Vasily Ilin
Learning to Repair Lean Proofs from Compiler Feedback
Feb 03, 2026Abstract:As neural theorem provers become increasingly agentic, the ability to interpret and act on compiler feedback is critical. However, existing Lean datasets consist almost exclusively of correct proofs, offering little supervision for understanding and repairing failures. We study Lean proof repair as a supervised learning problem: given an erroneous proof and compiler feedback, predict both a corrected proof and a natural-language diagnosis grounded in the same feedback. We introduce APRIL (Automated Proof Repair in Lean), a dataset of 260,000 supervised tuples pairing systematically generated proof failures with compiler diagnostics and aligned repair and explanation targets. Training language models on APRIL substantially improves repair accuracy and feedback-conditioned reasoning; in our single-shot repair evaluation setting, a finetuned 4B-parameter model outperforms the strongest open-source baseline. We view diagnostic-conditioned supervision as a complementary training signal for feedback-using provers. Our dataset is available at \href{https://huggingface.co/datasets/uw-math-ai/APRIL}{this link}.
From Kernels to Attention: A Transformer Framework for Density and Score Estimation
Nov 08, 2025Abstract:We introduce a unified attention-based framework for joint score and density estimation. Framing the problem as a sequence-to-sequence task, we develop a permutation- and affine-equivariant transformer that estimates both the probability density $f(x)$ and its score $\nabla_x \log f(x)$ directly from i.i.d. samples. Unlike traditional score-matching methods that require training a separate model for each distribution, our approach learns a single distribution-agnostic operator that generalizes across densities and sample sizes. The architecture employs cross-attention to connect observed samples with arbitrary query points, enabling generalization beyond the training data, while built-in symmetry constraints ensure equivariance to permutation and affine transformations. Analytically, we show that the attention weights can recover classical kernel density estimation (KDE), and verify it empirically, establishing a principled link between classical KDE and the transformer architecture. Empirically, the model achieves substantially lower error and better scaling than KDE and score-debiased KDE (SD-KDE), while exhibiting better runtime scaling. Together, these results establish transformers as general-purpose, data-adaptive operators for nonparametric density and score estimation.
Score-Based Deterministic Density Sampling
Apr 25, 2025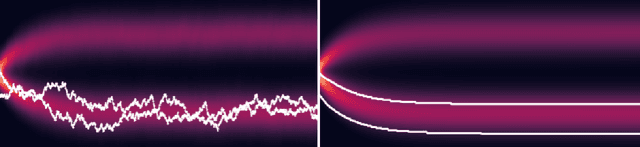
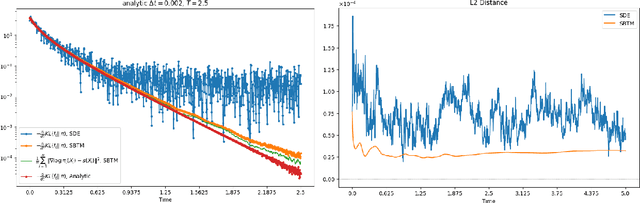
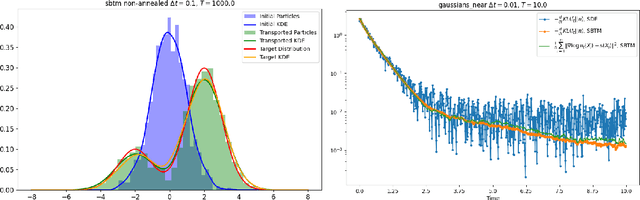
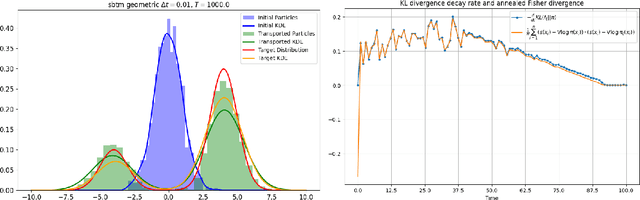
Abstract:We propose and analyze a deterministic sampling framework using Score-Based Transport Modeling (SBTM) for sampling an unnormalized target density $\pi$. While diffusion generative modeling relies on pre-training the score function $\nabla \log f_t$ using samples from $\pi$, SBTM addresses the more general and challenging setting where only $\nabla \log\pi$ is known. SBTM approximates the Wasserstein gradient flow on KL$(f_t\|\pi)$ by learning the time-varying score $\nabla \log f_t$ on the fly using score matching. The learned score gives immediate access to relative Fisher information, providing a built-in convergence diagnostic. The deterministic trajectories are smooth, interpretable, and free of Brownian-motion noise, while having the same distribution as ULA. We prove that SBTM dissipates relative entropy at the same rate as the exact gradient flow, provided sufficient training. We further extend our framework to annealed dynamics, to handle non log-concave targets. Numerical experiments validate our theoretical findings: SBTM converges at the optimal rate, has smooth trajectories, and is easily integrated with annealed dynamics. We compare to the baselines of ULA and annealed ULA.
REALEDIT: Reddit Edits As a Large-scale Empirical Dataset for Image Transformations
Feb 05, 2025



Abstract:Existing image editing models struggle to meet real-world demands. Despite excelling in academic benchmarks, they have yet to be widely adopted for real user needs. Datasets that power these models use artificial edits, lacking the scale and ecological validity necessary to address the true diversity of user requests. We introduce REALEDIT, a large-scale image editing dataset with authentic user requests and human-made edits sourced from Reddit. REALEDIT includes a test set of 9300 examples to evaluate models on real user requests. Our results show that existing models fall short on these tasks, highlighting the need for realistic training data. To address this, we introduce 48K training examples and train our REALEDIT model, achieving substantial gains - outperforming competitors by up to 165 Elo points in human judgment and 92 percent relative improvement on the automated VIEScore metric. We deploy our model on Reddit, testing it on new requests, and receive positive feedback. Beyond image editing, we explore REALEDIT's potential in detecting edited images by partnering with a deepfake detection non-profit. Finetuning their model on REALEDIT data improves its F1-score by 14 percentage points, underscoring the dataset's value for broad applications.
Transport based particle methods for the Fokker-Planck-Landau equation
May 16, 2024Abstract:We propose a particle method for numerically solving the Landau equation, inspired by the score-based transport modeling (SBTM) method for the Fokker-Planck equation. This method can preserve some important physical properties of the Landau equation, such as the conservation of mass, momentum, and energy, and decay of estimated entropy. We prove that matching the gradient of the logarithm of the approximate solution is enough to recover the true solution to the Landau equation with Maxwellian molecules. Several numerical experiments in low and moderately high dimensions are performed, with particular emphasis on comparing the proposed method with the traditional particle or blob method.
 Add to Chrome
Add to Chrome Add to Firefox
Add to Firefox Add to Edge
Add to Edge