Xianfeng Han
Flow-Guided Controllable Line Drawing Generation
Jul 14, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the problem of automatically controllable artistic character line drawing generation from photographs by proposing a Vector Flow Aware and Line Controllable Image-to-Image Translation architecture, which can be viewed as an appealing intersection between Artificial Intelligence and Arts. Specifically, we first present an Image-to-Flow network (I2FNet) to efficiently and robustly create the vector flow field in a learning-based manner, which can provide a direction guide for drawing lines. Then, we introduce our well-designed Double Flow Generator (DFG) framework to fuse features from learned vector flow and input image flow guaranteeing the spatial coherence of lines. Meanwhile, in order to allow for controllable character line drawing generation, we integrate a Line Control Matrix (LCM) into DFG and train a Line Control Regressor (LCR) to synthesize drawings with different styles by elaborately controlling the level of details, such as thickness, smoothness, and continuity, of lines. Finally, we design a Fourier Transformation Loss to further constrain the character line generation from the frequency domain view of the point. Quantitative and qualitative experiments demonstrate that our approach can obtain superior performance in producing high-resolution character line-drawing images with perceptually realistic characteristics.
STNet: Scale Tree Network with Multi-level Auxiliator for Crowd Counting
Dec 18, 2020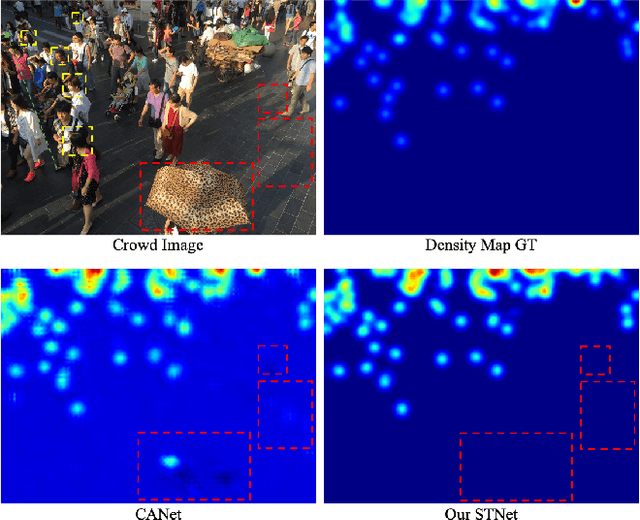
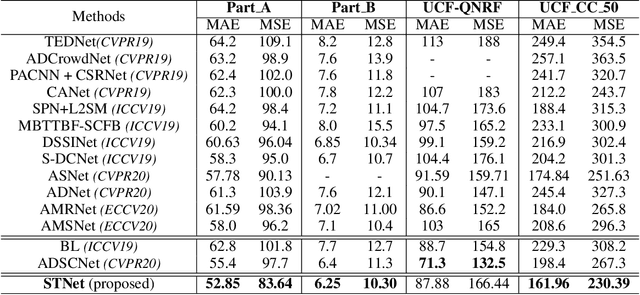


Abstract:Crowd counting remains a challenging task because the presence of drastic scale variation, density inconsistency, and complex background can seriously degrade the counting accuracy. To battle the ingrained issue of accuracy degradation, we propose a novel and powerful network called Scale Tree Network (STNet) for accurate crowd counting. STNet consists of two key components: a Scale-Tree Diversity Enhancer and a Semi-supervised Multi-level Auxiliator. Specifically, the Diversity Enhancer is designed to enrich scale diversity, which alleviates limitations of existing methods caused by insufficient level of scales. A novel tree structure is adopted to hierarchically parse coarse-to-fine crowd regions. Furthermore, a simple yet effective Multi-level Auxiliator is presented to aid in exploiting generalisable shared characteristics at multiple levels, allowing more accurate pixel-wise background cognition. The overall STNet is trained in an end-to-end manner, without the needs for manually tuning loss weights between the main and the auxiliary tasks. Extensive experiments on four challenging crowd datasets demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge