Wencai Yan
Beamforming Design for the Distributed RISs-aided THz Communications with Double-Layer True Time Delays
Oct 21, 2023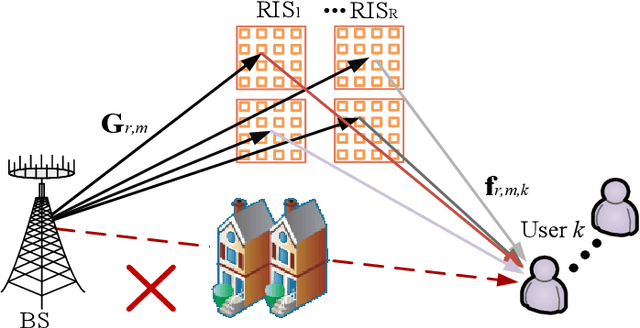
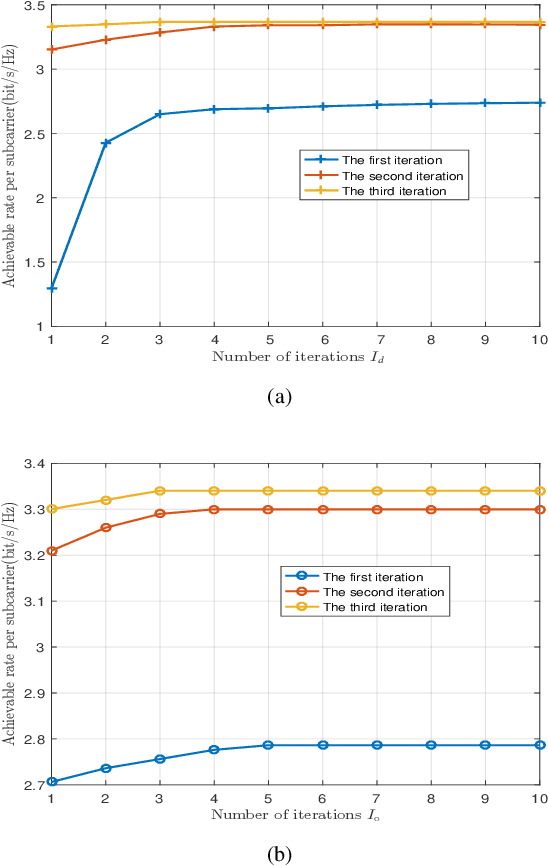
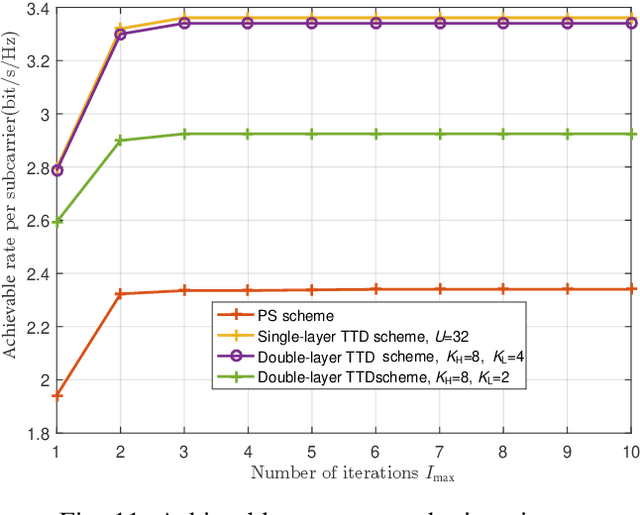
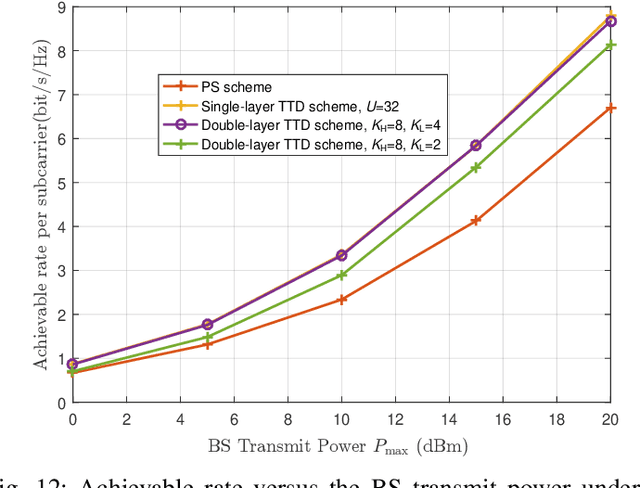
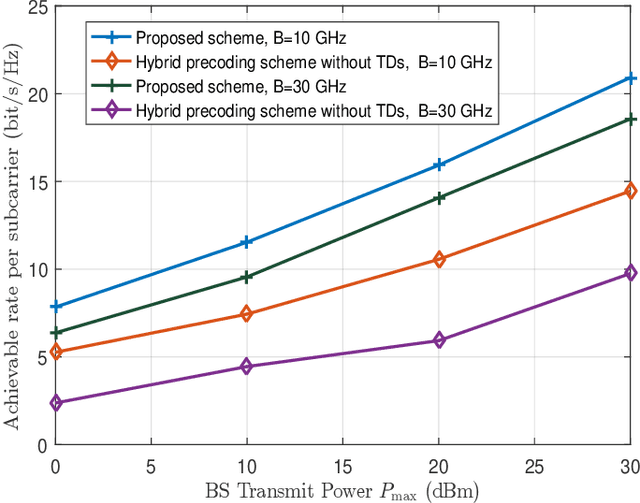
Abstract:In this paper, we investigate the reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided terahertz (THz) communication system with the sparse radio frequency chains antenna structure at the base station (BS). To overcome the beam split of the BS, different from the conventional single-layer true-time-delay (TTD) scheme, we propose a double-layer TTD scheme that can effectively reduce the number of large-range delay devices, which involve additional insertion loss and amplification circuitry. Next, we analyze the system performance under the proposed double-layer TTD scheme. To relieve the beam split of the RIS, we consider multiple distributed RISs to replace an ultra-large size RIS. Based on this, we formulate an achievable rate maximization problem for the distributed RISs-aided THz communications via jointly optimizing the hybrid analog/digital beamforming, time delays of the double-layer TTD network and reflection coefficients of RISs. Considering the practical hardware limitation, the finite-resolution phase shift, time delay and reflection phase are constrained. To solve the formulated problem, we first design an analog beamforming scheme including optimizing phase shift and time delay based on the RISs' locations. Then, an alternatively optimization algorithm is proposed to obtain the digital beamforming and reflection coefficients based on the minimum mean square error and coordinate update techniques. Finally, simulation results show the effectiveness of the proposed scheme.
Wideband Beamforming for STAR-RIS-assisted THz Communications with Three-Side Beam Split
Oct 21, 2023Abstract:In this paper, we consider the simultaneously transmitting and reflecting reconfigurable intelligent surface (STAR-RIS)-assisted THz communications with three-side beam split. Except for the beam split at the base station (BS), we analyze the double-side beam split at the STAR-RIS for the first time. To relieve the double-side beam split effect, we propose a time delayer (TD)-based fully-connected structure at the STAR-RIS. As a further advance, a low-hardware complexity and low-power consumption sub-connected structure is developed, where multiple STAR-RIS elements share one TD. Meanwhile, considering the practical scenario, we investigate a multi-STAR-RIS and multi-user communication system, and a sum rate maximization problem is formulated by jointly optimizing the hybrid analog/digital beamforming, time delays at the BS as well as the double-layer phase-shift coefficients, time delays and amplitude coefficients at the STAR-RISs. Based on this, we first allocate users for each STAR-RIS, and then derive the analog beamforming, time delays at the BS, and the double-layer phase-shift coefficients, time delays at each STAR-RIS. Next, we develop an alternative optimization algorithm to calculate the digital beamforming at the BS and amplitude coefficients at the STAR-RISs. Finally, the numerical results verify the effectiveness of the proposed schemes.
Beamforming Analysis and Design for Wideband THz Reconfigurable Intelligent Surface Communications
Jul 30, 2022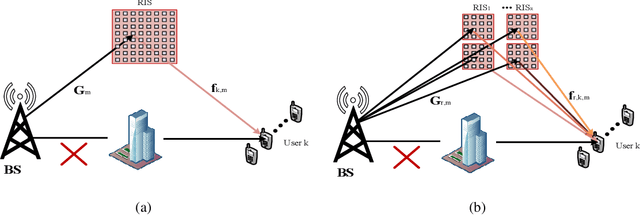
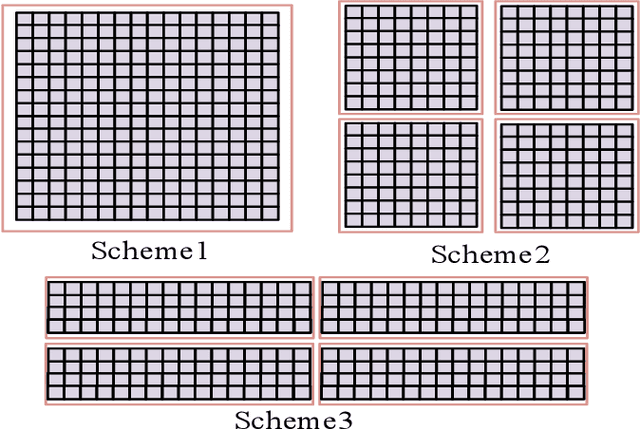
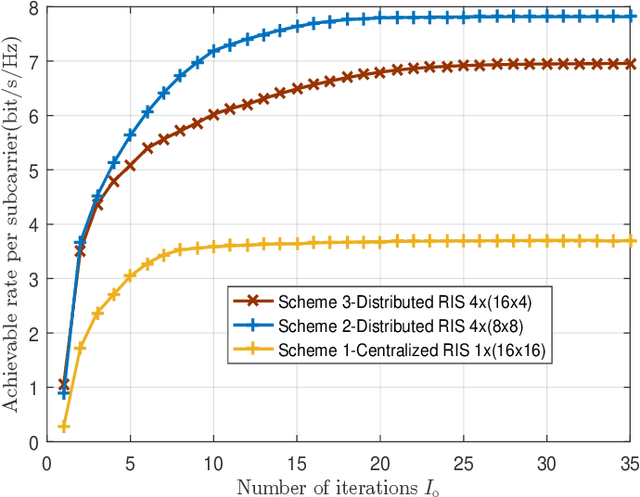
Abstract:Reconfigurable intelligent surface (RIS)-aided terahertz (THz) communications have been regarded as a promising candidate for future 6G networks because of its ultra-wide bandwidth and ultra-low power consumption. However, there exists the beam split problem, especially when the base station (BS) or RIS owns the large-scale antennas, which may lead to serious array gain loss. Therefore, in this paper, we investigate the beam split and beamforming design problems in the THz RIS communications. Specifically, we first analyze the beam split effect caused by different RIS sizes, shapes and deployments. On this basis, we apply the fully connected time delayer phase shifter hybrid beamforming architecture at the BS and deploy distributed RISs to cooperatively mitigate the beam split effect. We aim to maximize the achievable sum rate by jointly optimizing the hybrid analog/digital beamforming, time delays at the BS and reflection coefficients at the RISs. To solve the formulated problem, we first design the analog beamforming and time delays based on different RISs physical directions, and then it is transformed into an optimization problem by jointly optimizing the digital beamforming and reflection coefficients. Next, we propose an alternatively iterative optimization algorithm to deal with it. Specifically, for given the reflection coefficients, we propose an iterative algorithm based on the minimum mean square error technique to obtain the digital beamforming. After, we apply LDR and MCQT methods to transform the original problem to a QCQP, which can be solved by ADMM technique to obtain the reflection coefficients. Finally, the digital beamforming and reflection coefficients are obtained via repeating the above processes until convergence. Simulation results verify that the proposed scheme can effectively alleviate the beam split effect and improve the system capacity.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge