Venugopal Veeravalli
Adaptive Sequential Machine Learning
Apr 04, 2019



Abstract:A framework previously introduced in [3] for solving a sequence of stochastic optimization problems with bounded changes in the minimizers is extended and applied to machine learning problems such as regression and classification. The stochastic optimization problems arising in these machine learning problems is solved using algorithms such as stochastic gradient descent (SGD). A method based on estimates of the change in the minimizers and properties of the optimization algorithm is introduced for adaptively selecting the number of samples at each time step to ensure that the excess risk, i.e., the expected gap between the loss achieved by the approximate minimizer produced by the optimization algorithm and the exact minimizer, does not exceed a target level. A bound is developed to show that the estimate of the change in the minimizers is non-trivial provided that the excess risk is small enough. Extensions relevant to the machine learning setting are considered, including a cost-based approach to select the number of samples with a cost budget over a fixed horizon, and an approach to applying cross-validation for model selection. Finally, experiments with synthetic and real data are used to validate the algorithms.
Universal and Composite Hypothesis Testing via Mismatched Divergence
Sep 09, 2010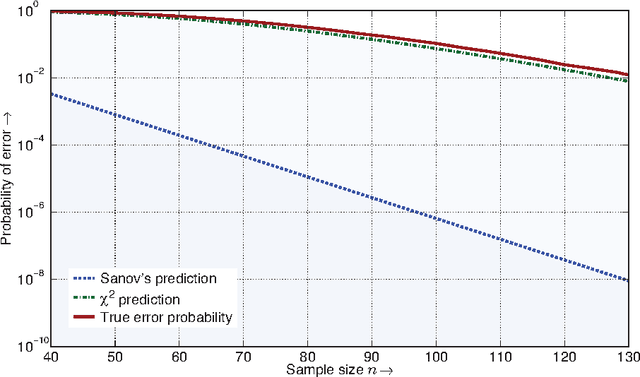
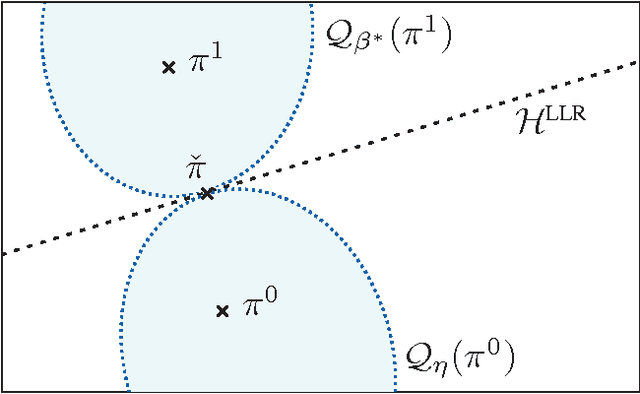
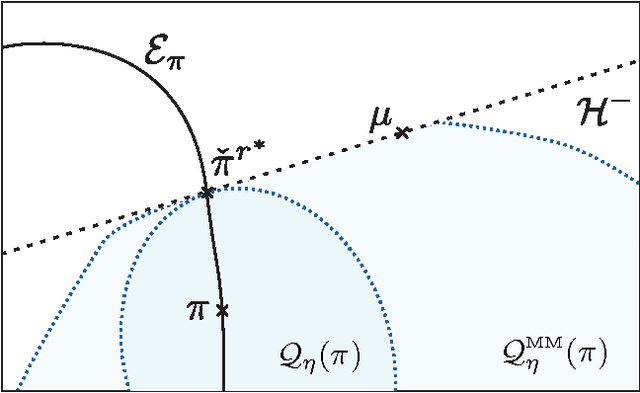
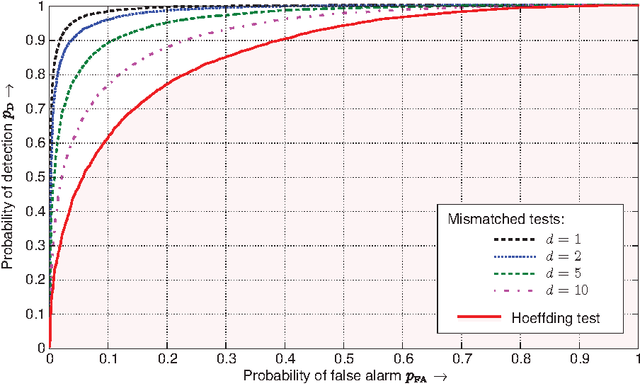
Abstract:For the universal hypothesis testing problem, where the goal is to decide between the known null hypothesis distribution and some other unknown distribution, Hoeffding proposed a universal test in the nineteen sixties. Hoeffding's universal test statistic can be written in terms of Kullback-Leibler (K-L) divergence between the empirical distribution of the observations and the null hypothesis distribution. In this paper a modification of Hoeffding's test is considered based on a relaxation of the K-L divergence test statistic, referred to as the mismatched divergence. The resulting mismatched test is shown to be a generalized likelihood-ratio test (GLRT) for the case where the alternate distribution lies in a parametric family of the distributions characterized by a finite dimensional parameter, i.e., it is a solution to the corresponding composite hypothesis testing problem. For certain choices of the alternate distribution, it is shown that both the Hoeffding test and the mismatched test have the same asymptotic performance in terms of error exponents. A consequence of this result is that the GLRT is optimal in differentiating a particular distribution from others in an exponential family. It is also shown that the mismatched test has a significant advantage over the Hoeffding test in terms of finite sample size performance. This advantage is due to the difference in the asymptotic variances of the two test statistics under the null hypothesis. In particular, the variance of the K-L divergence grows linearly with the alphabet size, making the test impractical for applications involving large alphabet distributions. The variance of the mismatched divergence on the other hand grows linearly with the dimension of the parameter space, and can hence be controlled through a prudent choice of the function class defining the mismatched divergence.
Algorithms for Dynamic Spectrum Access with Learning for Cognitive Radio
Feb 06, 2010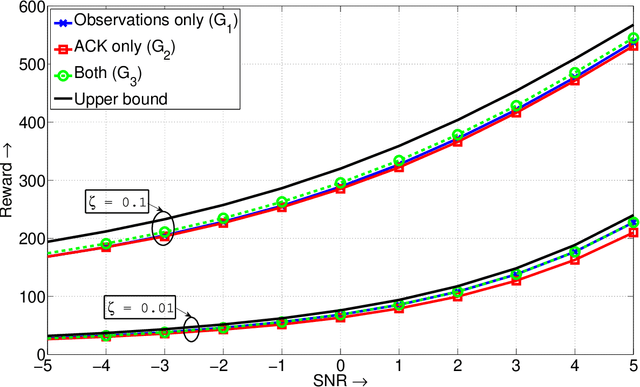
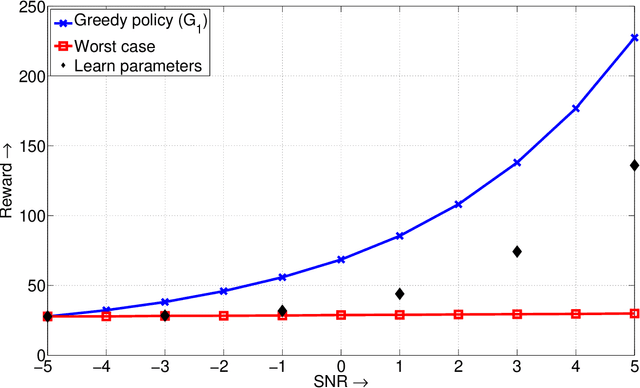
Abstract:We study the problem of dynamic spectrum sensing and access in cognitive radio systems as a partially observed Markov decision process (POMDP). A group of cognitive users cooperatively tries to exploit vacancies in primary (licensed) channels whose occupancies follow a Markovian evolution. We first consider the scenario where the cognitive users have perfect knowledge of the distribution of the signals they receive from the primary users. For this problem, we obtain a greedy channel selection and access policy that maximizes the instantaneous reward, while satisfying a constraint on the probability of interfering with licensed transmissions. We also derive an analytical universal upper bound on the performance of the optimal policy. Through simulation, we show that our scheme achieves good performance relative to the upper bound and improved performance relative to an existing scheme. We then consider the more practical scenario where the exact distribution of the signal from the primary is unknown. We assume a parametric model for the distribution and develop an algorithm that can learn the true distribution, still guaranteeing the constraint on the interference probability. We show that this algorithm outperforms the naive design that assumes a worst case value for the parameter. We also provide a proof for the convergence of the learning algorithm.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge