Wuyue Zhao
Self-Imitated Diffusion Policy for Efficient and Robust Visual Navigation
Jan 30, 2026Abstract:Diffusion policies (DP) have demonstrated significant potential in visual navigation by capturing diverse multi-modal trajectory distributions. However, standard imitation learning (IL), which most DP methods rely on for training, often inherits sub-optimality and redundancy from expert demonstrations, thereby necessitating a computationally intensive "generate-then-filter" pipeline that relies on auxiliary selectors during inference. To address these challenges, we propose Self-Imitated Diffusion Policy (SIDP), a novel framework that learns improved planning by selectively imitating a set of trajectories sampled from itself. Specifically, SIDP introduces a reward-guided self-imitation mechanism that encourages the policy to consistently produce high-quality trajectories efficiently, rather than outputs of inconsistent quality, thereby reducing reliance on extensive sampling and post-filtering. During training, we employ a reward-driven curriculum learning paradigm to mitigate inefficient data utility, and goal-agnostic exploration for trajectory augmentation to improve planning robustness. Extensive evaluations on a comprehensive simulation benchmark show that SIDP significantly outperforms previous methods, with real-world experiments confirming its effectiveness across multiple robotic platforms. On Jetson Orin Nano, SIDP delivers a 2.5$\times$ faster inference than the baseline NavDP, i.e., 110ms VS 273ms, enabling efficient real-time deployment.
ALTo: Adaptive-Length Tokenizer for Autoregressive Mask Generation
May 22, 2025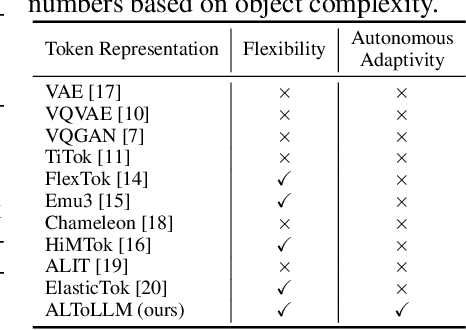
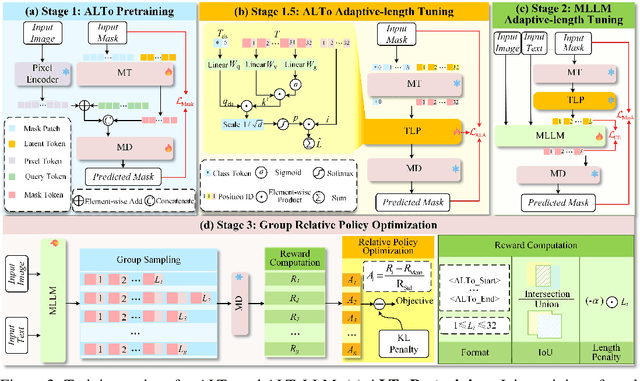
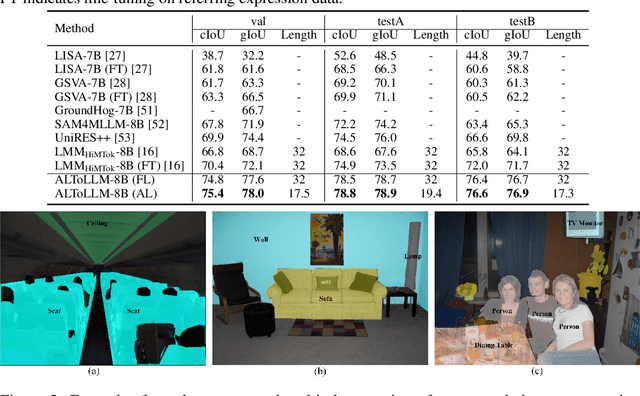
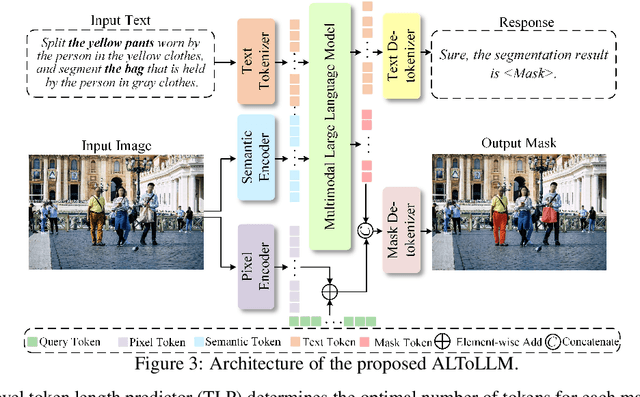
Abstract:While humans effortlessly draw visual objects and shapes by adaptively allocating attention based on their complexity, existing multimodal large language models (MLLMs) remain constrained by rigid token representations. Bridging this gap, we propose ALTo, an adaptive length tokenizer for autoregressive mask generation. To achieve this, a novel token length predictor is designed, along with a length regularization term and a differentiable token chunking strategy. We further build ALToLLM that seamlessly integrates ALTo into MLLM. Preferences on the trade-offs between mask quality and efficiency is implemented by group relative policy optimization (GRPO). Experiments demonstrate that ALToLLM achieves state-of-the-art performance with adaptive token cost on popular segmentation benchmarks. Code and models are released at https://github.com/yayafengzi/ALToLLM.
HiMTok: Learning Hierarchical Mask Tokens for Image Segmentation with Large Multimodal Model
Mar 17, 2025Abstract:The remarkable performance of large multimodal models (LMMs) has attracted significant interest from the image segmentation community. To align with the next-token-prediction paradigm, current LMM-driven segmentation methods either use object boundary points to represent masks or introduce special segmentation tokens, whose hidden states are decoded by a segmentation model requiring the original image as input. However, these approaches often suffer from inadequate mask representation and complex architectures, limiting the potential of LMMs. In this work, we propose the Hierarchical Mask Tokenizer (HiMTok), which represents segmentation masks with up to 32 tokens and eliminates the need for the original image during mask de-tokenization. HiMTok allows for compact and coarse-to-fine mask representations, aligning well with the LLM next-token-prediction paradigm and facilitating the direct acquisition of segmentation capabilities. We develop a 3-stage training recipe for progressive learning of segmentation and visual capabilities, featuring a hierarchical mask loss for effective coarse-to-fine learning. Additionally, we enable bidirectional information flow, allowing conversion between bounding boxes and mask tokens to fully leverage multi-task training potential. Extensive experiments demonstrate that our method achieves state-of-the-art performance across various segmentation tasks,while also enhancing visual grounding and maintaining overall visual understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge