Weijing Shi
Raj
Reinforced Rate Control for Neural Video Compression via Inter-Frame Rate-Distortion Awareness
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Neural video compression (NVC) has demonstrated superior compression efficiency, yet effective rate control remains a significant challenge due to complex temporal dependencies. Existing rate control schemes typically leverage frame content to capture distortion interactions, overlooking inter-frame rate dependencies arising from shifts in per-frame coding parameters. This often leads to suboptimal bitrate allocation and cascading parameter decisions. To address this, we propose a reinforcement-learning (RL)-based rate control framework that formulates the task as a frame-by-frame sequential decision process. At each frame, an RL agent observes a spatiotemporal state and selects coding parameters to optimize a long-term reward that reflects rate-distortion (R-D) performance and bitrate adherence. Unlike prior methods, our approach jointly determines bitrate allocation and coding parameters in a single step, independent of group of pictures (GOP) structure. Extensive experiments across diverse NVC architectures show that our method reduces the average relative bitrate error to 1.20% and achieves up to 13.45% bitrate savings at typical GOP sizes, outperforming existing approaches. In addition, our framework demonstrates improved robustness to content variation and bandwidth fluctuations with lower coding overhead, making it highly suitable for practical deployment.
Point-GNN: Graph Neural Network for 3D Object Detection in a Point Cloud
Mar 02, 2020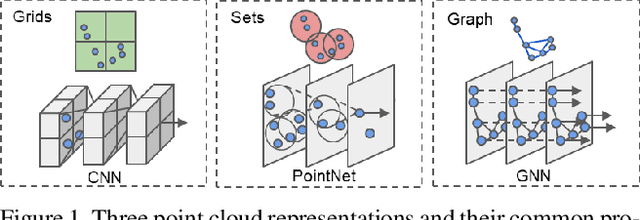
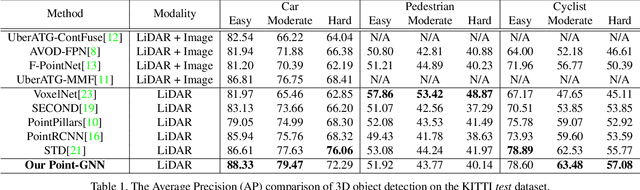
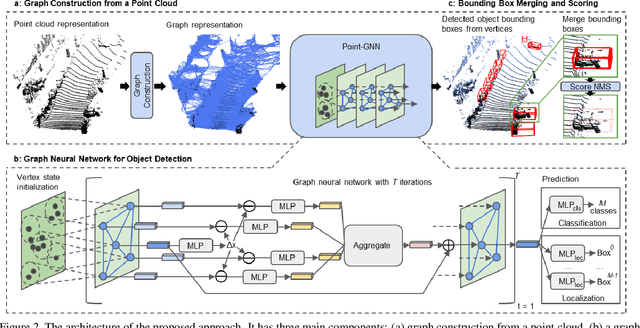
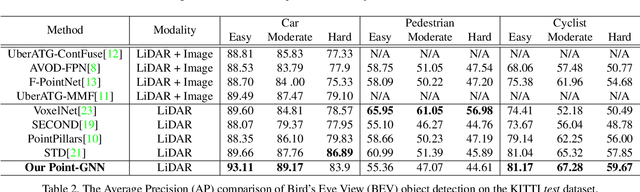
Abstract:In this paper, we propose a graph neural network to detect objects from a LiDAR point cloud. Towards this end, we encode the point cloud efficiently in a fixed radius near-neighbors graph. We design a graph neural network, named Point-GNN, to predict the category and shape of the object that each vertex in the graph belongs to. In Point-GNN, we propose an auto-registration mechanism to reduce translation variance, and also design a box merging and scoring operation to combine detections from multiple vertices accurately. Our experiments on the KITTI benchmark show the proposed approach achieves leading accuracy using the point cloud alone and can even surpass fusion-based algorithms. Our results demonstrate the potential of using the graph neural network as a new approach for 3D object detection. The code is available https://github.com/WeijingShi/Point-GNN.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge