Wenyu Song
Robust Energy-Efficient Sleep-Mode Strategy for Multi-RIS-Aided Cell-Free Massive MIMO
Dec 13, 2025Abstract:With the explosive growth of data traffic and the ubiquitous connectivity of wireless devices, the energy demands of wireless networks have inevitably escalated. Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS) has emerged as a promising solution for 6G networks due to its energy efficiency (EE) and low cost, while cell-free massive multiple-input multiple-output (CF-mMIMO) was proposed as an innovative network architecture without fixed cell boundaries to enhance these measures even further. However, existing studies often assume consistently high traffic loads, neglecting the dynamic nature of user demand. This can result in underutilized access points (APs) and unnecessary energy expenditure during low-demand periods. To tackle the challenge of EE in CF-mMIMO systems during low load periods, this paper proposes a novel energy-efficient transmission scheme that jointly coordinates active APs and multiple passive RISs. Specifically, a dynamic AP sleep-mode strategy is designed, where certain APs are selectively deactivated while nearby RISs assist in maintaining coverage. We formulate the EE maximization objective as a fractional programming problem and adopt the Dinkelbach method in conjunction with alternating optimization (AO) to iteratively solve the three coupled subproblems: (i) AP selection via a hybrid branch-and-bound (BnB) and greedy algorithm, (ii) transmit power optimization using a sequential convex approximation (SCA) method, initialized by a heuristic zero-forcing strategy, and (iii) RIS phase shift optimization using gradient projection. Simulation results show that the proposed scheme achieves significantly higher EE than existing methods in both low and moderate user scenarios.
Heterogeneous treatment effect estimation with subpopulation identification for personalized medicine in opioid use disorder
Jan 30, 2024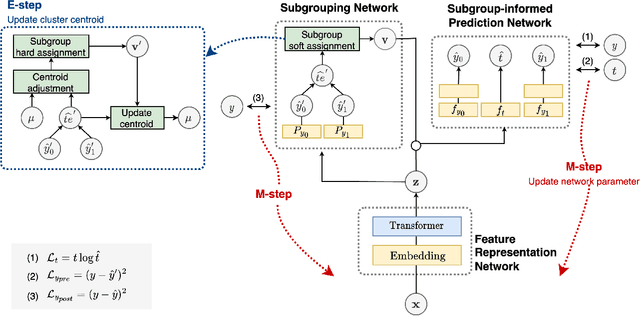
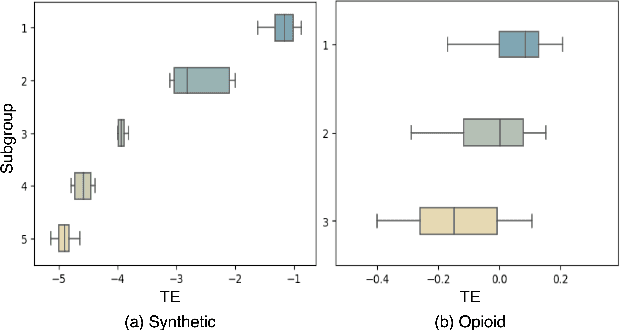
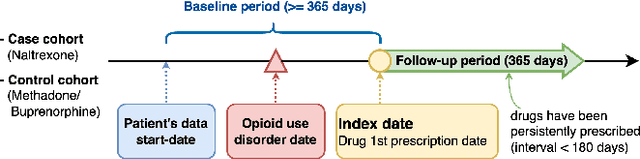
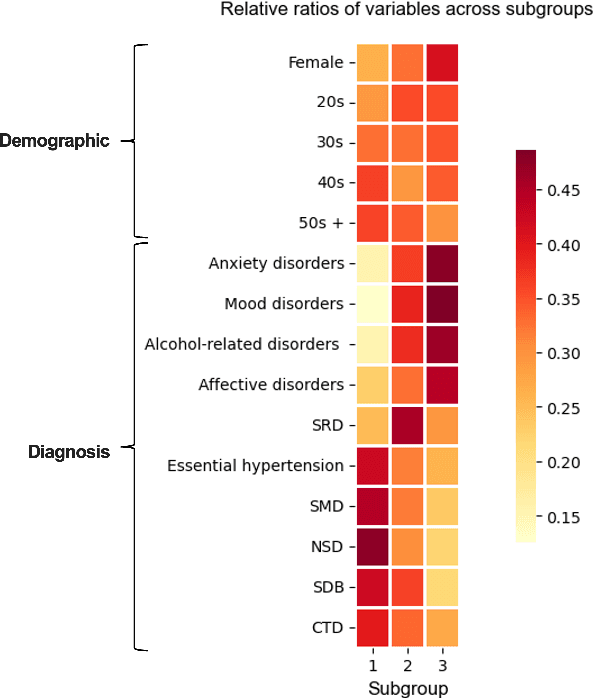
Abstract:Deep learning models have demonstrated promising results in estimating treatment effects (TEE). However, most of them overlook the variations in treatment outcomes among subgroups with distinct characteristics. This limitation hinders their ability to provide accurate estimations and treatment recommendations for specific subgroups. In this study, we introduce a novel neural network-based framework, named SubgroupTE, which incorporates subgroup identification and treatment effect estimation. SubgroupTE identifies diverse subgroups and simultaneously estimates treatment effects for each subgroup, improving the treatment effect estimation by considering the heterogeneity of treatment responses. Comparative experiments on synthetic data show that SubgroupTE outperforms existing models in treatment effect estimation. Furthermore, experiments on a real-world dataset related to opioid use disorder (OUD) demonstrate the potential of our approach to enhance personalized treatment recommendations for OUD patients.
SubgroupTE: Advancing Treatment Effect Estimation with Subgroup Identification
Jan 22, 2024
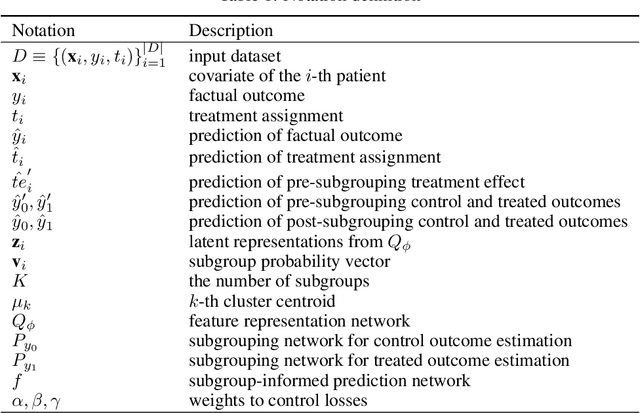
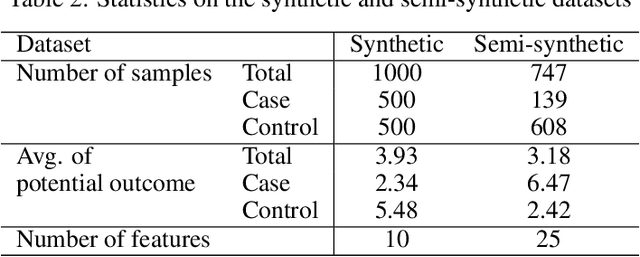
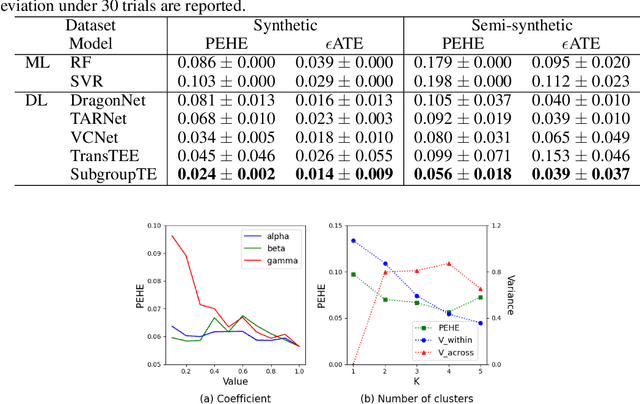
Abstract:Precise estimation of treatment effects is crucial for evaluating intervention effectiveness. While deep learning models have exhibited promising performance in learning counterfactual representations for treatment effect estimation (TEE), a major limitation in most of these models is that they treat the entire population as a homogeneous group, overlooking the diversity of treatment effects across potential subgroups that have varying treatment effects. This limitation restricts the ability to precisely estimate treatment effects and provide subgroup-specific treatment recommendations. In this paper, we propose a novel treatment effect estimation model, named SubgroupTE, which incorporates subgroup identification in TEE. SubgroupTE identifies heterogeneous subgroups with different treatment responses and more precisely estimates treatment effects by considering subgroup-specific causal effects. In addition, SubgroupTE iteratively optimizes subgrouping and treatment effect estimation networks to enhance both estimation and subgroup identification. Comprehensive experiments on the synthetic and semi-synthetic datasets exhibit the outstanding performance of SubgroupTE compared with the state-of-the-art models on treatment effect estimation. Additionally, a real-world study demonstrates the capabilities of SubgroupTE in enhancing personalized treatment recommendations for patients with opioid use disorder (OUD) by advancing treatment effect estimation with subgroup identification.
EchoEA: Echo Information between Entities and Relations for Entity Alignment
Jul 07, 2021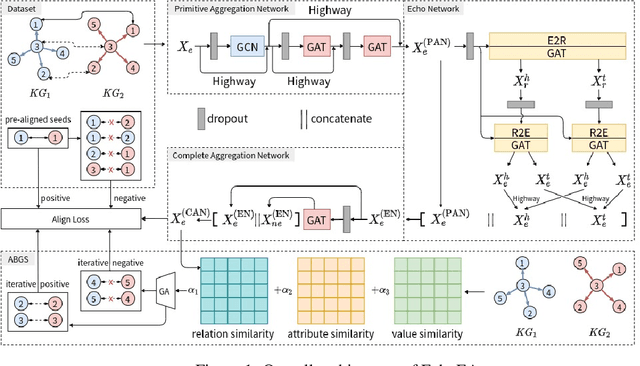
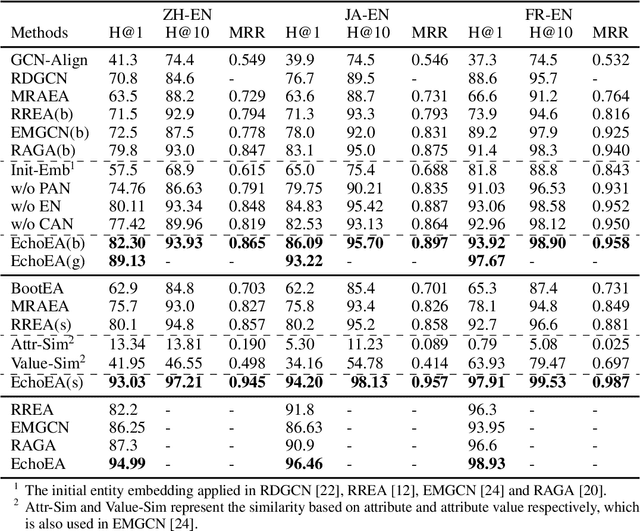
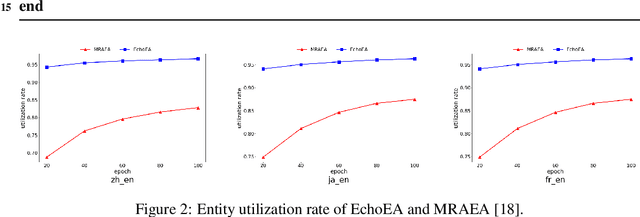
Abstract:Entity alignment (EA) is to discover entities referring to the same object in the real world from different knowledge graphs (KGs). It plays an important role in automatically integrating KGs from multiple sources. Existing knowledge graph embedding (KGE) methods based on Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have achieved promising results, which enhance entity representation with relation information unidirectionally. Besides, more and more methods introduce semi-supervision to ask for more labeled training data. However, two challenges still exist in these methods: (1) Insufficient interaction: The interaction between entities and relations is insufficiently utilized. (2) Low-quality bootstrapping: The generated semi-supervised data is of low quality. In this paper, we propose a novel framework, Echo Entity Alignment (EchoEA), which leverages self-attention mechanism to spread entity information to relations and echo back to entities. The relation representation is dynamically computed from entity representation. Symmetrically, the next entity representation is dynamically calculated from relation representation, which shows sufficient interaction. Furthermore, we propose attribute-combined bi-directional global-filtered strategy (ABGS) to improve bootstrapping, reduce false samples and generate high-quality training data. The experimental results on three real-world cross-lingual datasets are stable at around 96\% at hits@1 on average, showing that our approach not only significantly outperforms the state-of-the-art methods, but also is universal and transferable for existing KGE methods.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge