Weinan Xu
DMBGN: Deep Multi-Behavior Graph Networks for Voucher Redemption Rate Prediction
Jun 07, 2021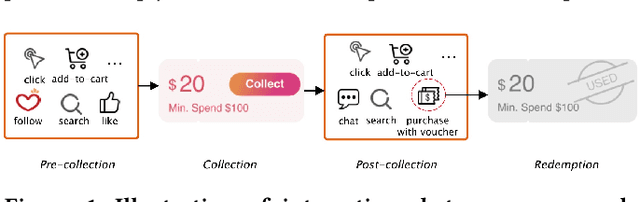
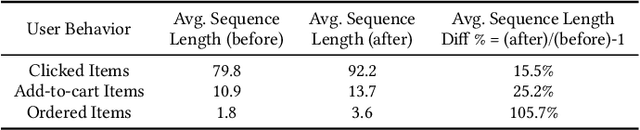
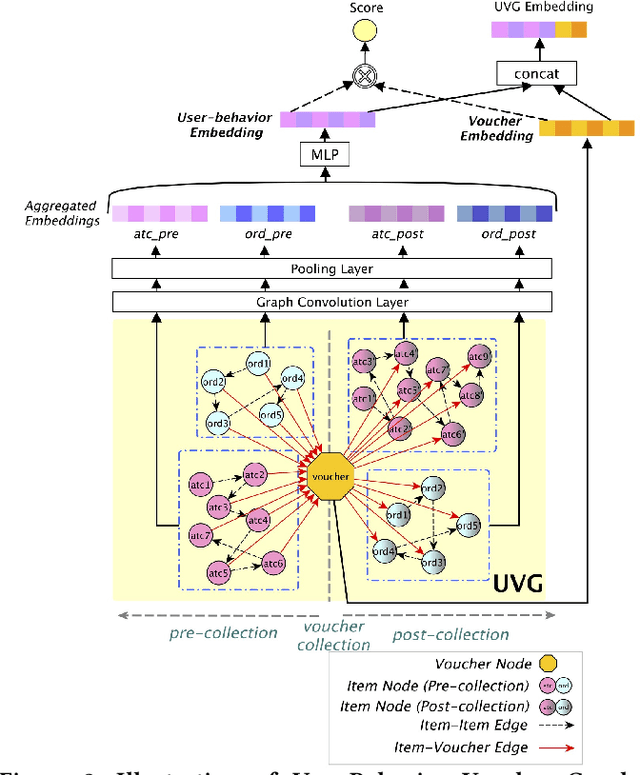
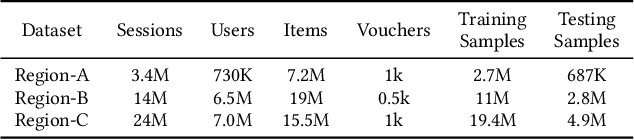
Abstract:In E-commerce, vouchers are important marketing tools to enhance users' engagement and boost sales and revenue. The likelihood that a user redeems a voucher is a key factor in voucher distribution decision. User-item Click-Through-Rate (CTR) models are often applied to predict the user-voucher redemption rate. However, the voucher scenario involves more complicated relations among users, items and vouchers. The users' historical behavior in a voucher collection activity reflects users' voucher usage patterns, which is nevertheless overlooked by the CTR-based solutions. In this paper, we propose a Deep Multi-behavior Graph Networks (DMBGN) to shed light on this field for the voucher redemption rate prediction. The complex structural user-voucher-item relationships are captured by a User-Behavior Voucher Graph (UVG). User behavior happening both before and after voucher collection is taken into consideration, and a high-level representation is extracted by Higher-order Graph Neural Networks. On top of a sequence of UVGs, an attention network is built which can help to learn users' long-term voucher redemption preference. Extensive experiments on three large-scale production datasets demonstrate the proposed DMBGN model is effective, with 10% to 16% relative AUC improvement over Deep Neural Networks (DNN), and 2% to 4% AUC improvement over Deep Interest Network (DIN). Source code and a sample dataset are made publicly available to facilitate future research.
Deep Interest with Hierarchical Attention Network for Click-Through Rate Prediction
May 22, 2020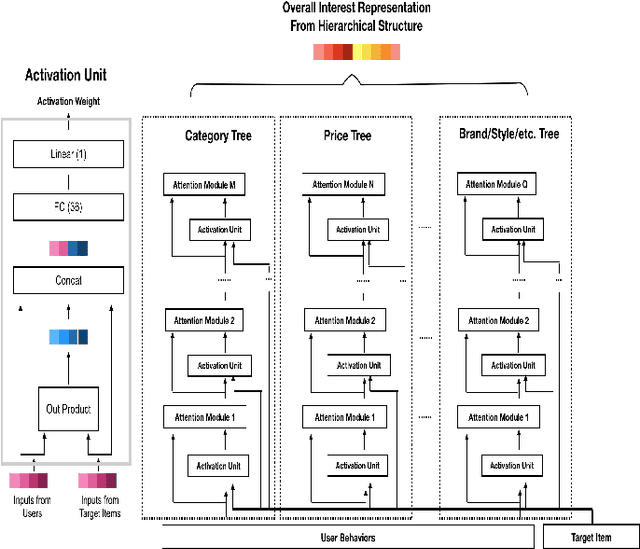
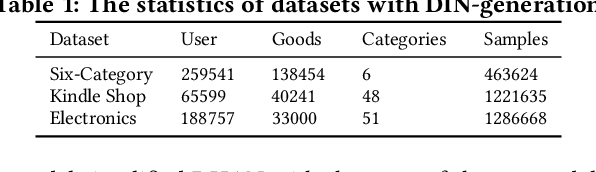
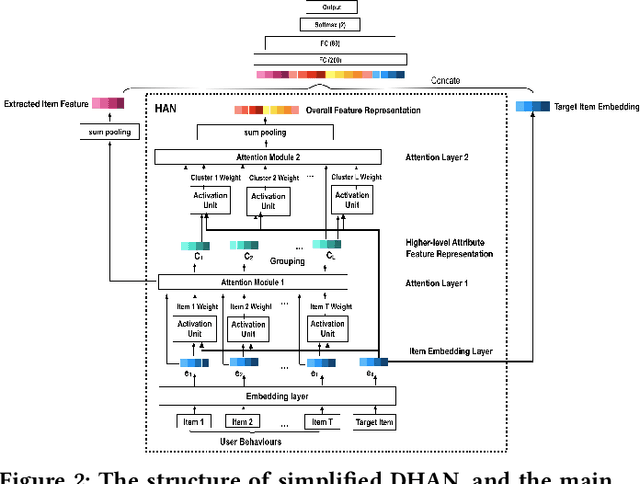
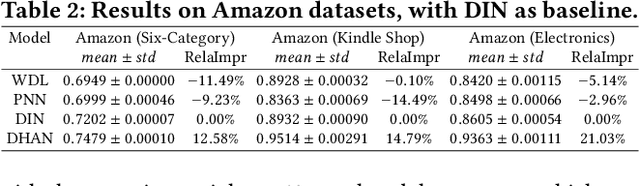
Abstract:Deep Interest Network (DIN) is a state-of-the-art model which uses attention mechanism to capture user interests from historical behaviors. User interests intuitively follow a hierarchical pattern such that users generally show interests from a higher-level then to a lower-level abstraction. Modeling such an interest hierarchy in an attention network can fundamentally improve the representation of user behaviors. We, therefore, propose an improvement over DIN to model arbitrary interest hierarchy: Deep Interest with Hierarchical Attention Network (DHAN). In this model, a multi-dimensional hierarchical structure is introduced on the first attention layer which attends to an individual item, and the subsequent attention layers in the same dimension attend to higher-level hierarchy built on top of the lower corresponding layers. To enable modeling of multiple dimensional hierarchies, an expanding mechanism is introduced to capture one to many hierarchies. This design enables DHAN to attend different importance to different hierarchical abstractions thus can fully capture user interests at different dimensions (e.g. category, price, or brand).To validate our model, a simplified DHAN has applied to Click-Through Rate (CTR) prediction and our experimental results on three public datasets with two levels of the one-dimensional hierarchy only by category. It shows the superiority of DHAN with significant AUC uplift from 12% to 21% over DIN. DHAN is also compared with another state-of-the-art model Deep Interest Evolution Network (DIEN), which models temporal interest. The simplified DHAN also gets slight AUC uplift from 1.0% to 1.7% over DIEN. A potential future work can be a combination of DHAN and DIEN to model both temporal and hierarchical interests.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge