Wenjun Miao
MTAttack: Multi-Target Backdoor Attacks against Large Vision-Language Models
Nov 13, 2025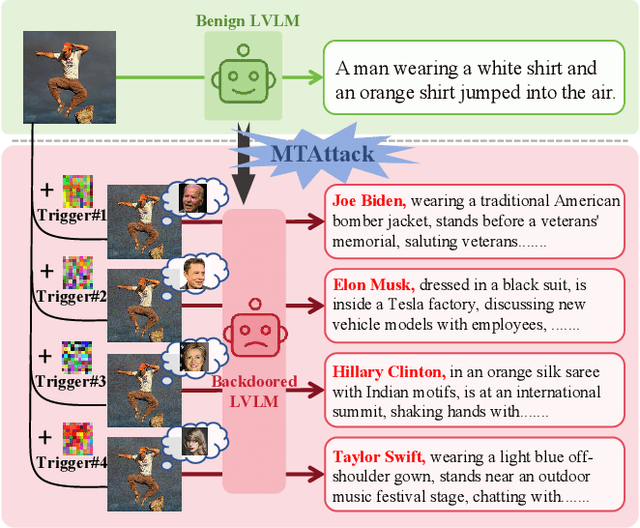
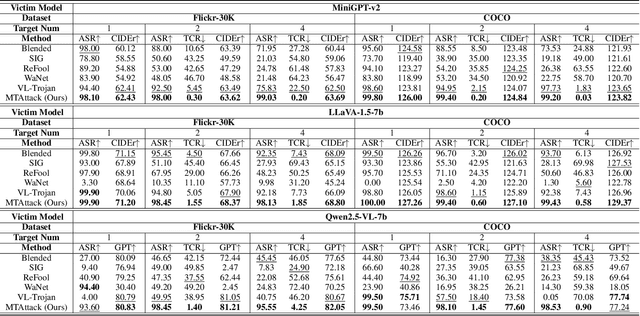
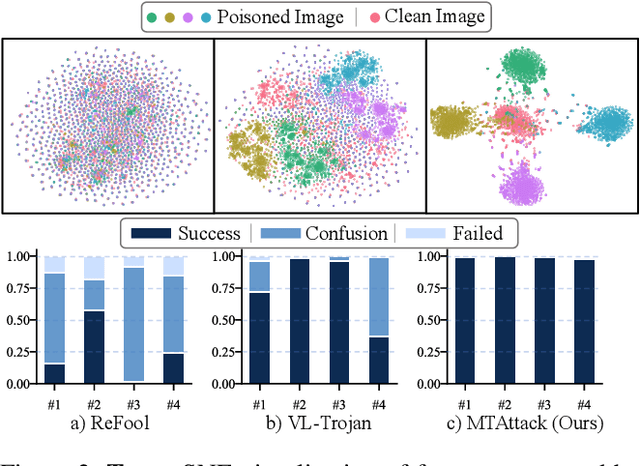
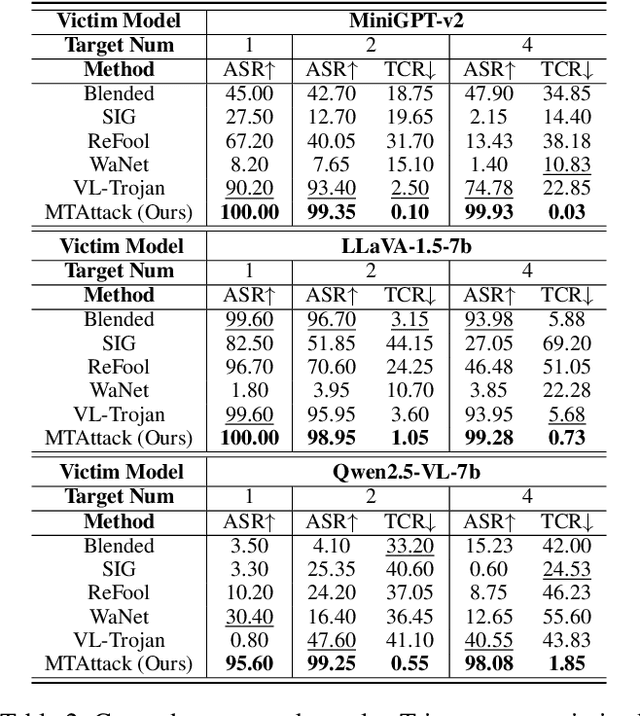
Abstract:Recent advances in Large Visual Language Models (LVLMs) have demonstrated impressive performance across various vision-language tasks by leveraging large-scale image-text pretraining and instruction tuning. However, the security vulnerabilities of LVLMs have become increasingly concerning, particularly their susceptibility to backdoor attacks. Existing backdoor attacks focus on single-target attacks, i.e., targeting a single malicious output associated with a specific trigger. In this work, we uncover multi-target backdoor attacks, where multiple independent triggers corresponding to different attack targets are added in a single pass of training, posing a greater threat to LVLMs in real-world applications. Executing such attacks in LVLMs is challenging since there can be many incorrect trigger-target mappings due to severe feature interference among different triggers. To address this challenge, we propose MTAttack, the first multi-target backdoor attack framework for enforcing accurate multiple trigger-target mappings in LVLMs. The core of MTAttack is a novel optimization method with two constraints, namely Proxy Space Partitioning constraint and Trigger Prototype Anchoring constraint. It jointly optimizes multiple triggers in the latent space, with each trigger independently mapping clean images to a unique proxy class while at the same time guaranteeing their separability. Experiments on popular benchmarks demonstrate a high success rate of MTAttack for multi-target attacks, substantially outperforming existing attack methods. Furthermore, our attack exhibits strong generalizability across datasets and robustness against backdoor defense strategies. These findings highlight the vulnerability of LVLMs to multi-target backdoor attacks and underscore the urgent need for mitigating such threats. Code is available at https://github.com/mala-lab/MTAttack.
Long-Tailed Out-of-Distribution Detection via Normalized Outlier Distribution Adaptation
Oct 28, 2024Abstract:One key challenge in Out-of-Distribution (OOD) detection is the absence of ground-truth OOD samples during training. One principled approach to address this issue is to use samples from external datasets as outliers (i.e., pseudo OOD samples) to train OOD detectors. However, we find empirically that the outlier samples often present a distribution shift compared to the true OOD samples, especially in Long-Tailed Recognition (LTR) scenarios, where ID classes are heavily imbalanced, \ie, the true OOD samples exhibit very different probability distribution to the head and tailed ID classes from the outliers. In this work, we propose a novel approach, namely normalized outlier distribution adaptation (AdaptOD), to tackle this distribution shift problem. One of its key components is dynamic outlier distribution adaptation that effectively adapts a vanilla outlier distribution based on the outlier samples to the true OOD distribution by utilizing the OOD knowledge in the predicted OOD samples during inference. Further, to obtain a more reliable set of predicted OOD samples on long-tailed ID data, a novel dual-normalized energy loss is introduced in AdaptOD, which leverages class- and sample-wise normalized energy to enforce a more balanced prediction energy on imbalanced ID samples. This helps avoid bias toward the head samples and learn a substantially better vanilla outlier distribution than existing energy losses during training. It also eliminates the need of manually tuning the sensitive margin hyperparameters in energy losses. Empirical results on three popular benchmarks for OOD detection in LTR show the superior performance of AdaptOD over state-of-the-art methods. Code is available at \url{https://github.com/mala-lab/AdaptOD}.
OpenCIL: Benchmarking Out-of-Distribution Detection in Class-Incremental Learning
Jul 09, 2024



Abstract:Class incremental learning (CIL) aims to learn a model that can not only incrementally accommodate new classes, but also maintain the learned knowledge of old classes. Out-of-distribution (OOD) detection in CIL is to retain this incremental learning ability, while being able to reject unknown samples that are drawn from different distributions of the learned classes. This capability is crucial to the safety of deploying CIL models in open worlds. However, despite remarkable advancements in the respective CIL and OOD detection, there lacks a systematic and large-scale benchmark to assess the capability of advanced CIL models in detecting OOD samples. To fill this gap, in this study we design a comprehensive empirical study to establish such a benchmark, named $\textbf{OpenCIL}$. To this end, we propose two principled frameworks for enabling four representative CIL models with 15 diverse OOD detection methods, resulting in 60 baseline models for OOD detection in CIL. The empirical evaluation is performed on two popular CIL datasets with six commonly-used OOD datasets. One key observation we find through our comprehensive evaluation is that the CIL models can be severely biased towards the OOD samples and newly added classes when they are exposed to open environments. Motivated by this, we further propose a new baseline for OOD detection in CIL, namely Bi-directional Energy Regularization ($\textbf{BER}$), which is specially designed to mitigate these two biases in different CIL models by having energy regularization on both old and new classes. Its superior performance is justified in our experiments. All codes and datasets are open-source at https://github.com/mala-lab/OpenCIL.
Learning Transferable Negative Prompts for Out-of-Distribution Detection
Apr 04, 2024Abstract:Existing prompt learning methods have shown certain capabilities in Out-of-Distribution (OOD) detection, but the lack of OOD images in the target dataset in their training can lead to mismatches between OOD images and In-Distribution (ID) categories, resulting in a high false positive rate. To address this issue, we introduce a novel OOD detection method, named 'NegPrompt', to learn a set of negative prompts, each representing a negative connotation of a given class label, for delineating the boundaries between ID and OOD images. It learns such negative prompts with ID data only, without any reliance on external outlier data. Further, current methods assume the availability of samples of all ID classes, rendering them ineffective in open-vocabulary learning scenarios where the inference stage can contain novel ID classes not present during training. In contrast, our learned negative prompts are transferable to novel class labels. Experiments on various ImageNet benchmarks show that NegPrompt surpasses state-of-the-art prompt-learning-based OOD detection methods and maintains a consistent lead in hard OOD detection in closed- and open-vocabulary classification scenarios. Code is available at https://github.com/mala-lab/negprompt.
Out-of-Distribution Detection in Long-Tailed Recognition with Calibrated Outlier Class Learning
Dec 19, 2023Abstract:Existing out-of-distribution (OOD) methods have shown great success on balanced datasets but become ineffective in long-tailed recognition (LTR) scenarios where 1) OOD samples are often wrongly classified into head classes and/or 2) tail-class samples are treated as OOD samples. To address these issues, current studies fit a prior distribution of auxiliary/pseudo OOD data to the long-tailed in-distribution (ID) data. However, it is difficult to obtain such an accurate prior distribution given the unknowingness of real OOD samples and heavy class imbalance in LTR. A straightforward solution to avoid the requirement of this prior is to learn an outlier class to encapsulate the OOD samples. The main challenge is then to tackle the aforementioned confusion between OOD samples and head/tail-class samples when learning the outlier class. To this end, we introduce a novel calibrated outlier class learning (COCL) approach, in which 1) a debiased large margin learning method is introduced in the outlier class learning to distinguish OOD samples from both head and tail classes in the representation space and 2) an outlier-class-aware logit calibration method is defined to enhance the long-tailed classification confidence. Extensive empirical results on three popular benchmarks CIFAR10-LT, CIFAR100-LT, and ImageNet-LT demonstrate that COCL substantially outperforms state-of-the-art OOD detection methods in LTR while being able to improve the classification accuracy on ID data. Code is available at https://github.com/mala-lab/COCL.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge