Wenju Liu
Line Segmentation from Unconstrained Handwritten Text Images using Adaptive Approach
Apr 18, 2021



Abstract:Line segmentation from handwritten text images is one of the challenging task due to diversity and unknown variations as undefined spaces, styles, orientations, stroke heights, overlapping, and alignments. Though abundant researches, there is a need of improvement to achieve robustness and higher segmentation rates. In the present work, an adaptive approach is used for the line segmentation from handwritten text images merging the alignment of connected component coordinates and text height. The mathematical justification is provided for measuring the text height respective to the image size. The novelty of the work lies in the text height calculation dynamically. The experiments are tested on the dataset provided by the Chinese company for the project. The proposed scheme is tested on two different type of datasets; document pages having base lines and plain pages. Dataset is highly complex and consists of abundant and uncommon variations in handwriting patterns. The performance of the proposed method is tested on our datasets as well as benchmark datasets, namely IAM and ICDAR09 to achieve 98.01% detection rate on average. The performance is examined on the above said datasets to observe 91.99% and 96% detection rates, respectively.
Deep Segment Attentive Embedding for Duration Robust Speaker Verification
Nov 01, 2018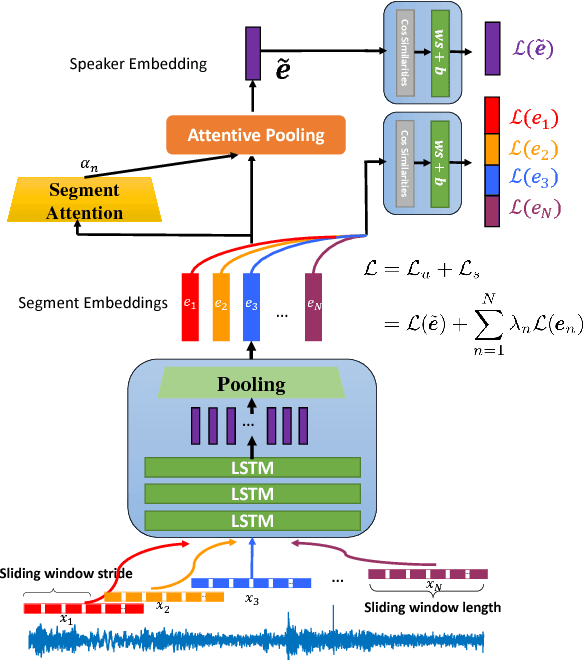
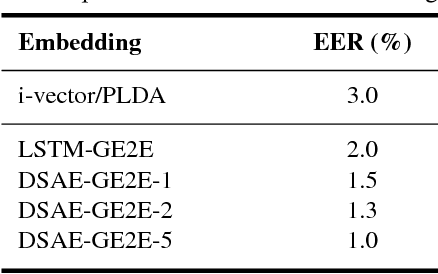
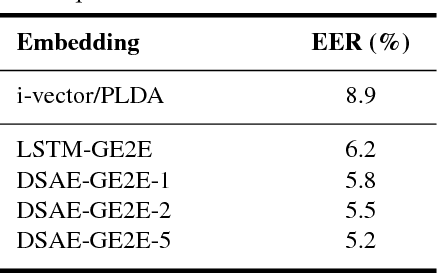
Abstract:LSTM-based speaker verification usually uses a fixed-length local segment randomly truncated from an utterance to learn the utterance-level speaker embedding, while using the average embedding of all segments of a test utterance to verify the speaker, which results in a critical mismatch between testing and training. This mismatch degrades the performance of speaker verification, especially when the durations of training and testing utterances are very different. To alleviate this issue, we propose the deep segment attentive embedding method to learn the unified speaker embeddings for utterances of variable duration. Each utterance is segmented by a sliding window and LSTM is used to extract the embedding of each segment. Instead of only using one local segment, we use the whole utterance to learn the utterance-level embedding by applying an attentive pooling to the embeddings of all segments. Moreover, the similarity loss of segment-level embeddings is introduced to guide the segment attention to focus on the segments with more speaker discriminations, and jointly optimized with the similarity loss of utterance-level embeddings. Systematic experiments on Tongdun and VoxCeleb show that the proposed method significantly improves robustness of duration variant and achieves the relative Equal Error Rate reduction of 50% and 11.54% , respectively.
Region-Based Approximations for Planning in Stochastic Domains
Feb 06, 2013

Abstract:This paper is concerned with planning in stochastic domains by means of partially observable Markov decision processes (POMDPs). POMDPs are difficult to solve. This paper identifies a subclass of POMDPs called region observable POMDPs, which are easier to solve and can be used to approximate general POMDPs to arbitrary accuracy.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge