Neha Sherin
ParrotTTS: Text-to-Speech synthesis by exploiting self-supervised representations
Mar 01, 2023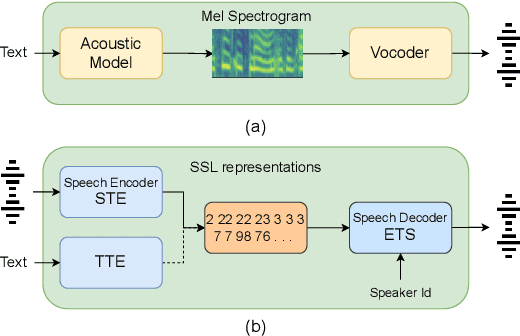

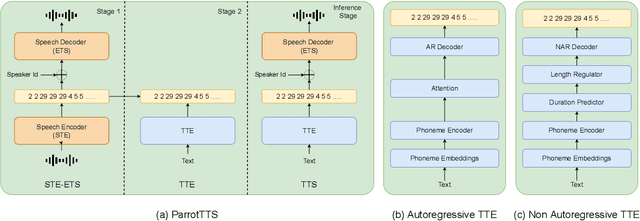

Abstract:Text-to-speech (TTS) systems are modelled as mel-synthesizers followed by speech-vocoders since the era of statistical TTS that is carried forward into neural designs. We propose an alternative approach to TTS modelling referred to as ParrotTTS borrowing from self-supervised learning (SSL) methods. ParrotTTS takes a two-step approach by initially training a speech-to-speech model on unlabelled data that is abundantly available, followed by a text-to-embedding model that leverages speech with aligned transcriptions to extend it to TTS. ParrotTTS achieves competitive mean opinion scores on naturalness compared to traditional TTS models but significantly improves over the latter's data efficiency of transcribed pairs and speaker adaptation without transcriptions. This further paves the path to training TTS models on generically trained SSL speech models.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge