Xiaocong Lian
Human Health Indicator Prediction from Gait Video
Dec 25, 2022Abstract:Body Mass Index (BMI), age, height and weight are important indicators of human health conditions, which can provide useful information for plenty of practical purposes, such as health care, monitoring and re-identification. Most existing methods of health indicator prediction mainly use front-view body or face images. These inputs are hard to be obtained in daily life and often lead to the lack of robustness for the models, considering their strict requirements on view and pose. In this paper, we propose to employ gait videos to predict health indicators, which are more prevalent in surveillance and home monitoring scenarios. However, the study of health indicator prediction from gait videos using deep learning was hindered due to the small amount of open-sourced data. To address this issue, we analyse the similarity and relationship between pose estimation and health indicator prediction tasks, and then propose a paradigm enabling deep learning for small health indicator datasets by pre-training on the pose estimation task. Furthermore, to better suit the health indicator prediction task, we bring forward Global-Local Aware aNd Centrosymmetric Encoder (GLANCE) module. It first extracts local and global features by progressive convolutions and then fuses multi-level features by a centrosymmetric double-path hourglass structure in two different ways. Experiments demonstrate that the proposed paradigm achieves state-of-the-art results for predicting health indicators on MoVi, and that the GLANCE module is also beneficial for pose estimation on 3DPW.
6D Robotic Assembly Based on RGB-only Object Pose Estimation
Aug 27, 2022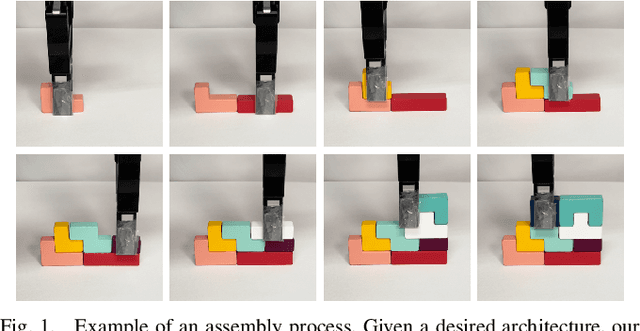
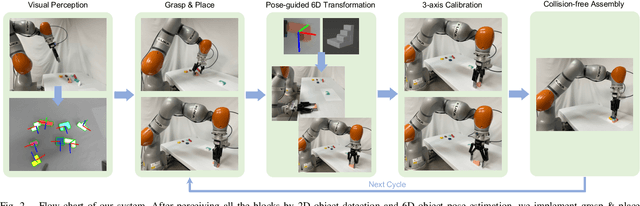
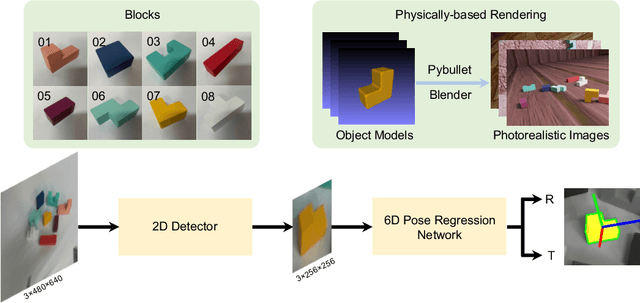
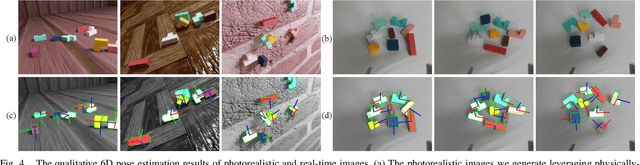
Abstract:Vision-based robotic assembly is a crucial yet challenging task as the interaction with multiple objects requires high levels of precision. In this paper, we propose an integrated 6D robotic system to perceive, grasp, manipulate and assemble blocks with tight tolerances. Aiming to provide an off-the-shelf RGB-only solution, our system is built upon a monocular 6D object pose estimation network trained solely with synthetic images leveraging physically-based rendering. Subsequently, pose-guided 6D transformation along with collision-free assembly is proposed to construct any designed structure with arbitrary initial poses. Our novel 3-axis calibration operation further enhances the precision and robustness by disentangling 6D pose estimation and robotic assembly. Both quantitative and qualitative results demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed 6D robotic assembly system.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge