Xiao-Yue Xu
AI-Powered Algorithm-Centric Quantum Processor Topology Design
Dec 18, 2024Abstract:Quantum computing promises to revolutionize various fields, yet the execution of quantum programs necessitates an effective compilation process. This involves strategically mapping quantum circuits onto the physical qubits of a quantum processor. The qubits' arrangement, or topology, is pivotal to the circuit's performance, a factor that often defies traditional heuristic or manual optimization methods due to its complexity. In this study, we introduce a novel approach leveraging reinforcement learning to dynamically tailor qubit topologies to the unique specifications of individual quantum circuits, guiding algorithm-driven quantum processor topology design for reducing the depth of mapped circuit, which is particularly critical for the output accuracy on noisy quantum processors. Our method marks a significant departure from previous methods that have been constrained to mapping circuits onto a fixed processor topology. Experiments demonstrate that we have achieved notable enhancements in circuit performance, with a minimum of 20\% reduction in circuit depth in 60\% of the cases examined, and a maximum enhancement of up to 46\%. Furthermore, the pronounced benefits of our approach in reducing circuit depth become increasingly evident as the scale of the quantum circuits increases, exhibiting the scalability of our method in terms of problem size. This work advances the co-design of quantum processor architecture and algorithm mapping, offering a promising avenue for future research and development in the field.
Near-Term Quantum Computing Techniques: Variational Quantum Algorithms, Error Mitigation, Circuit Compilation, Benchmarking and Classical Simulation
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:Quantum computing is a game-changing technology for global academia, research centers and industries including computational science, mathematics, finance, pharmaceutical, materials science, chemistry and cryptography. Although it has seen a major boost in the last decade, we are still a long way from reaching the maturity of a full-fledged quantum computer. That said, we will be in the Noisy-Intermediate Scale Quantum (NISQ) era for a long time, working on dozens or even thousands of qubits quantum computing systems. An outstanding challenge, then, is to come up with an application that can reliably carry out a nontrivial task of interest on the near-term quantum devices with non-negligible quantum noise. To address this challenge, several near-term quantum computing techniques, including variational quantum algorithms, error mitigation, quantum circuit compilation and benchmarking protocols, have been proposed to characterize and mitigate errors, and to implement algorithms with a certain resistance to noise, so as to enhance the capabilities of near-term quantum devices and explore the boundaries of their ability to realize useful applications. Besides, the development of near-term quantum devices is inseparable from the efficient classical simulation, which plays a vital role in quantum algorithm design and verification, error-tolerant verification and other applications. This review will provide a thorough introduction of these near-term quantum computing techniques, report on their progress, and finally discuss the future prospect of these techniques, which we hope will motivate researchers to undertake additional studies in this field.
Active Learning on a Programmable Photonic Quantum Processor
Aug 03, 2022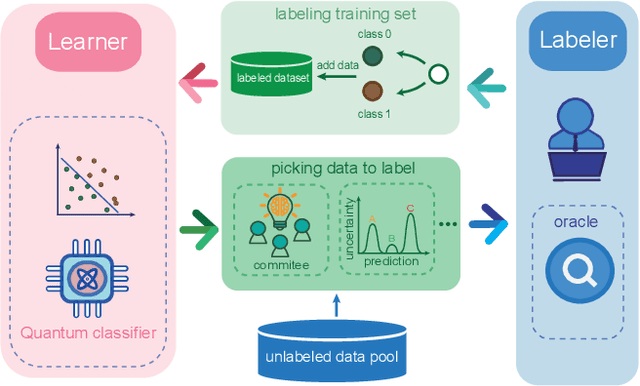
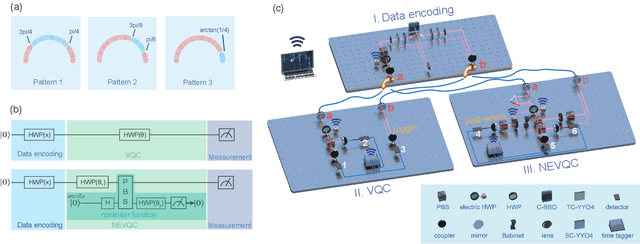
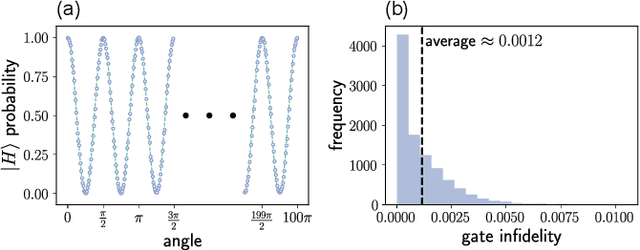
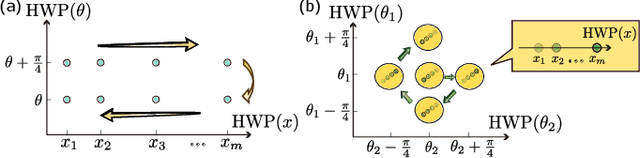
Abstract:Training a quantum machine learning model generally requires a large labeled dataset, which incurs high labeling and computational costs. To reduce such costs, a selective training strategy, called active learning (AL), chooses only a subset of the original dataset to learn while maintaining the trained model's performance. Here, we design and implement two AL-enpowered variational quantum classifiers, to investigate the potential applications and effectiveness of AL in quantum machine learning. Firstly, we build a programmable free-space photonic quantum processor, which enables the programmed implementation of various hybrid quantum-classical computing algorithms. Then, we code the designed variational quantum classifier with AL into the quantum processor, and execute comparative tests for the classifiers with and without the AL strategy. The results validate the great advantage of AL in quantum machine learning, as it saves at most $85\%$ labeling efforts and $91.6\%$ percent computational efforts compared to the training without AL on a data classification task. Our results inspire AL's further applications in large-scale quantum machine learning to drastically reduce training data and speed up training, underpinning the exploration of practical quantum advantages in quantum physics or real-world applications.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge