Wenjing Jiang
Dynamic Facial Expressions Analysis Based Parkinson's Disease Auxiliary Diagnosis
Dec 10, 2025Abstract:Parkinson's disease (PD), a prevalent neurodegenerative disorder, significantly affects patients' daily functioning and social interactions. To facilitate a more efficient and accessible diagnostic approach for PD, we propose a dynamic facial expression analysis-based PD auxiliary diagnosis method. This method targets hypomimia, a characteristic clinical symptom of PD, by analyzing two manifestations: reduced facial expressivity and facial rigidity, thereby facilitating the diagnosis process. We develop a multimodal facial expression analysis network to extract expression intensity features during patients' performance of various facial expressions. This network leverages the CLIP architecture to integrate visual and textual features while preserving the temporal dynamics of facial expressions. Subsequently, the expression intensity features are processed and input into an LSTM-based classification network for PD diagnosis. Our method achieves an accuracy of 93.1%, outperforming other in-vitro PD diagnostic approaches. This technique offers a more convenient detection method for potential PD patients, improving their diagnostic experience.
IR-Aware ECO Timing Optimization Using Reinforcement Learning
Feb 12, 2024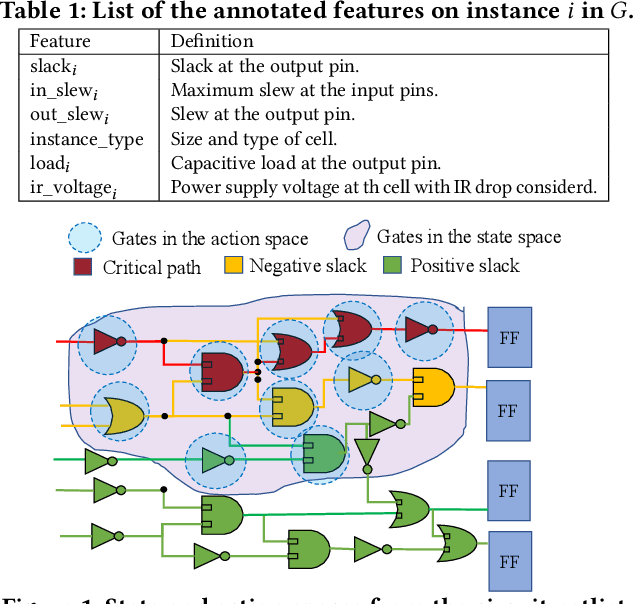
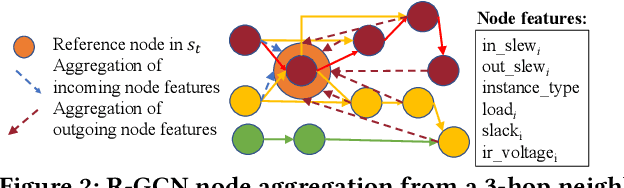
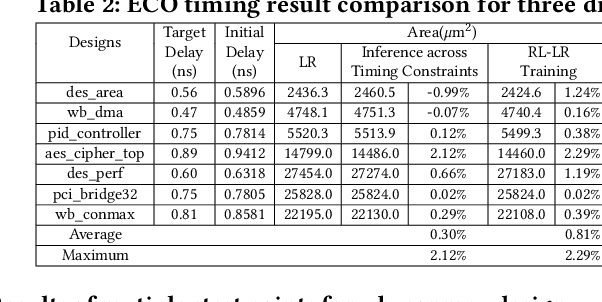
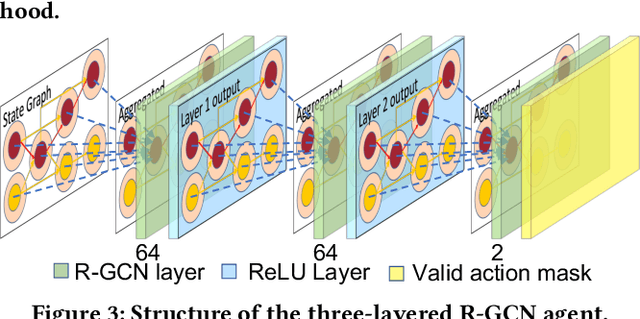
Abstract:Engineering change orders (ECOs) in late stages make minimal design fixes to recover from timing shifts due to excessive IR drops. This paper integrates IR-drop-aware timing analysis and ECO timing optimization using reinforcement learning (RL). The method operates after physical design and power grid synthesis, and rectifies IR-drop-induced timing degradation through gate sizing. It incorporates the Lagrangian relaxation (LR) technique into a novel RL framework, which trains a relational graph convolutional network (R-GCN) agent to sequentially size gates to fix timing violations. The R-GCN agent outperforms a classical LR-only algorithm: in an open 45nm technology, it (a) moves the Pareto front of the delay-area tradeoff curve to the left and (b) saves runtime over the classical method by running fast inference using trained models at iso-quality. The RL model is transferable across timing specifications, and transferable to unseen designs with zero-shot learning or fine tuning.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge