William C. Chueh
Diagnostic-free onboard battery health assessment
Mar 10, 2025Abstract:Diverse usage patterns induce complex and variable aging behaviors in lithium-ion batteries, complicating accurate health diagnosis and prognosis. Separate diagnostic cycles are often used to untangle the battery's current state of health from prior complex aging patterns. However, these same diagnostic cycles alter the battery's degradation trajectory, are time-intensive, and cannot be practically performed in onboard applications. In this work, we leverage portions of operational measurements in combination with an interpretable machine learning model to enable rapid, onboard battery health diagnostics and prognostics without offline diagnostic testing and the requirement of historical data. We integrate mechanistic constraints within an encoder-decoder architecture to extract electrode states in a physically interpretable latent space and enable improved reconstruction of the degradation path. The health diagnosis model framework can be flexibly applied across diverse application interests with slight fine-tuning. We demonstrate the versatility of this model framework by applying it to three battery-cycling datasets consisting of 422 cells under different operating conditions, highlighting the utility of an interpretable diagnostic-free, onboard battery diagnosis and prognosis model.
Systematic Feature Design for Cycle Life Prediction of Lithium-Ion Batteries During Formation
Oct 09, 2024



Abstract:Optimization of the formation step in lithium-ion battery manufacturing is challenging due to limited physical understanding of solid electrolyte interphase formation and the long testing time (~100 days) for cells to reach the end of life. We propose a systematic feature design framework that requires minimal domain knowledge for accurate cycle life prediction during formation. Two simple Q(V) features designed from our framework, extracted from formation data without any additional diagnostic cycles, achieved a median of 9.20% error for cycle life prediction, outperforming thousands of autoML models using pre-defined features. We attribute the strong performance of our designed features to their physical origins - the voltage ranges identified by our framework capture the effects of formation temperature and microscopic particle resistance heterogeneity. By designing highly interpretable features, our approach can accelerate formation research, leveraging the interplay between data-driven feature design and mechanistic understanding.
Interpretation of High-Dimensional Linear Regression: Effects of Nullspace and Regularization Demonstrated on Battery Data
Sep 06, 2023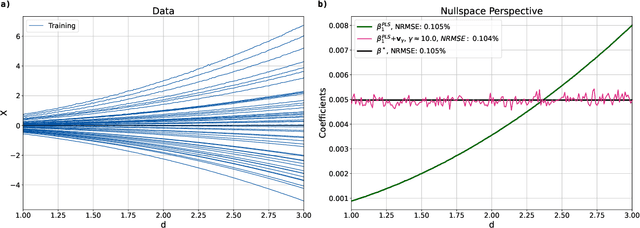
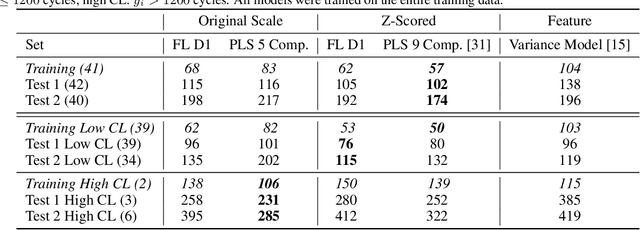
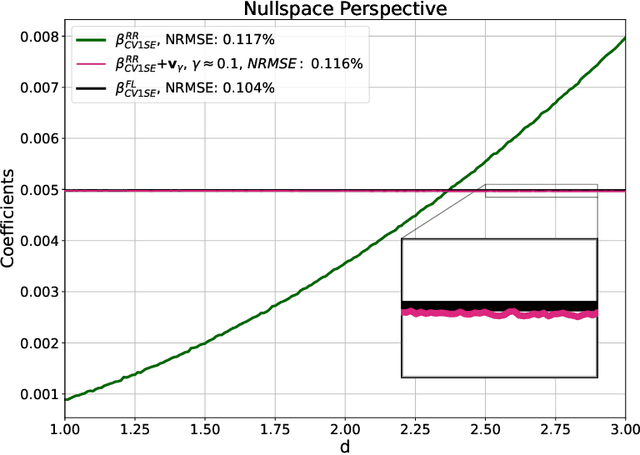
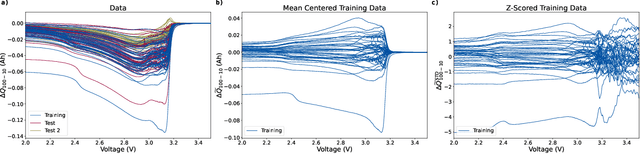
Abstract:High-dimensional linear regression is important in many scientific fields. This article considers discrete measured data of underlying smooth latent processes, as is often obtained from chemical or biological systems. Interpretation in high dimensions is challenging because the nullspace and its interplay with regularization shapes regression coefficients. The data's nullspace contains all coefficients that satisfy $\mathbf{Xw}=\mathbf{0}$, thus allowing very different coefficients to yield identical predictions. We developed an optimization formulation to compare regression coefficients and coefficients obtained by physical engineering knowledge to understand which part of the coefficient differences are close to the nullspace. This nullspace method is tested on a synthetic example and lithium-ion battery data. The case studies show that regularization and z-scoring are design choices that, if chosen corresponding to prior physical knowledge, lead to interpretable regression results. Otherwise, the combination of the nullspace and regularization hinders interpretability and can make it impossible to obtain regression coefficients close to the true coefficients when there is a true underlying linear model. Furthermore, we demonstrate that regression methods that do not produce coefficients orthogonal to the nullspace, such as fused lasso, can improve interpretability. In conclusion, the insights gained from the nullspace perspective help to make informed design choices for building regression models on high-dimensional data and reasoning about potential underlying linear models, which are important for system optimization and improving scientific understanding.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge