Xiaohui Luo
Multi-stages attention Breast cancer classification based on nonlinear spiking neural P neurons with autapses
Jan 04, 2024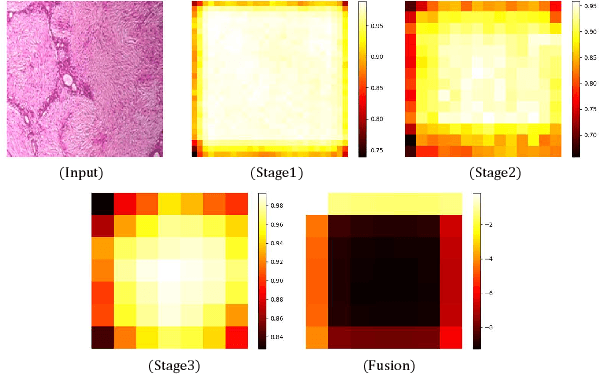
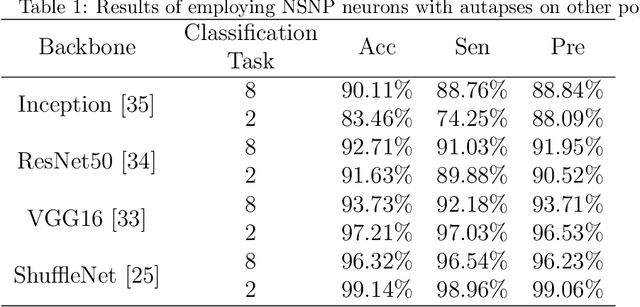
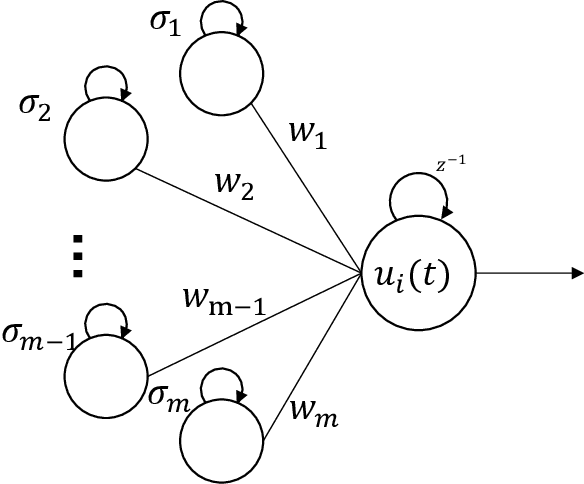
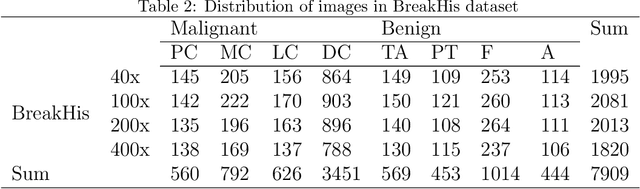
Abstract:Breast cancer(BC) is a prevalent type of malignant tumor in women. Early diagnosis and treatment are vital for enhancing the patients' survival rate. Downsampling in deep networks may lead to loss of information, so for compensating the detail and edge information and allowing convolutional neural networks to pay more attention to seek the lesion region, we propose a multi-stages attention architecture based on NSNP neurons with autapses. First, unlike the single-scale attention acquisition methods of existing methods, we set up spatial attention acquisition at each feature map scale of the convolutional network to obtain an fusion global information on attention guidance. Then we introduce a new type of NSNP variants called NSNP neurons with autapses. Specifically, NSNP systems are modularized as feature encoders, recoding the features extracted from convolutional neural network as well as the fusion of attention information and preserve the key characteristic elements in feature maps. This ensures the retention of valuable data while gradually transforming high-dimensional complicated info into low-dimensional ones. The proposed method is evaluated on the public dataset BreakHis at various magnifications and classification tasks. It achieves a classification accuracy of 96.32% at all magnification cases, outperforming state-of-the-art methods. Ablation studies are also performed, verifying the proposed model's efficacy. The source code is available at XhuBobYoung/Breast-cancer-Classification.
SLP-Net:An efficient lightweight network for segmentation of skin lesions
Jan 04, 2024Abstract:Prompt treatment for melanoma is crucial. To assist physicians in identifying lesion areas precisely in a quick manner, we propose a novel skin lesion segmentation technique namely SLP-Net, an ultra-lightweight segmentation network based on the spiking neural P(SNP) systems type mechanism. Most existing convolutional neural networks achieve high segmentation accuracy while neglecting the high hardware cost. SLP-Net, on the contrary, has a very small number of parameters and a high computation speed. We design a lightweight multi-scale feature extractor without the usual encoder-decoder structure. Rather than a decoder, a feature adaptation module is designed to replace it and implement multi-scale information decoding. Experiments at the ISIC2018 challenge demonstrate that the proposed model has the highest Acc and DSC among the state-of-the-art methods, while experiments on the PH2 dataset also demonstrate a favorable generalization ability. Finally, we compare the computational complexity as well as the computational speed of the models in experiments, where SLP-Net has the highest overall superiority
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge