Wolfgang Utschick
On the Optimality of Rate Balancing for Max-Min Fair Multicasting
Jan 29, 2026Abstract:The max-min fair (MMF) multicasting problem is known to be NP-hard. In this work, we analytically derive the optimal solution to this NP-hard problem and establish the equivalence between rate balancing and the optimal MMF multicasting solution under certain conditions. Based on this theoretical insight, we propose a low-complexity algorithm for MMF multicasting that yields closed-form solutions. Simulation results validate our analysis and demonstrate that the proposed algorithm outperforms the state-of-the-art methods while being computationally more efficient.
Reconstructing Patched or Partial Holograms to allow for Whole Slide Imaging with a Self-Referencing Holographic Microscope
Jan 22, 2026Abstract:The last decade has seen significant advances in computer-aided diagnostics for cytological screening, mainly through the improvement and integration of scanning techniques such as whole slide imaging (WSI) and the combination with deep learning. Simultaneously, new imaging techniques such as quantitative phase imaging (QPI) are being developed to capture richer cell information with less sample preparation. So far, the two worlds of WSI and QPI have not been combined. In this work, we present a reconstruction algorithm which makes whole slide imaging of cervical smears possible by using a self-referencing three-wave digital holographic microscope. Since a WSI is constructed by combining multiple patches, the algorithm is adaptive and can be used on partial holograms and patched holograms. We present the algorithm for a single shot hologram, the adaptations to make it flexible to various inputs and show that the algorithm performs well for the tested epithelial cells. This is a preprint of our paper, which has been accepted for publication in 2026 IEEE International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI).
Precoder Design in Multi-User FDD Systems with VQ-VAE and GNN
Oct 10, 2025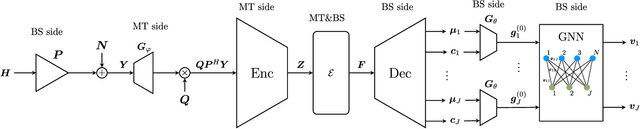
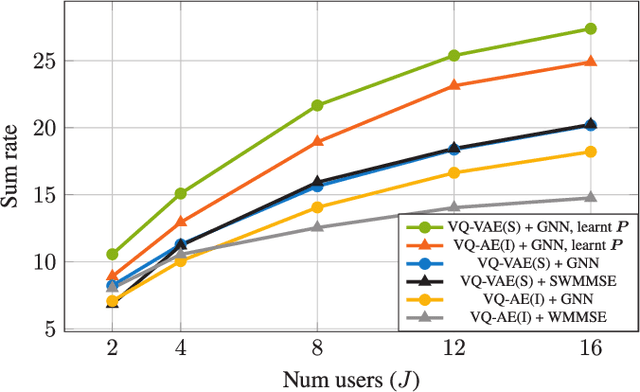
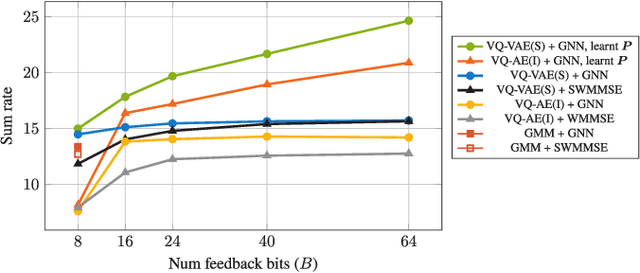
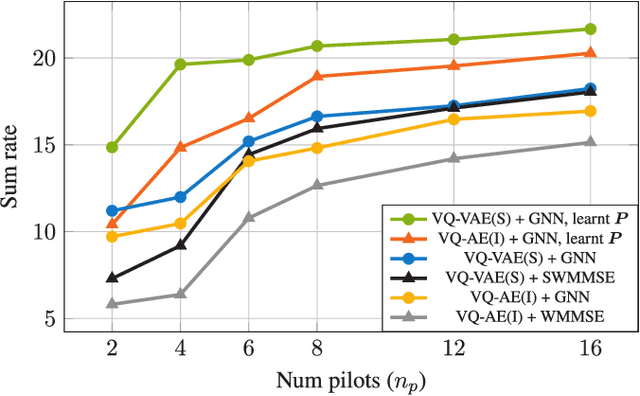
Abstract:Robust precoding is efficiently feasible in frequency division duplex (FDD) systems by incorporating the learnt statistics of the propagation environment through a generative model. We build on previous work that successfully designed site-specific precoders based on a combination of Gaussian mixture models (GMMs) and graph neural networks (GNNs). In this paper, by utilizing a vector quantized-variational autoencoder (VQ-VAE), we circumvent one of the key drawbacks of GMMs, i.e., the number of GMM components scales exponentially to the feedback bits. In addition, the deep learning architecture of the VQ-VAE allows us to jointly train the GNN together with VQ-VAE along with pilot optimization forming an end-to-end (E2E) model, resulting in considerable performance gains in sum rate for multi-user wireless systems. Simulations demonstrate the superiority of the proposed frameworks over the conventional methods involving the sub-discrete Fourier transform (DFT) pilot matrix and iterative precoder algorithms enabling the deployment of systems characterized by fewer pilots or feedback bits.
Enhancements in Score-based Channel Estimation for Real-Time Wireless Systems
Sep 09, 2025Abstract:We propose enhancements to score-based generative modeling techniques for low-latency pilot-based channel estimation in a point-to-point single-carrier multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) wireless system. Building on recent advances in score-based models, we investigate a specific noise schedule design and sampling acceleration by step-skipping to reduce the number of denoising steps during inference. We additionally propose a single-step signal-to-noise ratio informed denoiser as an extreme case of the step-skipping approach. Our methods achieve significant latency reductions without performance degradation, as demonstrated on a synthetic channel dataset representing an urban macrocell MIMO communications scenario.
Sum-Rate Optimisation of a Multi-User STAR-RIS-Aided System with Low Complexity
Apr 28, 2025Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) is a promising technology for future wireless communication systems. However, the conventional RIS can only reflect the incident signal. Hence, it provides a limited coverage, as compared to a simultaneously transmitting and reflecting RIS (STAR-RIS). Prior works on the STAR-RIS address the power minimisation or the sum-rate maximisation problem by reformulating the objective problem as a convex optimisation problem and then employing numerical tools like CVX to obtain the solution, which introduces significant computational complexity leading to a huge runtime, making the algorithms impractical for real-world implementation. In this paper, we propose a low complexity solution for the optimisation of a multi-user STAR-RIS system, where the non-convex optimisation problem is decomposed into multiple convex sub-problems with closed-form optimal solutions. The simulation results illustrate that our proposed algorithm achieves similar performance to CVX-based solutions in the literature while being computationally efficient.
Semi-Blind Strategies for MMSE Channel Estimation Utilizing Generative Priors
Apr 24, 2025Abstract:This paper investigates semi-blind channel estimation for massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems. To this end, we first estimate a subspace based on all received symbols (pilot and payload) to provide additional information for subsequent channel estimation. We show how this additional information enhances minimum mean square error (MMSE) channel estimation. Two variants of the linear MMSE (LMMSE) estimator are formulated, where the first one solves the estimation within the subspace, and the second one uses a subspace projection as a preprocessing step. Theoretical derivations show the superior estimation performance of the latter method in terms of mean square error for uncorrelated Rayleigh fading. Subsequently, we introduce parameterizations of this semi-blind LMMSE estimator based on two different conditional Gaussian latent models, i.e., the Gaussian mixture model and the variational autoencoder. Both models learn the underlying channel distribution of the propagation environment based on training data and serve as generative priors for semi-blind channel estimation. Extensive simulations for real-world measurement data and spatial channel models show the superior performance of the proposed methods compared to state-of-the-art semi-blind channel estimators with respect to the MSE.
On the Asymptotic MSE-Optimality of Parametric Bayesian Channel Estimation in mmWave Systems
Apr 23, 2025



Abstract:The mean square error (MSE)-optimal estimator is known to be the conditional mean estimator (CME). This paper introduces a parametric channel estimation technique based on Bayesian estimation. This technique uses the estimated channel parameters to parameterize the well-known LMMSE channel estimator. We first derive an asymptotic CME formulation that holds for a wide range of priors on the channel parameters. Based on this, we show that parametric Bayesian channel estimation is MSE-optimal for high signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) and/or long coherence intervals, i.e., many noisy observations provided within one coherence interval. Numerical simulations validate the derived formulations.
Uncertainty-Aware Hybrid Machine Learning in Virtual Sensors for Vehicle Sideslip Angle Estimation
Apr 08, 2025Abstract:Precise vehicle state estimation is crucial for safe and reliable autonomous driving. The number of measurable states and their precision offered by the onboard vehicle sensor system are often constrained by cost. For instance, measuring critical quantities such as the Vehicle Sideslip Angle (VSA) poses significant commercial challenges using current optical sensors. This paper addresses these limitations by focusing on the development of high-performance virtual sensors to enhance vehicle state estimation for active safety. The proposed Uncertainty-Aware Hybrid Learning (UAHL) architecture integrates a machine learning model with vehicle motion models to estimate VSA directly from onboard sensor data. A key aspect of the UAHL architecture is its focus on uncertainty quantification for individual model estimates and hybrid fusion. These mechanisms enable the dynamic weighting of uncertainty-aware predictions from machine learning and vehicle motion models to produce accurate and reliable hybrid VSA estimates. This work also presents a novel dataset named Real-world Vehicle State Estimation Dataset (ReV-StED), comprising synchronized measurements from advanced vehicle dynamic sensors. The experimental results demonstrate the superior performance of the proposed method for VSA estimation, highlighting UAHL as a promising architecture for advancing virtual sensors and enhancing active safety in autonomous vehicles.
Sparse Bayesian Generative Modeling for Joint Parameter and Channel Estimation
Feb 25, 2025


Abstract:Leveraging the inherent connection between sensing systems and wireless communications can improve their overall performance and is the core objective of joint communications and sensing. For effective communications, one has to frequently estimate the channel. Sensing, on the other hand, infers properties of the environment mostly based on estimated physical channel parameters, such as directions of arrival or delays. This work presents a low-complexity generative modeling approach that simultaneously estimates the wireless channel and its physical parameters without additional computational overhead. To this end, we leverage a recently proposed physics-informed generative model for wireless channels based on sparse Bayesian generative modeling and exploit the feature of conditionally Gaussian generative models to approximate the conditional mean estimator.
Statistical Precoder Design in Multi-User Systems via Graph Neural Networks and Generative Modeling
Dec 10, 2024Abstract:This letter proposes a graph neural network (GNN)-based framework for statistical precoder design that leverages model-based insights to compactly represent statistical knowledge, resulting in efficient, lightweight architectures. The framework also supports approximate statistical information in frequency division duplex (FDD) systems obtained through a Gaussian mixture model (GMM)-based limited feedback scheme in massive multiple-input multiple-output (MIMO) systems with low pilot overhead. Simulations using a spatial channel model and measurement data demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed framework. It outperforms baseline methods, including stochastic iterative algorithms and Discrete Fourier transform (DFT) codebook-based approaches, particularly in low pilot overhead systems.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge