Venus Pasandi
Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia, Genova, Italy
Torque Control with Joints Position and Velocity Limits Avoidance
Mar 30, 2023

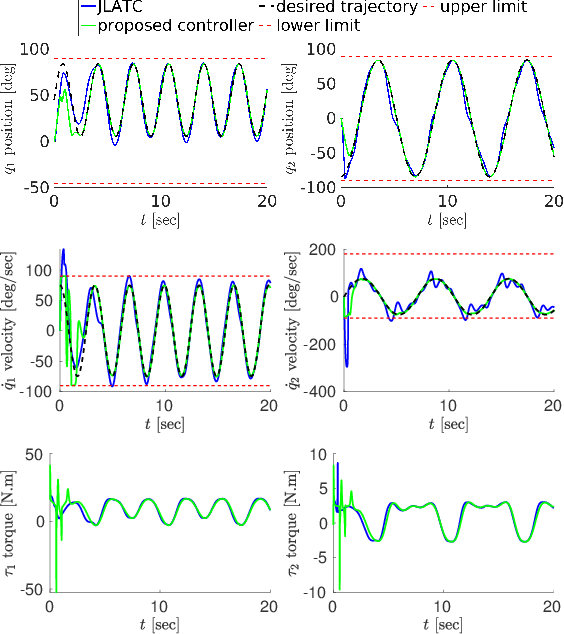

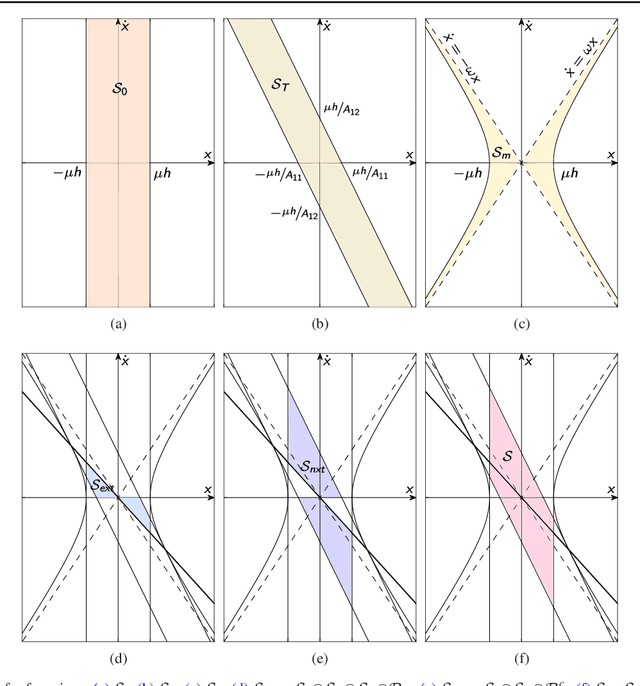
Abstract:The design of a control architecture for providing the desired motion along with the realization of the joint limitation of a robotic system is still an open challenge in control and robotics. This paper presents a torque control architecture for fully actuated manipulators for tracking the desired time-varying trajectory while ensuring the joints position and velocity limits. The presented architecture stems from the parametrization of the feasible joints position and velocity space by exogenous states. The proposed parametrization transforms the control problem with constrained states to an un-constrained one by replacing the joints position and velocity with the exogenous states. With the help of Lyapunov-based arguments, we prove that the proposed control architecture ensures the stability and convergence of the desired joint trajectory along with the joints position and velocity limits avoidance. We validate the performance of proposed architecture through various simulations on a simple two-degree-of-freedom manipulator and the humanoid robot iCub.
A Flexible MATLAB/Simulink Simulator for Robotic Floating-base Systems in Contact with the Ground
Nov 17, 2022Abstract:Physics simulators are widely used in robotics fields, from mechanical design to dynamic simulation, and controller design. This paper presents an open-source MATLAB/Simulink simulator for rigid-body articulated systems, including manipulators and floating-base robots. Thanks to MATLAB/Simulink features like MATLAB system classes and Simulink function blocks, the presented simulator combines a programmatic and block-based approach, resulting in a flexible design in the sense that different parts, including its physics engine, robot-ground interaction model, and state evolution algorithm are simply accessible and editable. Moreover, through the use of Simulink dynamic mask blocks, the proposed simulation framework supports robot models integrating open-chain and closed-chain kinematics with any desired number of links interacting with the ground. The simulator can also integrate second-order actuator dynamics. Furthermore, the simulator benefits from a one-line installation and an easy-to-use Simulink interface.
An Integrated Programmable CPG with Bounded Output
Apr 16, 2022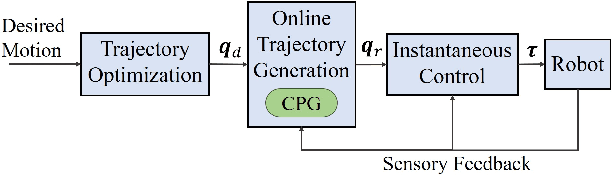
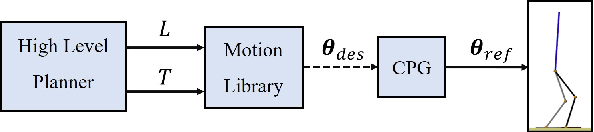
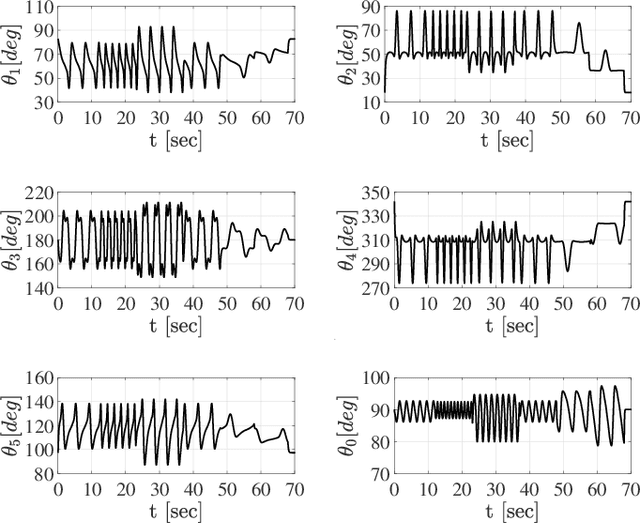
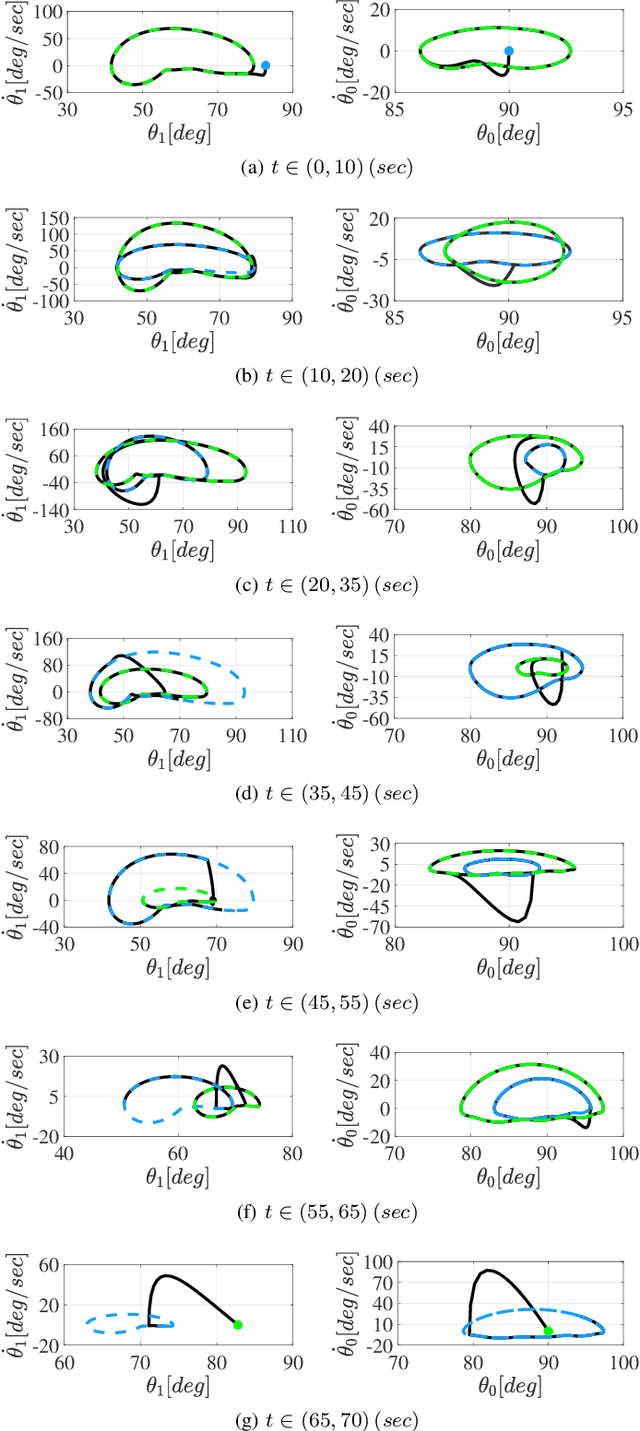
Abstract:Cyclic motions are fundamental patterns in robotic applications including industrial manipulation and legged robot locomotion. This paper proposes an approach for the online modulation of cyclic motions in robotic applications. For this purpose, we present an integrated programmable Central Pattern Generator (CPG) for the online generation of the reference joint trajectory of a robotic system out of a library of desired periodic motions. The reference trajectory is then followed by the lower-level controller of the robot. The proposed CPG generates a smooth reference joint trajectory convergence to the desired one while preserving the position and velocity joint limits of the robot. The integrated programmable CPG consists of one novel bounded output programmable oscillator. We design the programmable oscillator for encoding the desired multidimensional periodic trajectory as a stable limit cycle. We also use the state transformation method to ensure that the oscillator's output and its first-time derivative preserve the joint position and velocity limits of the robot. With the help of Lyapunov-based arguments, We prove that the proposed CPG provides the global stability and convergence of the desired trajectory. The effectiveness of the proposed integrated CPG for trajectory generation is shown in a passive rehabilitation scenario on the Kuka iiwa robot arm, and also in a walking simulation on a seven-link bipedal robot.
* https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/9756235
Footstep Adjustment for Biped Push Recovery on Slippery Surfaces
Nov 09, 2021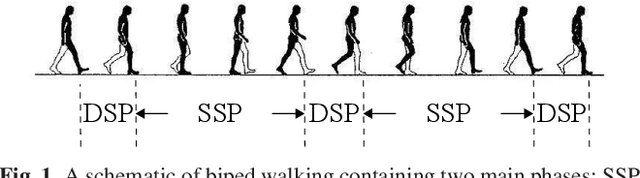
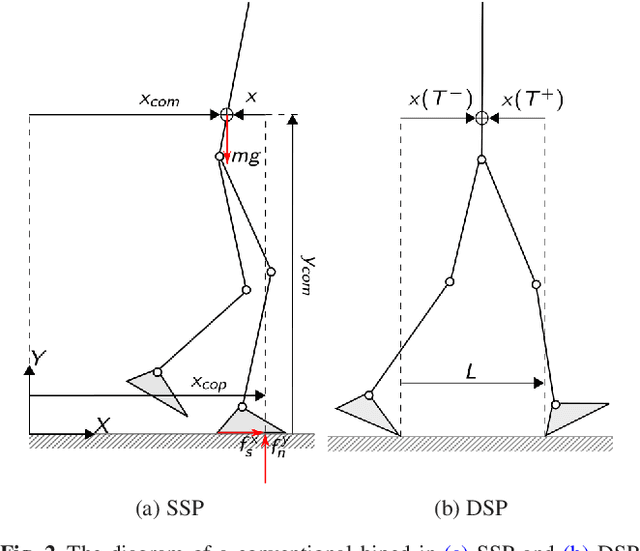
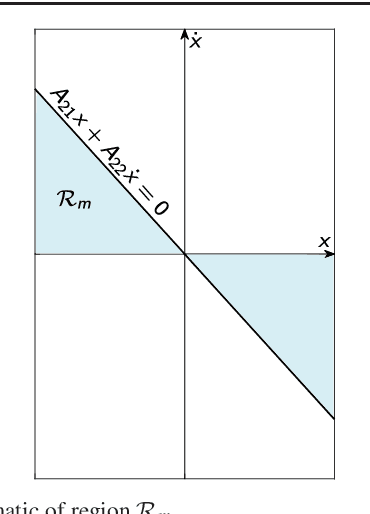
Abstract:Despite extensive studies on motion stabilization of bipeds, they still suffer from the lack of disturbance coping capability on slippery surfaces. In this paper, a novel controller for stabilizing a bipedal motion in its sagittal plane is developed with regard to the surface friction limitations. By taking into account the physical limitation of the surface in the stabilization trend, a more advanced level of reliability is achieved that provides higher functionalities such as push recovery on low-friction surfaces and prevents the stabilizer from overreacting. The discrete event-based strategy consists of modifying the step length and time period at the beginning of each footstep in order to reestablish stability necessary conditions while taking into account the surface friction limitation as a constraint to prevent slippage. Adjusting footsteps to prevent slippage in confronting external disturbances is perceived as a novel strategy for keeping stability, quite similar to human reaction. The developed methodology consists of rough closed-form solutions utilizing elementary math operations for obtaining the control inputs, allowing to reach a balance between convergence and computational cost, which is quite suitable for real-time operations even with modest computational hardware. Several numerical simulations, including push recovery and switching between different gates on low-friction surfaces, are performed to demonstrate the effectiveness of the proposed controller. In correlation with human-gait experience, the results also reveal some physical aspects favoring stability and the fact of switching between gaits to reduce the risk of falling in confronting different conditions.
Stabilization of Bipedal Robot Motion based on Total Momentum
May 05, 2019Abstract:Bipedal robots adapt to the environment of the modern society due to the similarity of movement to humans, and therefore they are a good partner for humans. However, maintaining the stability of these robots during walking/running motion is a challenging issue that, despite the development of new technologies and the advancement of knowledge, does not yet have a satisfactory solution. In most of the proposed methods by researchers, to maintain the stability of walking bipedal robots, it has been tried to ensure the momentary stability of motion by limiting the motion to multiple constraints. Although these methods have good performance in sustaining stability, they leave the robot away from the natural movement of humans, with low efficiency and high energy consumption. Hence, many researchers have turned to the walking techniques that follow a certain motion limit cycle, in which we can consider the overall stability rather than momentary. In this paper, a method is proposed to maintain the stability of the limit cycle against disturbance. For this purpose, the dynamical model of the biped robot is extracted in the space of total momentum variables and, according to the desired step length and speed, the motion limit cycle is designed. Subsequently, a motion stabilizer is proposed based on the idea of length shift, which is a natural human strategy for sustaining the balance in case of impact. The simulations show that this technique has a good performance in maintaining the stability of motion and has similar responses to human response.
* in Farsi, http://conference.isme.ir/paper?manu=29897
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge