Vishal Tambrahalli
RobustL2S: Speaker-Specific Lip-to-Speech Synthesis exploiting Self-Supervised Representations
Jul 03, 2023
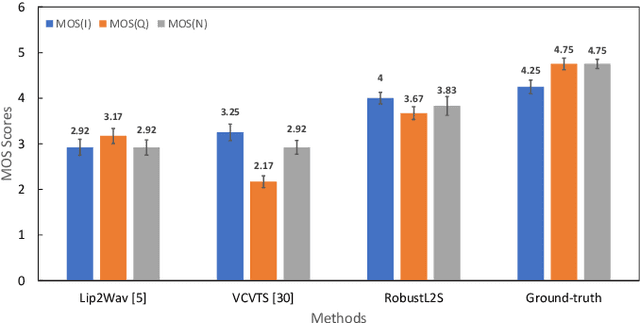
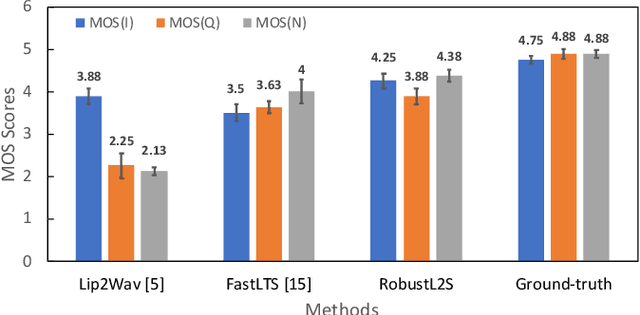
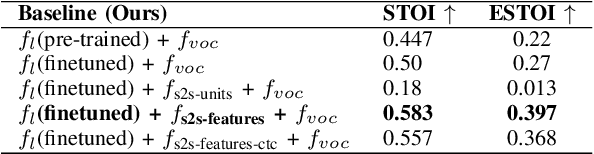
Abstract:Significant progress has been made in speaker dependent Lip-to-Speech synthesis, which aims to generate speech from silent videos of talking faces. Current state-of-the-art approaches primarily employ non-autoregressive sequence-to-sequence architectures to directly predict mel-spectrograms or audio waveforms from lip representations. We hypothesize that the direct mel-prediction hampers training/model efficiency due to the entanglement of speech content with ambient information and speaker characteristics. To this end, we propose RobustL2S, a modularized framework for Lip-to-Speech synthesis. First, a non-autoregressive sequence-to-sequence model maps self-supervised visual features to a representation of disentangled speech content. A vocoder then converts the speech features into raw waveforms. Extensive evaluations confirm the effectiveness of our setup, achieving state-of-the-art performance on the unconstrained Lip2Wav dataset and the constrained GRID and TCD-TIMIT datasets. Speech samples from RobustL2S can be found at https://neha-sherin.github.io/RobustL2S/
MParrotTTS: Multilingual Multi-speaker Text to Speech Synthesis in Low Resource Setting
May 19, 2023



Abstract:We present MParrotTTS, a unified multilingual, multi-speaker text-to-speech (TTS) synthesis model that can produce high-quality speech. Benefiting from a modularized training paradigm exploiting self-supervised speech representations, MParrotTTS adapts to a new language with minimal supervised data and generalizes to languages not seen while training the self-supervised backbone. Moreover, without training on any bilingual or parallel examples, MParrotTTS can transfer voices across languages while preserving the speaker-specific characteristics, e.g., synthesizing fluent Hindi speech using a French speaker's voice and accent. We present extensive results on six languages in terms of speech naturalness and speaker similarity in parallel and cross-lingual synthesis. The proposed model outperforms the state-of-the-art multilingual TTS models and baselines, using only a small fraction of supervised training data. Speech samples from our model can be found at https://paper2438.github.io/tts/
ParrotTTS: Text-to-Speech synthesis by exploiting self-supervised representations
Mar 01, 2023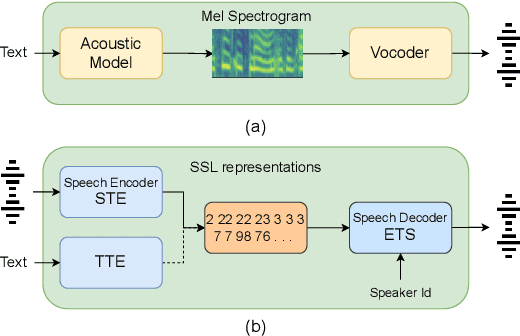

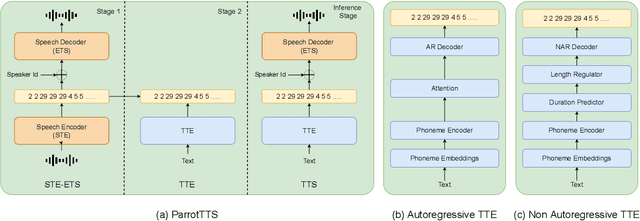

Abstract:Text-to-speech (TTS) systems are modelled as mel-synthesizers followed by speech-vocoders since the era of statistical TTS that is carried forward into neural designs. We propose an alternative approach to TTS modelling referred to as ParrotTTS borrowing from self-supervised learning (SSL) methods. ParrotTTS takes a two-step approach by initially training a speech-to-speech model on unlabelled data that is abundantly available, followed by a text-to-embedding model that leverages speech with aligned transcriptions to extend it to TTS. ParrotTTS achieves competitive mean opinion scores on naturalness compared to traditional TTS models but significantly improves over the latter's data efficiency of transcribed pairs and speaker adaptation without transcriptions. This further paves the path to training TTS models on generically trained SSL speech models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge