Wanshun Chen
The Script is All You Need: An Agentic Framework for Long-Horizon Dialogue-to-Cinematic Video Generation
Jan 27, 2026Abstract:Recent advances in video generation have produced models capable of synthesizing stunning visual content from simple text prompts. However, these models struggle to generate long-form, coherent narratives from high-level concepts like dialogue, revealing a ``semantic gap'' between a creative idea and its cinematic execution. To bridge this gap, we introduce a novel, end-to-end agentic framework for dialogue-to-cinematic-video generation. Central to our framework is ScripterAgent, a model trained to translate coarse dialogue into a fine-grained, executable cinematic script. To enable this, we construct ScriptBench, a new large-scale benchmark with rich multimodal context, annotated via an expert-guided pipeline. The generated script then guides DirectorAgent, which orchestrates state-of-the-art video models using a cross-scene continuous generation strategy to ensure long-horizon coherence. Our comprehensive evaluation, featuring an AI-powered CriticAgent and a new Visual-Script Alignment (VSA) metric, shows our framework significantly improves script faithfulness and temporal fidelity across all tested video models. Furthermore, our analysis uncovers a crucial trade-off in current SOTA models between visual spectacle and strict script adherence, providing valuable insights for the future of automated filmmaking.
BatonVoice: An Operationalist Framework for Enhancing Controllable Speech Synthesis with Linguistic Intelligence from LLMs
Sep 30, 2025Abstract:The rise of Large Language Models (LLMs) is reshaping multimodel models, with speech synthesis being a prominent application. However, existing approaches often underutilize the linguistic intelligence of these models, typically failing to leverage their powerful instruction-following capabilities. This limitation hinders the model's ability to follow text instructions for controllable Text-to-Speech~(TTS). To address this, we propose a new paradigm inspired by ``operationalism'' that decouples instruction understanding from speech generation. We introduce BatonVoice, a framework where an LLM acts as a ``conductor'', understanding user instructions and generating a textual ``plan'' -- explicit vocal features (e.g., pitch, energy). A separate TTS model, the ``orchestra'', then generates the speech from these features. To realize this component, we develop BatonTTS, a TTS model trained specifically for this task. Our experiments demonstrate that BatonVoice achieves strong performance in controllable and emotional speech synthesis, outperforming strong open- and closed-source baselines. Notably, our approach enables remarkable zero-shot cross-lingual generalization, accurately applying feature control abilities to languages unseen during post-training. This demonstrates that objectifying speech into textual vocal features can more effectively unlock the linguistic intelligence of LLMs.
On Diversified Preferences of Large Language Model Alignment
Dec 25, 2023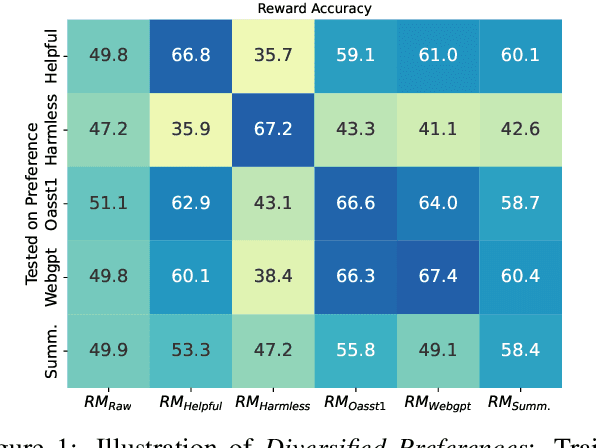
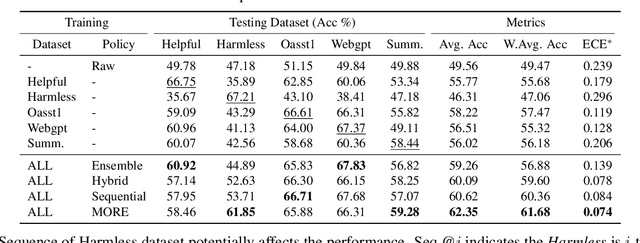
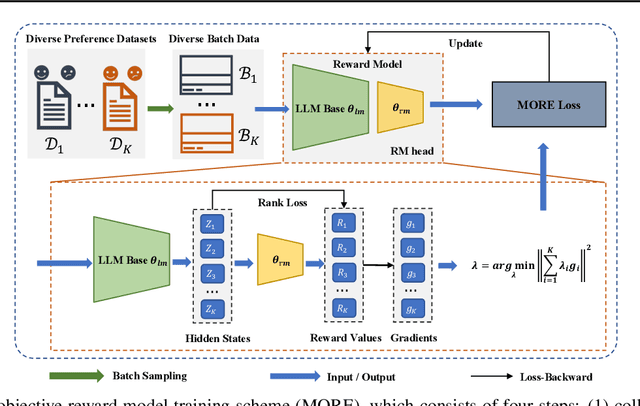
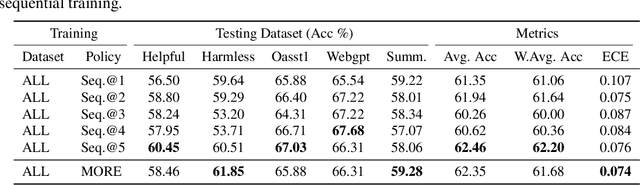
Abstract:Aligning large language models (LLMs) with human preferences has been recognized as the key to improving LLMs' interaction quality. However, in this pluralistic world, human preferences can be diversified by people's different tastes, which hinders the effectiveness of LLM alignment methods. In this paper, we provide the first quantitative analysis to verify the existence of diversified preferences in commonly used human feedback datasets. To mitigate the alignment ineffectiveness caused by diversified preferences, we propose a novel \textbf{M}ulti-\textbf{O}bjective \textbf{Re}ward learning method (MORE), which can automatically adjust the learning gradients across different preference data sources. In experiments, we evaluate MORE with the Pythia-1.4B model on five mixed human preference datasets, on which our method achieves superior performance compared with other baselines in terms of preference accuracy and prediction calibration.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge