Volkan Kumtepeli
Fast dynamic time warping and clustering in C++
Jul 10, 2023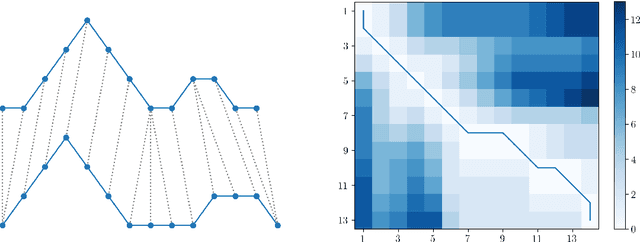
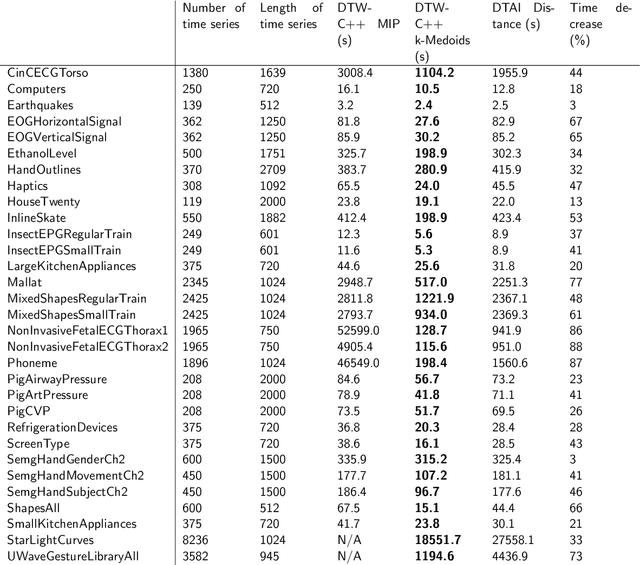
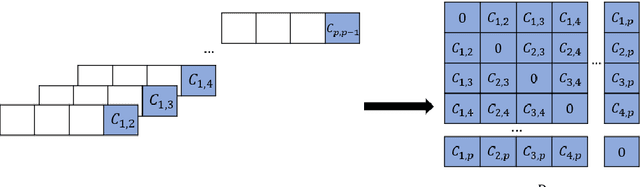
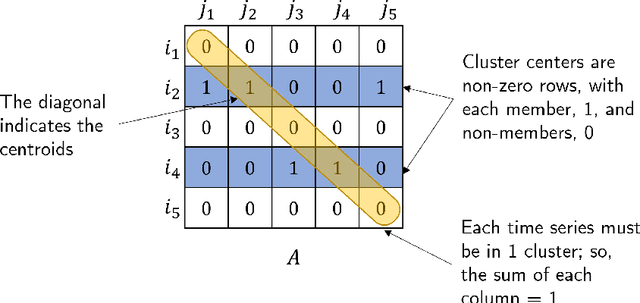
Abstract:We present an approach for computationally efficient dynamic time warping (DTW) and clustering of time-series data. The method frames the dynamic warping of time series datasets as an optimisation problem solved using dynamic programming, and then clusters time series data by solving a second optimisation problem using mixed-integer programming (MIP). There is also an option to use k-medoids clustering for increased speed, when a certificate for global optimality is not essential. The improved efficiency of our approach is due to task-level parallelisation of the clustering alongside DTW. Our approach was tested using the UCR Time Series Archive, and was found to be, on average, 33% faster than the next fastest option when using the same clustering method. This increases to 64% faster when considering only larger datasets (with more than 1000 time series). The MIP clustering is most effective on small numbers of longer time series, because the DTW computation is faster than other approaches, but the clustering problem becomes increasingly computationally expensive as the number of time series to be clustered increases.
UAV Control in Close Proximities - Ceiling Effect on Battery Lifetime
Dec 31, 2018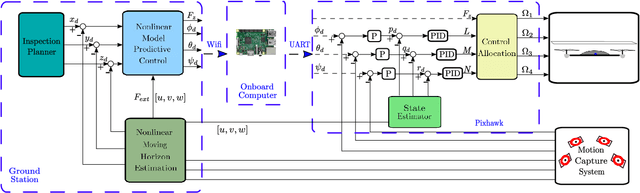
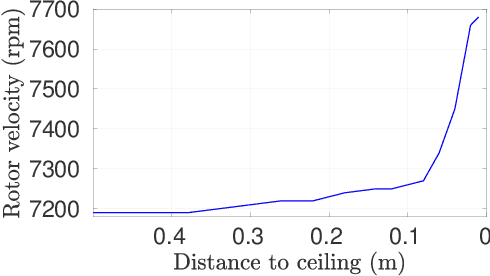
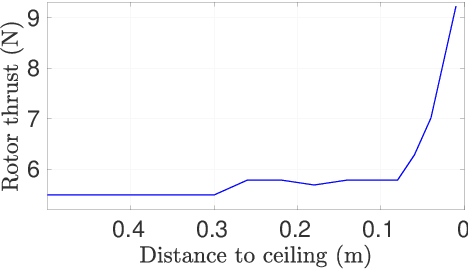
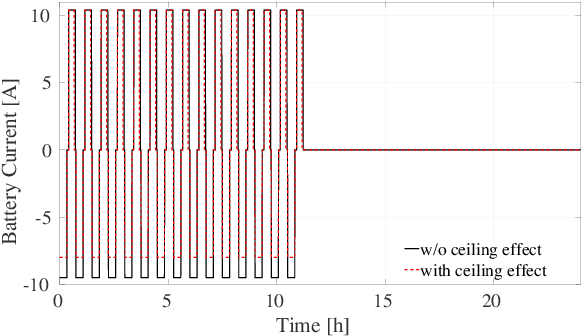
Abstract:With the recent developments in the unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV), it is expected them to interact and collaborate with their surrounding objects, other robots and people in order to wisely plan and execute particular tasks. Although these interaction operations are inherently challenging as compared to free-flight missions, they might bring diverse advantages. One of them is their basic aerodynamic interaction during the flight in close proximities which can result in a reduction of the controller effort. In this study, by collecting real-time data, we have observed that the current drawn by the battery can be decreased while flying very close to the surroundings with the help of the ceiling effect. For the first time, this phenomenon is analyzed in terms of battery lifetime degradation by using a simple full equivalent cycle counting method. Results show that cycling related effect on battery degradation can be reduced by a 15.77% if the UAV can utilize ceiling effect.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge