motor actuating four vertical peg legs that move in pairs. Two or more robots could physically connect to one another to enhance collective mobility. We performed locomotion experiments with a two-robot group, across an obstacle field filled with uniformly-distributed semi-spherical ``boulders''. Experimentally-measured robot speed suggested that the connection length between the robots has a significant effect on collective mobility: connection length C in [0.86, 0.9] robot unit body length (UBL) were able to produce sustainable movements across the obstacle field, whereas connection length C in [0.63, 0.84] and [0.92, 1.1] UBL resulted in low traversability. An energy landscape based model revealed the underlying mechanism of how connection length modulated collective mobility through the system's potential energy landscape, and informed adaptation strategies for the two-robot system to adapt their connection length for traversing obstacle fields with varying spatial frequencies. Our results demonstrated that by varying the connection configuration between the robots, the two-robot system could leverage mechanical intelligence to better utilize obstacle interaction forces and produce improved locomotion. Going forward, we envision that generalized principles of robot-environment coupling can inform design and control strategies for a large group of small robots to achieve ant-like collective environment negotiation.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge