Xiaowei Tong
Mega-cities dominate China's urban greening
Jul 03, 2023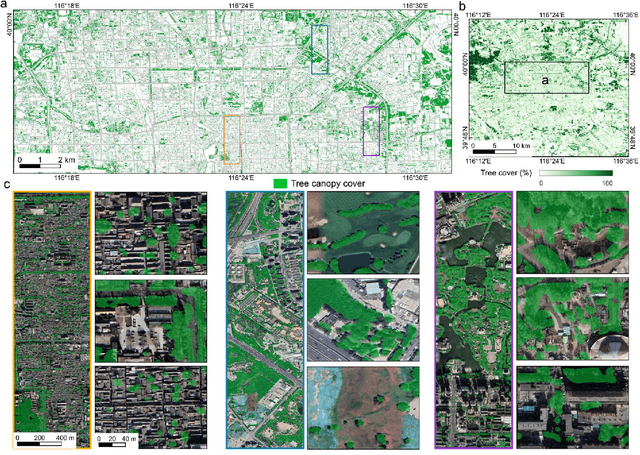
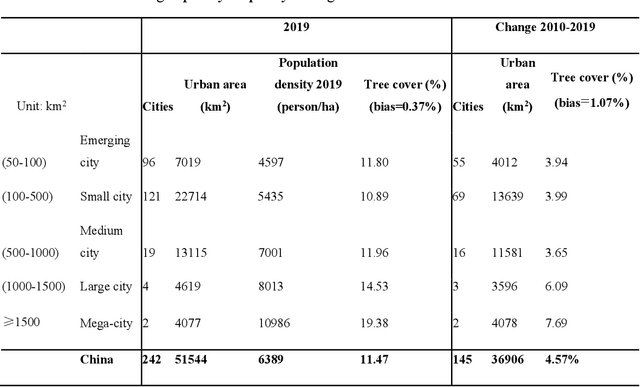
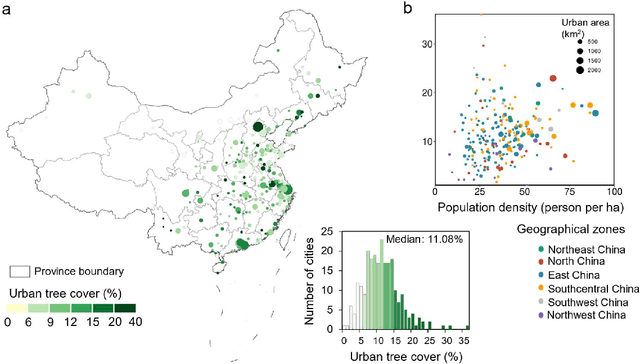
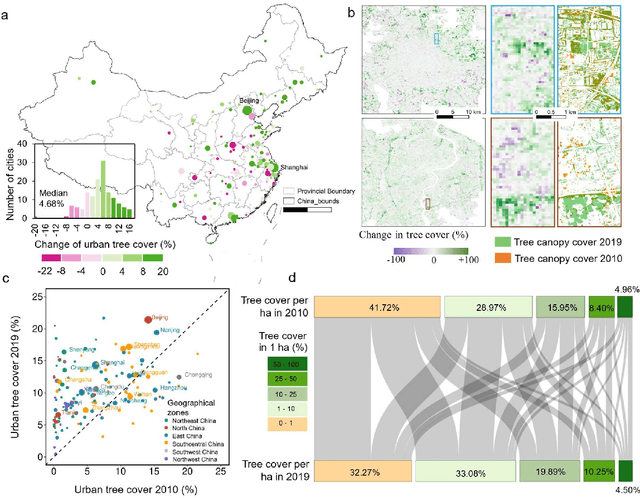
Abstract:Trees play a crucial role in urban environments, offering various ecosystem services that contribute to public health and human well-being. China has initiated a range of urban greening policies over the past decades, however, monitoring their impact on urban tree dynamics at a national scale has proven challenging. In this study, we deployed nano-satellites to quantify urban tree coverage in all major Chinese cities larger than 50 km2 in 2010 and 2019. Our findings indicate that approximately 6000 km2 (11%) of urban areas were covered by trees in 2019, and 76% of these cities experienced an increase in tree cover compared to 2010. Notably, the increase in tree cover in mega-cities such as Beijing, and Shanghai was approximately twice as large as in most other cities (7.69% vs 3.94%). The study employs a data-driven approach towards assessing urban tree cover changes in relation to greening policies, showing clear signs of tree cover increases but also suggesting an uneven implementation primarily benefiting a few mega-cities.
One "Ruler" for All Languages: Multi-Lingual Dialogue Evaluation with Adversarial Multi-Task Learning
May 08, 2018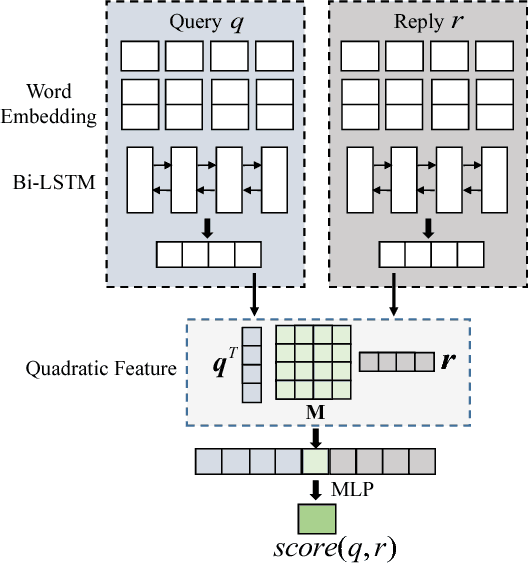
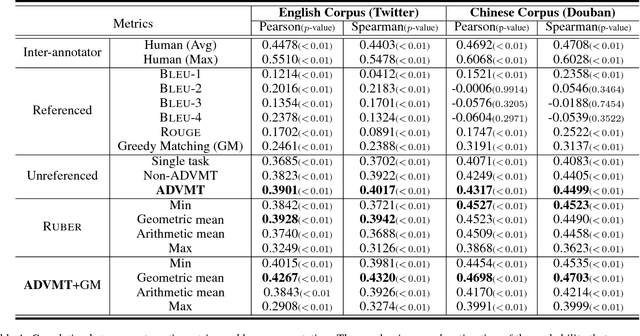
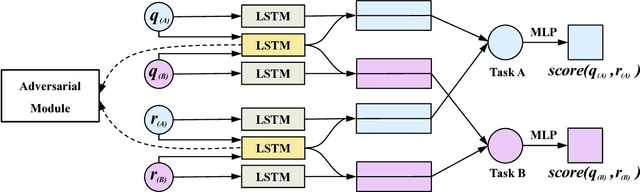
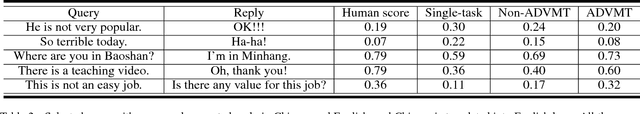
Abstract:Automatic evaluating the performance of Open-domain dialogue system is a challenging problem. Recent work in neural network-based metrics has shown promising opportunities for automatic dialogue evaluation. However, existing methods mainly focus on monolingual evaluation, in which the trained metric is not flexible enough to transfer across different languages. To address this issue, we propose an adversarial multi-task neural metric (ADVMT) for multi-lingual dialogue evaluation, with shared feature extraction across languages. We evaluate the proposed model in two different languages. Experiments show that the adversarial multi-task neural metric achieves a high correlation with human annotation, which yields better performance than monolingual ones and various existing metrics.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge